Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00057) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Paromomycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Aminosidin; Catenulin; Humatin; Hydroxymycin sulfate; Paramomycin Sulfate; Paromomycin I; Paromomycin sulfate Rx346208; Aminosidine, sulfate; HATT & Paromomycin; Humatin (TN); Paromomycin (INN); Paromomycin (TN); Paromomycin (complex); PA1-PA2-PA3-PA4; Human .alpha.-1-antitrypsin & Paromomyin; PAROMOMYCIN I, AMMINOSIDIN, CATENULIN, CRESTOMYCIN, MONOMYCIN A, NEOMYCIN E; (1R,2R,3S,4R,6S)-4,6-diamino-2-{[3-O-(2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-beta-L-idopyranosyl)-beta-D-ribofuranosyl]oxy}-3-hydroxycyclohexyl 2-amino-2-deoxy-alpha-D-glucopyranoside; (2S,3S,4R,5R,6R)-5-amino-2-(aminomethyl)-6-[(2R,3S,4R,5S)-5-[(1R,2R,3S,5R,6S)-3,5-diamino-2-[(2S,3R,4R,5S,6R)-3-amino-4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy-6-hydroxycyclohexyl]oxy-4-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-yl]oxyoxane-3,4-diol; O-2-Amino-2-deoxy-.alpha.-D-glucopyranosyl-(1->4)-O-[O-2,6-diamino-2,6-dideoxy-.beta.-L-idopyranosyl-(1->3)-.beta.D-ribofuranosyl(1->5)]-2-deoxy-D-streptamine
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
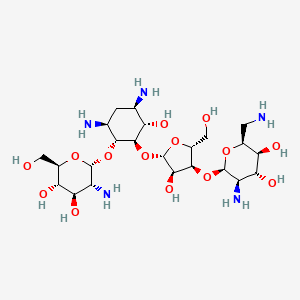
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[3]
|
||||
| Target | Staphylococcus 30S ribosomal subunit (Stap-coc pbp2) | F4NA87_STAAU | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C23H45N5O14
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]1N)O[C@@H]2[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O2)CO)O)O)N)O[C@H]3[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@H](O3)CO)O[C@@H]4[C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](O4)CN)O)O)N)O)O)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C23H45N5O14/c24-2-7-13(32)15(34)10(27)21(37-7)41-19-9(4-30)39-23(17(19)36)42-20-12(31)5(25)1-6(26)18(20)40-22-11(28)16(35)14(33)8(3-29)38-22/h5-23,29-36H,1-4,24-28H2/t5-,6+,7+,8-,9-,10-,11-,12+,13-,14-,15-,16-,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
UOZODPSAJZTQNH-LSWIJEOBSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Stenotrophomonas maltophilia infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli | 668369 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Aph(3')-IIc significantly increases MICs of kanamycin, neomycin, butirosin, and paromomycin when expressed in Escherichia coli. Disruption of aph(3')-IIc results in decreased MICs of these drugs. | |||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Serratia marcescens infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
ICD-12: Respiratory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Aminoglycoside 3'-phosphotransferase (A3AP) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Klebsiella pneumoniae infection [ICD-11: CA40.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli C41(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Escherichia coli DH5alpha | 668369 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs144 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs150 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli Ecmrs151 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-125 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain 83-75 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain JM83(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain M8820Mu | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain MC1065(pRPG101) | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain POII1681 | 562 | |||
| Escherichia coli strain PRC930(pAO43::Tn9O3) | 562 | |||
| Klebsiella pneumoniae strains | 573 | |||
| Serratia marcescens strains | 615 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Restriction enzyme treating assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cation-supplemented Mueller-Hinton broth assay; agar dilution with MH agar assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Clinical isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Serratia marcescens at a hospital that had used amikacin as its principal aminoglycoside for the preceding 42 months demonstrated high-level resistance to amikacin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), kanamycin (greater than or equal to 256 micrograms/ml), gentamicin (greater than or equal to 64 micrograms/ml), netilmicin (64 micrograms/ml), and tobramycin (greater than or equal to 16 micrograms/ml). The clinical isolates and transformants produced a novel 3'-phosphotransferase, APH(3'), that modified amikacin and kanamycin in vitro. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
