Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02016) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Pitavastatin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Pitavastatin; Itavastatin; Livalo; NK 104; Pitavastatin [INN]; Pitavastatin calcium; UNII-M5681Q5F9P; NK-104; C25H24FNO4; M5681Q5F9P; Zypitamag; Flovas; (3R,5S,6E)-7-(2-Cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl)-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; P 872441; P-872441; (3R,5S,6E)-7-[2-cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinolin-3-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyhept-6-enoic acid; ( )-(3R,5S,6E)-7-(2-Cyclopropyl-4-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-quinolyl)-3,5-dihydroxy-6-heptenoic acid; NK 104 (acid); Pitavastatin calcium (JAN)
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
.
|
||||
| Structure |
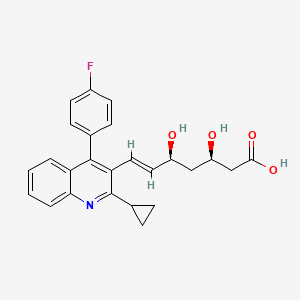
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C25H24FNO4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1CC1C2=NC3=CC=CC=C3C(=C2C=CC(CC(CC(=O)O)O)O)C4=CC=C(C=C4)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H24FNO4/c26-17-9-7-15(8-10-17)24-20-3-1-2-4-22(20)27-25(16-5-6-16)21(24)12-11-18(28)13-19(29)14-23(30)31/h1-4,7-12,16,18-19,28-29H,5-6,13-14H2,(H,30,31)/b12-11+/t18-,19-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VGYFMXBACGZSIL-MCBHFWOFSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Hippo signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04390 | |
| Insulin signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04910 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Female BALB/c-nu mice, with PC9 and PC9GR cells | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | PC9 gefitinib resistant strains were induced by low-dose maintenance. Cell culture and animal-related studies validated that the application of pitavastatin inhibited the proliferation of lung cancer cells, promoted cell apoptosis, and restrained the acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs. KEGG pathway analysis showed that the hippo/YAP signaling pathway was activated in PC9GR cells relative to PC12 cells, and the YAP expression was inhibited by pitavastatin administration. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Lipid metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Hippo signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04390 | |
| Insulin signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04910 | ||
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | PC9 gefitinib resistant strains were induced by low-dose maintenance. Cell culture and animal-related studies validated that the application of pitavastatin inhibited the proliferation of lung cancer cells, promoted cell apoptosis, and restrained the acquired resistance to EGFR-TKIs. KEGG pathway analysis showed that the hippo/YAP signaling pathway was activated in PC9GR cells relative to PC10 cells, and the YAP expression was inhibited by pitavastatin administration. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
