Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02031) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pimozide
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Antalon; Neoperidole; Opiran; Orap; Pimozida; Pimozidum; Primozida; ASTA Medica Brand of Pimozide; Janssen Brand of Pimozide;Orap forte; Pharmascience Brand of Pimozide; P 1793; R 6238; McN-JR 6238; Orap (TN); Pimozida [INN-Spanish]; Pimozidum [INN-Latin]; Primozida [INN-Spanish]; R-6238; McN-JR-6238; Pimozide (JAN/USP/INN); Pimozide [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; 1-(1-(4,4-Bis(p-fluorophenyl)butyl)-4-piperidyl)-2-benzimidazolinone; 1-(4,4-Bis(p-fluorophenyl)butyl)-4-(2-oxo-1-benzimidazolinyl)piperidine; 1-[1-[4,4-Bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-piperidinyl]-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one; 1-[1-[4,4-Bis(p-fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-piperidyl]-2-benzimidazolinone; 1-[1-[4,4-bis(4-Fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-piperidinyl]-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one; 1-[4,4-Bis(p-fluorophenyl)butyl]-4-(2-oxo-1-benzimidazolinyl)piperidine; 1-{1-[4,4-bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]piperidin-4-yl}-1,3-dihydro-2H-benzimidazol-2-one; 1-{1-[4,4-bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]piperidin-4-yl}-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,3-benzodiazol-2-one; 3-[1-[4,4-bis(4-fluorophenyl)butyl]piperidin-4-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-one
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Approved
|
||||
| Structure |
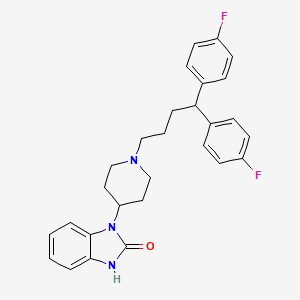
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Dopamine D2 receptor (D2R) | DRD2_HUMAN | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C28H29F2N3O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CN(CCC1N2C3=CC=CC=C3NC2=O)CCCC(C4=CC=C(C=C4)F)C5=CC=C(C=C5)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C28H29F2N3O/c29-22-11-7-20(8-12-22)25(21-9-13-23(30)14-10-21)4-3-17-32-18-15-24(16-19-32)33-27-6-2-1-5-26(27)31-28(33)34/h1-2,5-14,24-25H,3-4,15-19H2,(H,31,34)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YVUQSNJEYSNKRX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP-1) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | LN cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| T98 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B368 | |
| U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 | |
| U373 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2219 | |
| U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These elevations are driven by SREBP-1, which we find upregulates the expression of ASCT2, a key glutamine transporter. Glutamine, in turn, intensifies SREBP-1 activation through the release of ammonia, creating a feedforward loop that amplifies both glutamine metabolism and lipid synthesis, leading to drug resistance. Disrupting this loop via pharmacological targeting of ASCT2 or glutaminase, in combination with pimozide, induces remarkable mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress, leading to GBM cell death in vitro and in vivo. | |||
| Key Molecule: Alanine-serine-cysteine transporter 2 (ASCT2) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | LN cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| T98 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B368 | |
| U251 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0021 | |
| U373 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2219 | |
| U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These elevations are driven by SREBP-1, which we find upregulates the expression of ASCT2, a key glutamine transporter. Glutamine, in turn, intensifies SREBP-1 activation through the release of ammonia, creating a feedforward loop that amplifies both glutamine metabolism and lipid synthesis, leading to drug resistance. Disrupting this loop via pharmacological targeting of ASCT2 or glutaminase, in combination with pimozide, induces remarkable mitochondrial damage and oxidative stress, leading to GBM cell death in vitro and in vivo. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
