Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02038) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Orlistat
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
orlistat; 96829-58-2; Tetrahydrolipstatin; Xenical; Alli; Orlipastat; (-)-Tetrahydrolipstatin; Orlipastatum; Orlipastatum [INN-Latin]; THLP; Ro-18-0647; UNII-95M8R751W8; C29H53NO5; Ro 18-0647/002; N-Formyl-L-leucine (1S)-1-[[(2S,3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl]methyl]dodecyl ester; (2S)-1-[(2S,3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxooxetan-2-yl]tridecan-2-yl (2S)-2-formamido-4-methylpentanoate; Orlistat (Alli, Xenical); MLS002207022; [(2S)-1-[(2S,3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxooxetan-2-yl]tridecan-2-yl] (2S)-2-formamido-4-methylpentanoate; CHEMBL175247; Alli; GlaxoSmithKline brand of orlistat; Roche brand of orlistat; Alli (TN); Hoffmann-La Roche brand of orlistat; KS-1183; Orlistat [USAN:INN]; R-212; Xenical (TN); Orlistat (USAN/INN); Ro 18-0647/008; Alli, Xenical, Tetrahydrolipstatin, Orlistat; N-Formyl-L-leucine, ester with (3S,4S)-3-hexyl-4-((2S)-2-hydroxytridecyl)-2-oxetanone; L-Leucine, N-formyl-, (1S)-1-(((2S,3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl)methyl)dodecyl ester; L-Leucine,N-formyl-, (1S)-1-(((2S,3S)-3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl)methyl)dodecyl ester; 1-((3-hexyl-4-oxo-2-oxetanyl)methyl)dodecyl-2-formamido-4-methylvalerate; TETRAHYDROLIPSTATIN
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Approved
|
||||
| Structure |
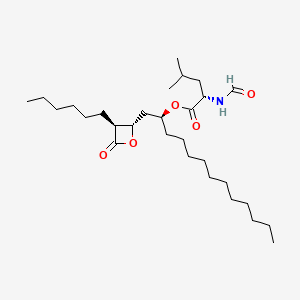
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Pancreatic triacylglycerol lipase (PNLIP) | LIPP_HUMAN | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C29H53NO5
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCCCCCCCCCC[C@@H](C[C@H]1[C@@H](C(=O)O1)CCCCCC)OC(=O)[C@H](CC(C)C)NC=O
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C29H53NO5/c1-5-7-9-11-12-13-14-15-16-18-24(34-29(33)26(30-22-31)20-23(3)4)21-27-25(28(32)35-27)19-17-10-8-6-2/h22-27H,5-21H2,1-4H3,(H,30,31)/t24-,25-,26-,27-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AHLBNYSZXLDEJQ-FWEHEUNISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Acyl-CoA thioesterase 8 (ACOT8) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.82E-14 Fold-change: 6.86E-01 Z-score: 8.55E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse subcutaneous tumorigenic models | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Transcriptome sequencing and analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, ACOT8 regulates cellular cholesterol ester (CE) levels, decreases the levels of phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) that bind to polyunsaturated fatty acids and promote peroxisome activation. The knockdown of ACOT8 promotes ferroptosis and increases the chemosensitivity of tumors to GEM by inducing ferroptosis-associated pathway activation in PDAC cell lines. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acyl-CoA thioesterase 8 (ACOT8) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.82E-14 Fold-change: 6.86E-01 Z-score: 8.55E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | AsPC1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0152 |
| MiaPaCa-2 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0428 | |
| Panc1 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0480 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Transcriptome sequencing and analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, ACOT8 regulates cellular cholesterol ester (CE) levels, decreases the levels of phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) that bind to polyunsaturated fatty acids and promote peroxisome activation. The knockdown of ACOT8 promotes ferroptosis and increases the chemosensitivity of tumors to GEM by inducing ferroptosis-associated pathway activation in PDAC cell lines. | |||
| Key Molecule: Acyl-CoA thioesterase 8 (ACOT8) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Pancreatic cancer [ICD-11: 2C10] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.82E-14 Fold-change: 6.86E-01 Z-score: 8.55E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | Patient-derived PDAC organoids | Homo Sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Transcriptome sequencing and analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Mechanistically, ACOT8 regulates cellular cholesterol ester (CE) levels, decreases the levels of phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) that bind to polyunsaturated fatty acids and promote peroxisome activation. The knockdown of ACOT8 promotes ferroptosis and increases the chemosensitivity of tumors to GEM by inducing ferroptosis-associated pathway activation in PDAC cell lines. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
