Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02029) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
BX795
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
702675-74-9|BX795|BX-795|BX 795|N-[3-[[5-IODO-4-[[3-[(2-THIENYLCARBONYL)AMINO]PROPYL]AMINO]-2-PYRIMIDINYL]AMINO]PHENYL]-1-PYRROLIDINECARBOXAMIDE|N-(3-((5-iodo-4-((3-(thiophene-2-carboxamido)propyl)amino)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide|N-[3-[[5-iodo-4-[3-(thiophene-2-carbonylamino)propylamino]pyrimidin-2-yl]amino]phenyl]pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide|N-{3-[(5-iodo-4-{[3-(thiophen-2-ylformamido)propyl]amino}pyrimidin-2-yl)amino]phenyl}pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide|N-(3-{[5-Iodo-4-({3-[(Thiophen-2-Ylcarbonyl)amino]propyl}amino)pyrimidin-2-Yl]amino}phenyl)pyrrolidine-1-Carboxamide|N-(3-(4-(3-(Thiophene-2-carbonylamino)propylamino)-5-iodopyrimidin-2-ylamino)phenyl)pyrrolidine-1-carboxamide|C23H26IN7O2S|BX7|MFCD12546134|CID 10077147|MLS006011190|CHEMBL577784|GTPL8006|SCHEMBL3865995|BDBM17051|CHEBI:91439|DTXSID50435186|EX-A262|BCPP000310|GLXC-04290|HMS3244G15|HMS3244G16|HMS3244H15|HMS3651A07|HMS3672K09|BCP01899|BX795/BX-795|BX795?|s1274|AKOS016369934|BCP9000467|CCG-264884|CS-0259|SB13079|SDCCGSBI-0645948.P001|NCGC00250386-01|NCGC00250386-02|NCGC00250386-12|AC-32825|AS-16196|HY-10514|SMR004702959|BCP0726000131|BX-795, 3|SW208681-3|BRD-K47983010-001-01-3|BRD-K47983010-001-09-6|BRD-K47983010-001-12-0|BRD-K47983010-001-14-6|Q27075609|N-(3-((5-Iodo-4-((3-(2-thienylcarbonyl)amino)propyl)amino)-2-pyrimidinyl)amino)phenyl)-1-pyrrolidinecarboxamide|Pyrrolidine-1-carboxylic acid [3-(5-iodo-4-{3-[(thiophene-2-carbonyl)-amino]-propylamino}-pyrimidin-2-ylamino)-phenyl]-amide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Investigative
|
||||
| Structure |
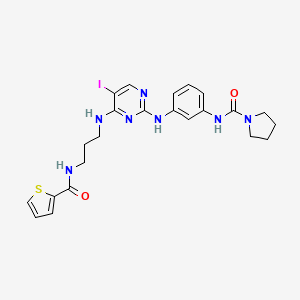
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK-3B) | GSK3B_HUMAN | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C23H26IN7O2S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CCN(C1)C(=O)NC2=CC=CC(=C2)NC3=NC=C(C(=N3)NCCCNC(=O)C4=CC=CS4)I
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C23H26IN7O2S/c24-18-15-27-22(30-20(18)25-9-5-10-26-21(32)19-8-4-13-34-19)28-16-6-3-7-17(14-16)29-23(33)31-11-1-2-12-31/h3-4,6-8,13-15H,1-2,5,9-12H2,(H,26,32)(H,29,33)(H2,25,27,28,30)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VAVXGGRQQJZYBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: phosphoinositide-3-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDPK1) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SAS cells | Oral | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1675 |
| TW2.6 cells | Mouth | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GZ05 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Immunohistochemical analysis revealed that higher PDK1 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in OSCC. The immunoprecipitation assay indicated PDK1/CD47 binding. PDK1 ligation significantly impaired OSCC orosphere formation and downregulated Sox2, Oct4, and CD133 expression. The combination of BX795 and cisplatin markedly reduced in OSCC cell's epithelial-mesenchymal transition, implying its synergistic effect. p-PDK1, CD47, Akt, PFKP, PDK3 and LDHA protein expression were significantly reduced, with the strongest inhibition in the combination group. Chemo/radiotherapy together with abrogation of PDK1 inhibits the oncogenic (Akt/CD47) and glycolytic (LDHA/PFKP/PDK3) signaling and, enhanced or sensitizes OSCC to the anticancer drug effect through inducing apoptosis and DNA damage together with metabolic reprogramming. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
