Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00413)
| Name |
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U (HNRNPU)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
hnRNP U; GRIP120; Nuclear p120 ribonucleoprotein; Scaffold-attachment factor A; SAF-A; p120; pp120; C1orf199; HNRPU; SAFA; U21.1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
HNRNPU
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:244840638-244864560[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSSSPVNVKKLKVSELKEELKKRRLSDKGLKAELMERLQAALDDEEAGGRPAMEPGNGSL
DLGGDSAGRSGAGLEQEAAAGGDEEEEEEEEEEEGISALDGDQMELGEENGAAGAADSGP MEEEEAASEDENGDDQGFQEGEDELGDEEEGAGDENGHGEQQPQPPATQQQQPQQQRGAA KEAAGKSSGPTSLFAVTVAPPGARQGQQQAGGKKKAEGGGGGGRPGAPAAGDGKTEQKGG DKKRGVKRPREDHGRGYFEYIEENKYSRAKSPQPPVEEEDEHFDDTVVCLDTYNCDLHFK ISRDRLSASSLTMESFAFLWAGGRASYGVSKGKVCFEMKVTEKIPVRHLYTKDIDIHEVR IGWSLTTSGMLLGEEEFSYGYSLKGIKTCNCETEDYGEKFDENDVITCFANFESDEVELS YAKNGQDLGVAFKISKEVLAGRPLFPHVLCHNCAVEFNFGQKEKPYFPIPEEYTFIQNVP LEDRVRGPKGPEEKKDCEVVMMIGLPGAGKTTWVTKHAAENPGKYNILGTNTIMDKMMVA GFKKQMADTGKLNTLLQRAPQCLGKFIEIAARKKRNFILDQTNVSAAAQRRKMCLFAGFQ RKAVVVCPKDEDYKQRTQKKAEVEGKDLPEHAVLKMKGNFTLPEVAECFDEITYVELQKE EAQKLLEQYKEESKKALPPEKKQNTGSKKSNKNKSGKNQFNRGGGHRGRGGFNMRGGNFR GGAPGNRGGYNRRGNMPQRGGGGGGSGGIGYPYPRAPVFPGRGSYSNRGNYNRGGMPNRG NYNQNFRGRGNNRGYKNQSQGYNQWQQGQFWGQKPWSQHYHQGYY Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
DNA- and RNA-binding protein involved in several cellular processes such as nuclear chromatin organization, telomere-length regulation, transcription, mRNA alternative splicing and stability, Xist-mediated transcriptional silencing and mitotic cell progression. Plays a role in the regulation of interphase large-scale gene-rich chromatin organization through chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs) in a transcription-dependent manner, and thereby maintains genomic stability. Required for the localization of the long non-coding Xist RNA on the inactive chromosome X (Xi) and the subsequent initiation and maintenance of X-linked transcriptional gene silencing during