Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00126)
| Name |
NFE2-related factor 2 (NRF2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
NF-E2-related factor 2; NFE2-related factor 2; Nrf-2; HEBP1; Nuclear factor; erythroid derived 2; like 2; NRF2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NFE2L2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:177227595-177392697[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MMDLELPPPGLPSQQDMDLIDILWRQDIDLGVSREVFDFSQRRKEYELEKQKKLEKERQE
QLQKEQEKAFFAQLQLDEETGEFLPIQPAQHIQSETSGSANYSQVAHIPKSDALYFDDCM QLLAQTFPFVDDNEVSSATFQSLVPDIPGHIESPVFIATNQAQSPETSVAQVAPVDLDGM QQDIEQVWEELLSIPELQCLNIENDKLVETTMVPSPEAKLTEVDNYHFYSSIPSMEKEVG NCSPHFLNAFEDSFSSILSTEDPNQLTVNSLNSDATVNTDFGDEFYSAFIAEPSISNSMP SPATLSHSLSELLNGPIDVSDLSLCKAFNQNHPESTAEFNDSDSGISLNTSPSVASPEHS VESSSYGDTLLGLSDSEVEELDSAPGSVKQNGPKTPVHSSGDMVQPLSPSQGQSTHVHDA QCENTPEKELPVSPGHRKTPFTKDKHSSRLEAHLTRDELRAKALHIPFPVEKIINLPVVD FNEMMSKEQFNEAQLALIRDIRRRGKNKVAAQNCRKRKLENIVELEQDLDHLKDEKEKLL KEKGENDKSLHLLKKQLSTLYLEVFSMLRDEDGKPYSPSEYSLQQTRDGNVFLVPKSKKP DVKKN Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Transcription factor that plays a key role in the response to oxidative stress: binds to antioxidant response (ARE) elements present in the promoter region of many cytoprotective genes, such as phase 2 detoxifying enzymes, and promotes their expression, thereby neutralizing reactive electrophiles. In normal conditions, ubiquitinated and degraded in the cytoplasm by the BCR(KEAP1) complex. In response to oxidative stress, electrophile metabolites inhibit activity of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, promoting nuclear accumulation of NFE2L2/NRF2, heterodimerization with one of the small Maf proteins and binding to ARE elements of cytoprotective target genes. The NFE2L2/NRF2 pathway is also activated in response to selective autophagy: autophagy promotes interaction between KEAP1 and SQSTM1/p62 and subsequent inactivation of the BCR(KEAP1) complex, leading to NFE2L2/NRF2 nuclear accumulation and expression of cytoprotective genes. May also be involved in the transcriptional activation of genes of the beta-globin cluster by mediating enhancer activity of hypersensitive site 2 of the beta-globin locus control region. Plays also an important role in the regulation of the innate immune response and antiviral cytosolic DNA sensing. It is a critical regulator of the innate immune response and survival