Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00332)
| Name |
Dual specificity protein phosphatase 1 (DUSP1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Dual specificity protein phosphatase hVH1; Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase 1; MAP kinase phosphatase 1; MKP-1; Protein-tyrosine phosphatase CL100; CL100; MKP1; PTPN10; VH1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
DUSP1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr5:172768096-172771195[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MVMEVGTLDAGGLRALLGERAAQCLLLDCRSFFAFNAGHIAGSVNVRFSTIVRRRAKGAM
GLEHIVPNAELRGRLLAGAYHAVVLLDERSAALDGAKRDGTLALAAGALCREARAAQVFF LKGGYEAFSASCPELCSKQSTPMGLSLPLSTSVPDSAESGCSSCSTPLYDQGGPVEILPF LYLGSAYHASRKDMLDALGITALINVSANCPNHFEGHYQYKSIPVEDNHKADISSWFNEA IDFIDSIKNAGGRVFVHCQAGISRSATICLAYLMRTNRVKLDEAFEFVKQRRSIISPNFS FMGQLLQFESQVLAPHCSAEAGSPAMAVLDRGTSTTTVFNFPVSIPVHSTNSALSYLQSP ITTSPSC Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Dual specificity phosphatase that dephosphorylates MAP kinase MAPK1/ERK2 on both 'Thr-183' and 'Tyr-185', regulating its activity during the meiotic cell cycle.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.60E-50 Fold-change: -3.57E-01 Z-score: -1.93E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | ||