X-inactivation. Plays a role as a RNA polymerase II (Pol II) holoenzyme transcription regulator. Promotes transcription initiation by direct association with the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor complex for the assembly of a functional pre-initiation complex with Pol II in a actin-dependent manner. Blocks Pol II transcription elongation activity by inhibiting the C-terminal domain (CTD) phosphorylation of Pol II and dissociates from Pol II pre-initiation complex prior to productive transcription elongation. Positively regulates CBX5-induced transcriptional gene silencing and retention of CBX5 in the nucleus. Negatively regulates glucocorticoid-mediated transcriptional activation. Key regulator of transcription initiation and elongation in embryonic stem cells upon leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF) signaling. Involved in the long non-coding RNA H19-mediated Pol II transcriptional repression. Participates in the circadian regulation of the core clock component ARNTL/BMAL1 transcription. Plays a role in the regulation of telomere length. Plays a role as a global pre-mRNA alternative splicing modulator by regulating U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) biogenesis. Plays a role in mRNA stability. Component of the CRD-mediated complex that promotes MYC mRNA stabilization. Enhances the expression of specific genes, such as tumor necrosis factor TNFA, by regulating mRNA stability, possibly through binding to the 3'-untranslated region (UTR). Plays a role in mitotic cell cycle regulation. Involved in the formation of stable mitotic spindle microtubules (MTs) attachment to kinetochore, spindle organization and chromosome congression. Phosphorylation at Ser-59 by PLK1 is required for chromosome alignement and segregation and progression through mitosis. Contributes also to the targeting of AURKA to mitotic spindle MTs. Binds to double- and single-stranded DNA and RNA, poly(A), poly(C) and poly(G) oligoribonucleotides. Binds to chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs). Associates