during sepsis by maintaining redox homeostasis and restraint of the dysregulation of proinflammatory signaling pathways like MyD88-dependent and -independent and TNF-alpha signaling. Suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription and the induction of IL6. Binds to the proximity of proinflammatory genes in macrophages and inhibits RNA Pol II recruitment. The inhibition is independent of the NRF2-binding motif and reactive oxygen species level. Represses antiviral cytosolic DNA sensing by suppressing the expression of the adapter protein STING1 and decreasing responsiveness to STING1 agonists while increasing susceptibility to infection with DNA viruses. Once activated, limits the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines in response to human coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 infection and to virus-derived ligands through a mechanism that involves inhibition of IRF3 dimerization. Also inhibits both SARS-CoV-2 replication, as well as the replication of several other pathogenic viruses including Herpes Simplex Virus-1 and-2, Vaccinia virus, and Zika virus through a type I interferon (IFN)-independent mechanism.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.05E-01 Fold-change: -1.68E-02 Z-score: -5.21E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | KkU-100 cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3996 |
| KkU-M156 cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M260 | |
| KkU-M213 cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M261 | |
| KkU-M214 cells | Gallbladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_M264 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Acri-dine orange and ethidium bromide (AO/EB) fluorescent dyes assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a key transcription factor regulating antioxidant, cytoprotective, and metabolic enzymes, plays important roles in drug resistance and proliferation in cancer cells. Nrf2 mRNA expression of kkU-M156 and kkU-100 cells, representatives of low and high-Nrf2-expressing CCA cells, were silenced using siRNA. After knockdown of Nrf2, the sensitivity of those cells to the cytotoxicity of cisplatin (Cis) was enhanced in association with the increased release of AIF and downregulation of Bcl-xl in both cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Nrf2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05208 | |