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells and xenografts, MkP-1 knockdown triggered the down-regulation of the metabolic enzymes and cytoprotective proteins, which are the target genes of Nrf2. Consequently, the cell growth was markedly inhibited with decrease of tumor metabolisms and GSH contents. Moreover, MkP-1 silencing sensitized NSCLC cells to cisplatin treatment. Mechanistically, MkP-1 inhibited the ubiquitylation of Nrf2 via a direct interaction with the transcription factor. Thus, MkP-1 and Nrf2 form a forward feedback loop in lung cancer cells, which stabilizing and activating Nrf2 to promote anabolic metabolism and GSH biosynthesis. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.60E-50; Fold-change: -2.35E+00; Z-score: -1.86E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.95E-21; Fold-change: -2.29E+00; Z-score: -1.45E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
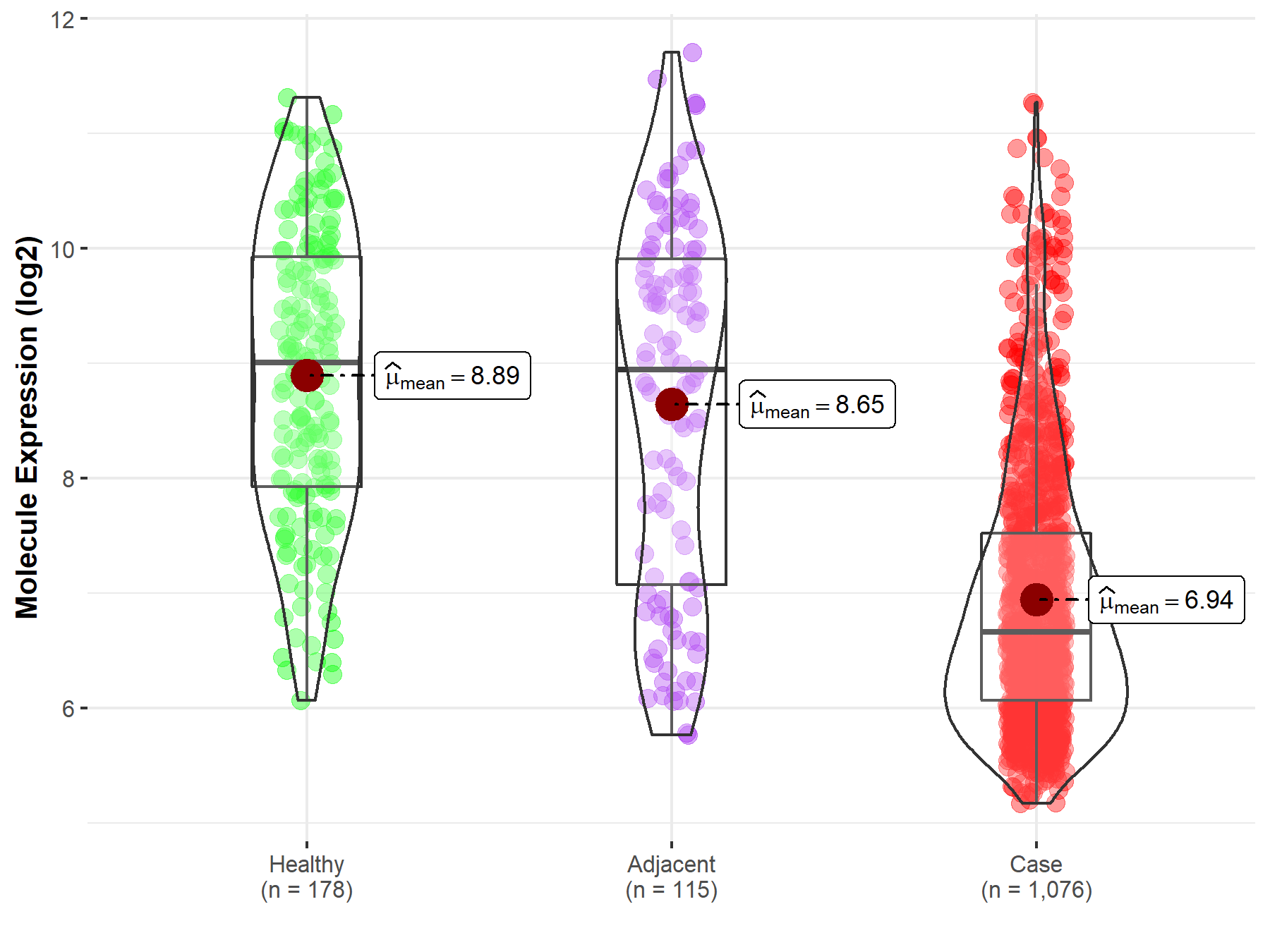
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

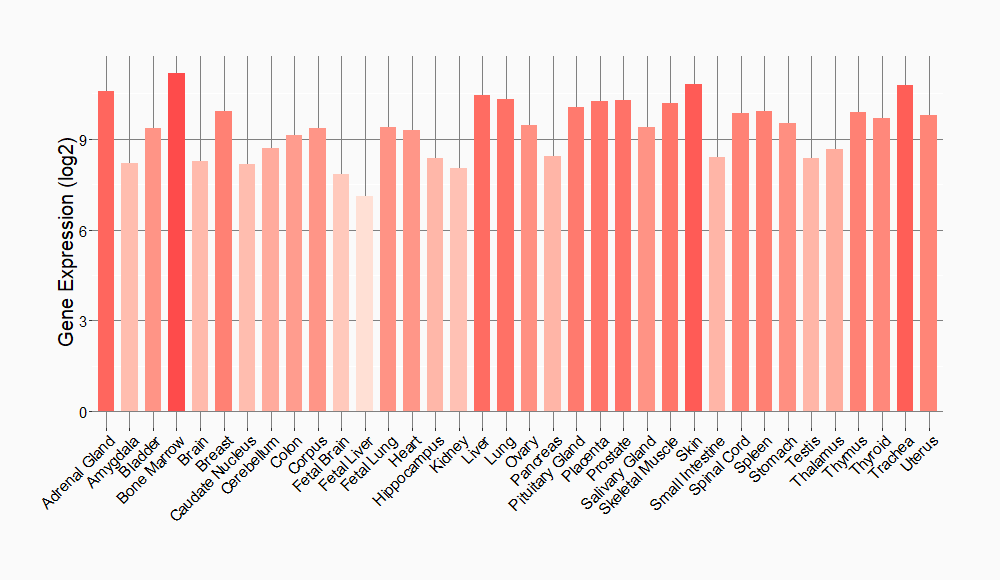
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