with chromatin to scaffold/matrix attachment region (S/MAR) elements in a chromatin-associated RNAs (caRNAs)-dependent manner. Binds to the Xist RNA. Binds the long non-coding H19 RNA. Binds to SMN1/2 pre-mRNAs at G/U-rich regions. Binds to small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). Binds to the 3'-UTR of TNFA mRNA. Binds (via RNA-binding RGG-box region) to the long non-coding Xist RNA; this binding is direct and bridges the Xist RNA and the inactive chromosome X (Xi). Also negatively regulates embryonic stem cell differentiation upon LIF signaling. Required for embryonic development. Binds to brown fat long non-coding RNA 1 (Blnc1); facilitates the recruitment of Blnc1 by ZBTB7B required to drive brown and beige fat development and thermogenesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.57E-29 Fold-change: 2.96E-01 Z-score: 1.37E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Sk-MES-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0630 | |
| 16HBE cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0112 | |
| A549-DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IP03 | |
| NCl-H226 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1544 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS Cell Proliferation Assay; EdU assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long noncoding RNA SFTA1P promoted apoptosis and increased cisplatin chemosensitivity via regulating the hnRNP-U-GADD45A axis in lung squamous cell carcinoma. SFTA1P could up-regulate hnRNP-U expression. hnRNP-U enhanced cisplatin-induced apoptosis through up-regulation of GADD45A. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.35E-26; Fold-change: -4.76E-01; Z-score: -1.15E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.29E-23; Fold-change: -4.46E-01; Z-score: -1.22E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
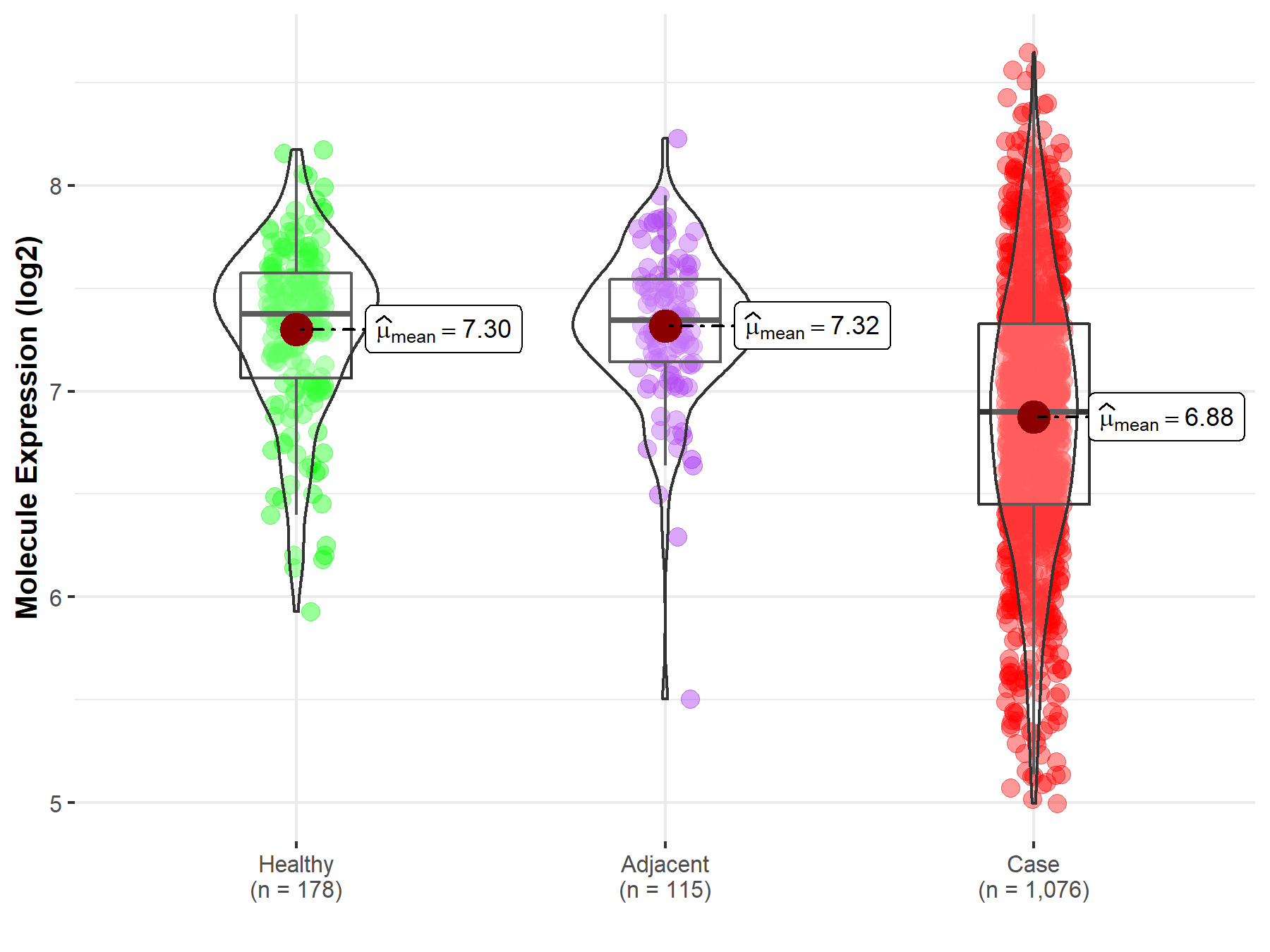
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

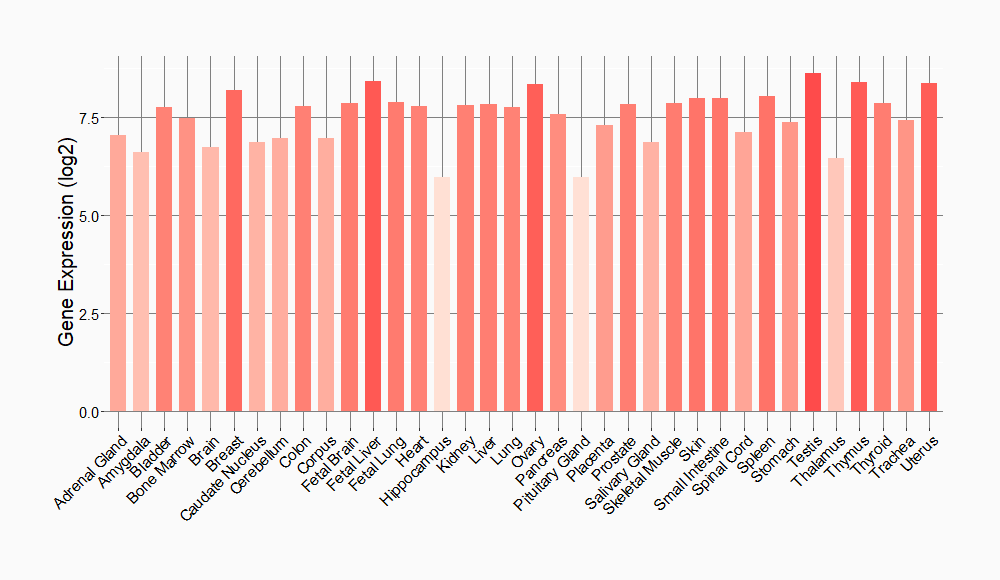
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
