Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00661)
| Name |
Antigen peptide transporter 1 (TAP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
APT1; ATP-binding cassette sub-family B member 2; Peptide supply factor 1; Peptide transporter PSF1; PSF-1; Peptide transporter TAP1; Peptide transporter involved in antigen processing 1; Really interesting new gene 4 protein; RING4; ABCB2; PSF1; RING4; Y3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
TAP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr6:32845209-32853816[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MASSRCPAPRGCRCLPGASLAWLGTVLLLLADWVLLRTALPRIFSLLVPTALPLLRVWAV
GLSRWAVLWLGACGVLRATVGSKSENAGAQGWLAALKPLAAALGLALPGLALFRELISWG APGSADSTRLLHWGSHPTAFVVSYAAALPAAALWHKLGSLWVPGGQGGSGNPVRRLLGCL GSETRRLSLFLVLVVLSSLGEMAIPFFTGRLTDWILQDGSADTFTRNLTLMSILTIASAV LEFVGDGIYNNTMGHVHSHLQGEVFGAVLRQETEFFQQNQTGNIMSRVTEDTSTLSDSLS ENLSLFLWYLVRGLCLLGIMLWGSVSLTMVTLITLPLLFLLPKKVGKWYQLLEVQVRESL AKSSQVAIEALSAMPTVRSFANEEGEAQKFREKLQEIKTLNQKEAVAYAVNSWTTSISGM LLKVGILYIGGQLVTSGAVSSGNLVTFVLYQMQFTQAVEVLLSIYPRVQKAVGSSEKIFE YLDRTPRCPPSGLLTPLHLEGLVQFQDVSFAYPNRPDVLVLQGLTFTLRPGEVTALVGPN GSGKSTVAALLQNLYQPTGGQLLLDGKPLPQYEHRYLHRQVAAVGQEPQVFGRSLQENIA YGLTQKPTMEEITAAAVKSGAHSFISGLPQGYDTEVDEAGSQLSGGQRQAVALARALIRK PCVLILDDATSALDANSQLQVEQLLYESPERYSRSVLLITQHLSLVEQADHILFLEGGAI REGGTHQQLMEKKGCYWAMVQAPADAPE Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
ABC transporter associated with antigen processing. In complex with TAP2 mediates unidirectional translocation of peptide antigens from cytosol to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for loading onto MHC class I (MHCI) molecules. Uses the chemical energy of ATP to export peptides against the concentration gradient. During the transport cycle alternates between 'inward-facing' state with peptide binding site facing the cytosol to 'outward-facing' state with peptide binding site facing the ER lumen. Peptide antigen binding to ATP-loaded