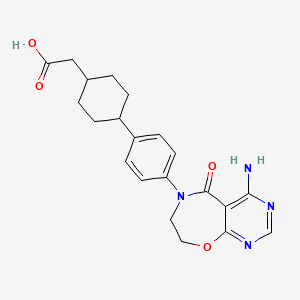
Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02020) and It's Reported Resistant Information
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Neurofibromin 1 (NF1) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | ER+ breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C61.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | Rat, with ER + MCF7 cell lines | Rats | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
LC-MS | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Incucyte proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Lastly,NF1deficiency alters the synergy between metabolic inhibitors and traditional targeted inhibitors. This includes increased synergy with inhibitors targeting glycolysis, glutamine metabolism, mitochondrial fatty acid transport, and TG synthesis. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.