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Bioinformatics analysis and luciferase assays ofNrf2-3'-untranslated region-based reporter constructor indicated that Nrf2 was the direct target gene of miR-340, miR-340 mimics suppressing Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway and enhancing the sensitivity of HepG2/CDDP cells to cisplatin. Interestingly, transfection with miR-340 mimics combined with miR-340 inhibitorsreactivated the Nrf2 related pathway and restored the resistance of HepG2/CDDP cells to CDDP. Collectively,the results first suggested that lower expression of miR-340 is involved in the development of CDDP resistancein hepatocellular carcinoma cell line, at least partly due to regulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant pathway. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.75E-12 Fold-change: -7.61E-02 Z-score: -7.11E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Nrf2 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa05208 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Cos-7 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0224 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-144-3p promotes cisplatin sensitivity by downregulating Nrf2 in lung cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | TE-1 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1759 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RNA pull-down assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TUG1 promoted cell resistance to DDP, at least in part, through upregulating Nrf2. | |||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | [5] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Redox metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HN30 cells | Nasopharyngeal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5525 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The CDDP-resistant cells had significantly higher expression of NRF2 pathway genes in the presence of newly acquired KEAP1 mutations, or via epigenomic activation of target genes. Knockdown of NRF2 or restoration of the wild-type KEAP1 genes resensitized resistant cells to CDDP and decreased distant metastasis (DM). Finally, treatment with inhibitor of glutaminase-1, a NRF2 target gene, alleviated CDDP resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Arsenic trioxide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Nrf2 signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05208 | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR155 mediates arsenic trioxide resistance by activating Nrf2 and suppressing apoptosis in lung cancer cells. miR155 mediated ATO resistance by upregulating the Nrf2 signaling pathway, but downregulating cellular apoptosis in lung cancer cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Arsenic trioxide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Oxidative stress response signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | MV4-11 ATO-R C4 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| MV4-11 ATO-R C6 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis analysis; Intracellular ROS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We examined the effects of molecular/pharmacological suppression of?NRF2?on acquired ATO resistance in the?FLT3-ITD?mutant AML cell line (MV4-11-ATO-R). ATO-R cells showed increased NRF2?expression, nuclear localization, and upregulation of bonafide?NRF2 targets. Molecular inhibition of?NRF2?in this resistant cell line improved ATO sensitivity in vitro. Digoxin treatment lowered p-AKT expression, abrogating nuclear NRF2 localization and sensitizing cells to ATO. However, digoxin and ATO did not sensitize non-ITD AML cell line THP1 with high NRF2 expression. Digoxin decreased leukemic burden and prolonged survival in MV4-11 ATO-R xenograft mice. We establish that altering NRF2 expression may reverse acquired ATO resistance in FLT3-ITD AML. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | APR-246 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | NRF2/SLC7A11/GSH signalling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | H460/CIS cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A9CH |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Colony formation assay; Apoptosis assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In this study, we identify NADPH metabolism and reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels as the main causes accounting for cisplatin resistance. Based on a small panel consisting of common chemotherapy drugs or compounds, APR-246 is proved to be an effective compound targeting cisplatin-resistant NSCLC cells. APR-246 specially inhibits proliferation and colony formation of cisplatin-resistant cells. In details, APR-246 can significantly cause G0/G1 accumulation and S phase arrest of cisplatin resistant cells and gives rise to severe mitochondria dysfunction as well as elevated apoptosis. Further study proves that it is the aberrant ROS levels as well as NRF2/SLC7A11/GSH axis dysfunction accounting for the specific antitumor effects of APR-246. Scavenging ROS with N-acetylcysteine (NAC) disrupts the inhibitory effect of APR-246 on cisplatin-resistant cells. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute promyelocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | ATO-Digoxin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Oxidative stress response signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | MV4-11 ATO-R C6 xenograft mice | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
In-vivo drug treatment assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We examined the effects of molecular/pharmacological suppression of?NRF2?on acquired ATO resistance in the?FLT3-ITD?mutant AML cell line (MV4-11-ATO-R). ATO-R cells showed increased NRF2?expression, nuclear localization, and upregulation of bonafide?NRF2 targets. Molecular inhibition of?NRF2?in this resistant cell line improved ATO sensitivity in vitro. Digoxin treatment lowered p-AKT expression, abrogating nuclear NRF2 localization and sensitizing cells to ATO. However, digoxin and ATO did not sensitize non-ITD AML cell line THP1 with high NRF2 expression. Digoxin decreased leukemic burden and prolonged survival in MV4-11 ATO-R xenograft mice. We establish that altering NRF2 expression may reverse acquired ATO resistance in FLT3-ITD AML. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.24E-07; Fold-change: -1.44E+00; Z-score: -6.31E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
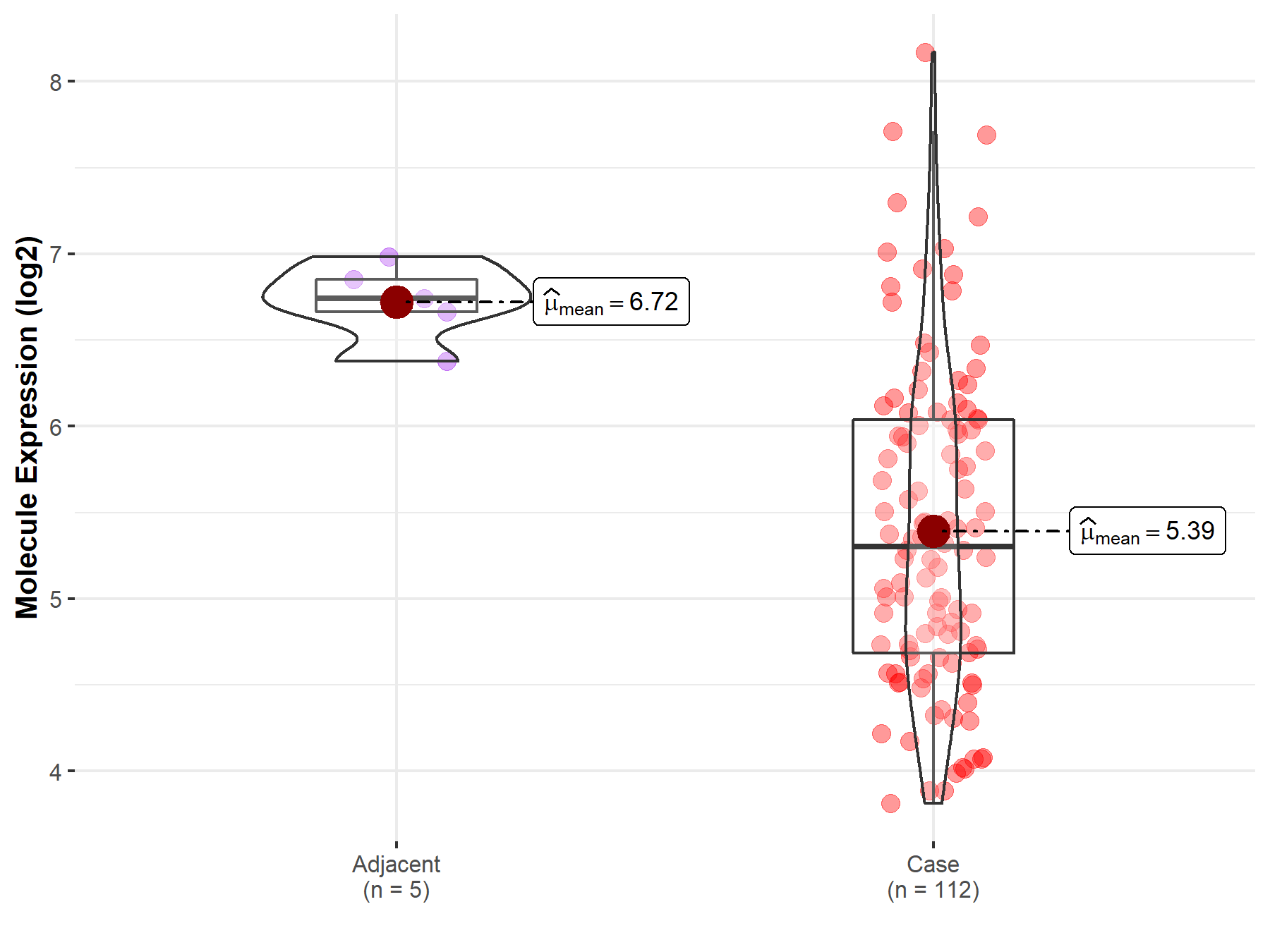
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.05E-01; Fold-change: -1.70E-01; Z-score: -2.16E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.14E-03; Fold-change: 2.57E-01; Z-score: 2.94E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 6.72E-01; Fold-change: -1.28E-01; Z-score: -1.86E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
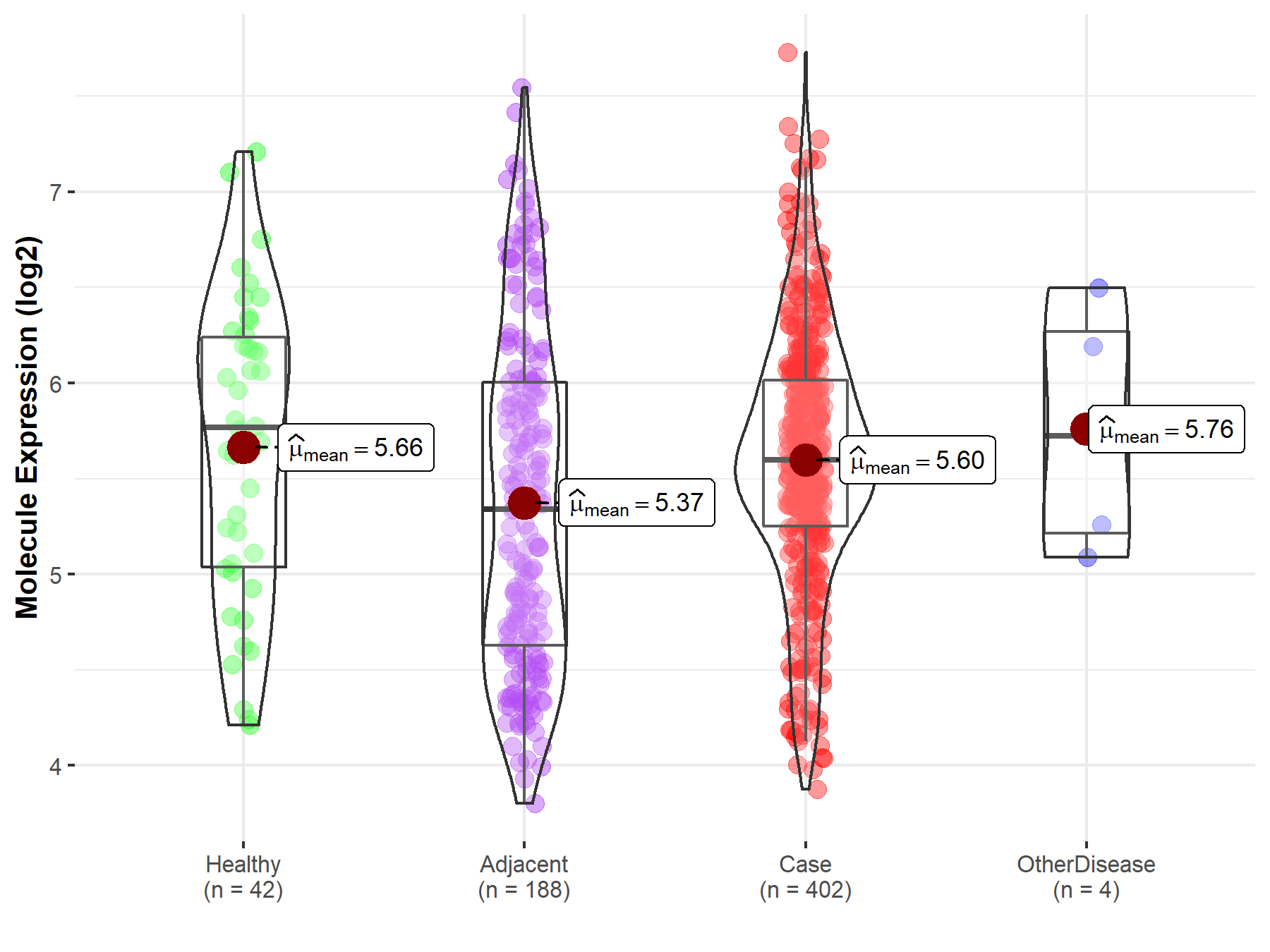
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.75E-12; Fold-change: -2.80E-01; Z-score: -5.80E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.13E-02; Fold-change: 7.37E-02; Z-score: 9.94E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
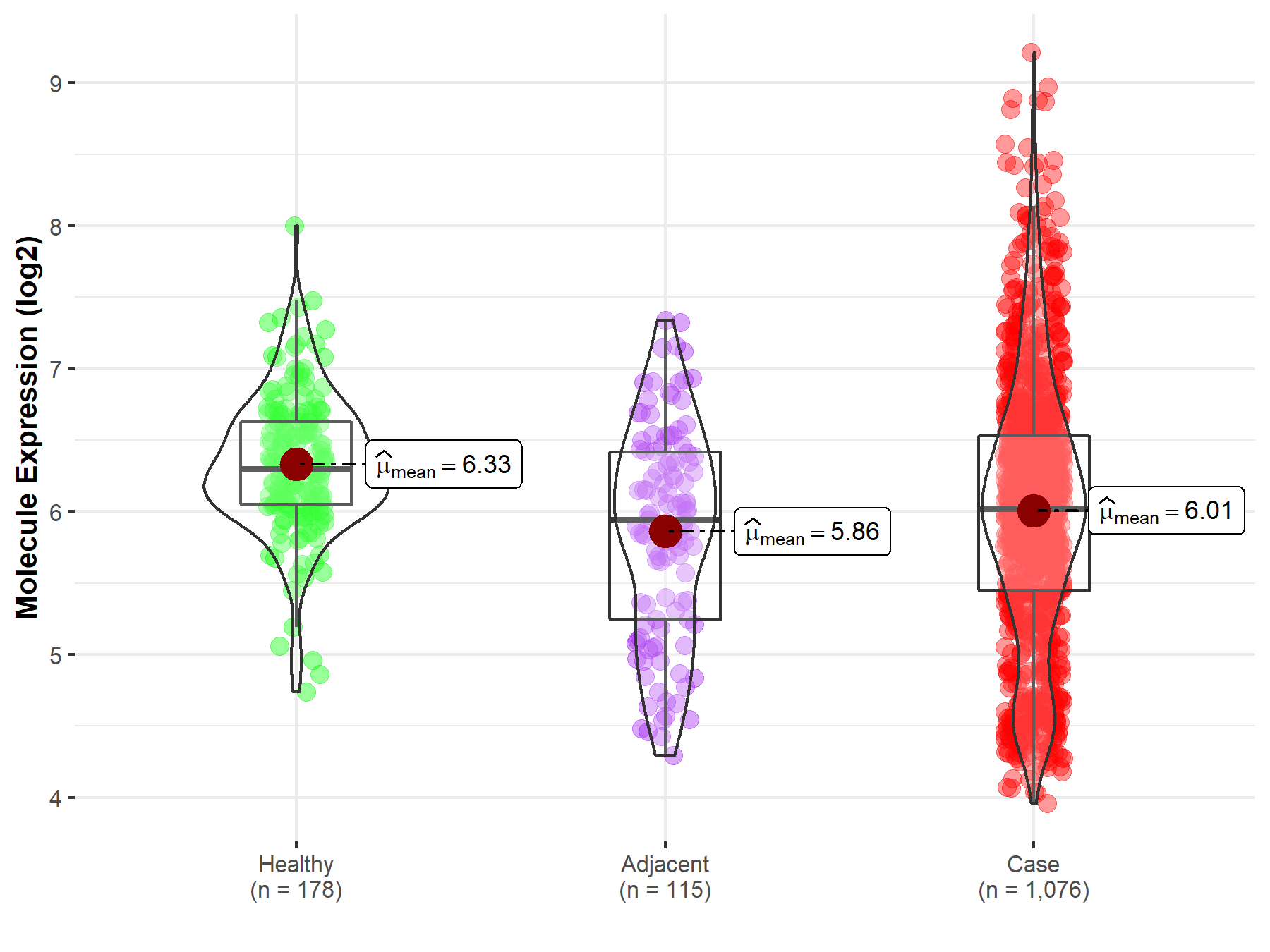
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