TAP1-TAP2 induces a switch to hydrolysis-competent 'outward-facing' conformation ready for peptide loading onto nascent MHCI molecules. Subsequently ATP hydrolysis resets the transporter to the 'inward facing' state for a new cycle. Typically transports intracellular peptide antigens of 8 to 13 amino acids that arise from cytosolic proteolysis via IFNG-induced immunoproteasome. Binds peptides with free N- and C-termini, the first three and the C-terminal residues being critical. Preferentially selects peptides having a highly hydrophobic residue at position 3 and hydrophobic or charged residues at the C-terminal anchor. Proline at position 2 has the most destabilizing effect. As a component of the peptide loading complex (PLC), acts as a molecular scaffold essential for peptide-MHCI assembly and antigen presentation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cefadroxil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ussing chamber system assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cefadroxil and methotrexate (each 10 uM) were selected as substrates to evaluate the functions of the uptake transport mediated by PEPT1 and PCFT, respectively. Gly-Sar (20 mM) and folate (200 uM), typical substrates of PEPT1 and PCFT, respectively, were used to saturate the functions of PEPT1 and PCFT. The mucosal-to-serosal transport and mucosal uptake of cefadroxil and methotrexate were significantly decreased in the presence of PEPT1/PCFT inhibitor cocktail in all batches of tissue sections. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 01

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gingival tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Bacterial infection of gingival | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.54E-01; Fold-change: 1.39E-01; Z-score: 2.53E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
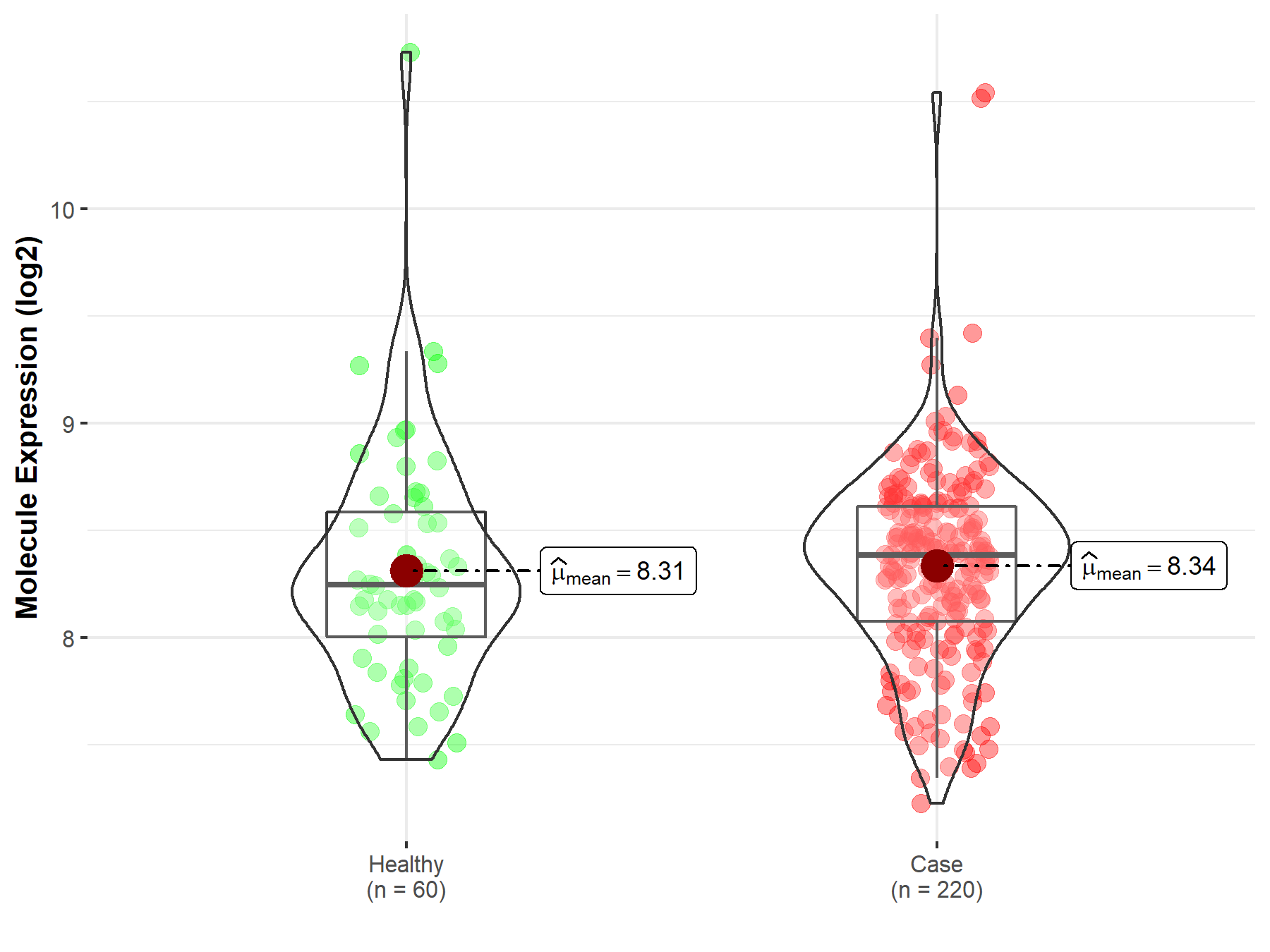
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
