Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02015) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
IACS-010759
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1570496-34-2|IACS-010759|IACS-10759|5-(5-methyl-1-(3-(4-(methylsulfonyl)piperidin-1-yl)benzyl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl)-3-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole|IACS-010759 free base|IACS 010759 - Bio-X|IACS 010759 [WHO-DD]|Iacs 010759|5-[5-methyl-1-[[3-(4-methylsulfonylpiperidin-1-yl)phenyl]methyl]-1,2,4-triazol-3-yl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazole|42W52V11DJ|Oxidative phosphorylation inhibitor IACS-010759|1570496-34-2 (free base)|IACS-010759 (IACS-10759)|4-Methanesulfonyl-1-{3-[(5-methyl-3-{3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl}-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}piperidine|Piperidine, 4-(methylsulfonyl)-1-(3-((5-methyl-3-(3-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)phenyl)-|4-(Methylsulfonyl)-1-[3-[[5-methyl-3-[3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]methyl]phenyl]piperidine (IACS-010759)|UNII-42W52V11DJ|C25H25F3N6O4S|CHEMBL4778699|SCHEMBL15498716|IACS10759|GLXC-15124|BCP20596|EX-A1907|OXPHOS Inhibitor IACS-010759|IACS-010759?|NSC809972|s8731|AKOS030527987|NSC-809972|AC-31606|BS-15465|FM165719|DB-196077|HY-112037|CS-0042459|C72972|4-(Methylsulfonyl)-1-(3-((5-methyl-3-(3-(4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl)phenyl)piperidine|4-(Methylsulfonyl)-1-[3-[[5-methyl-3-[3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]methyl]phenyl]piperidine (IACS-010759); 4-(Methylsulfonyl)-1-[3-[[5-methyl-3-[3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl]methyl]phenyl]piperidine (IACS-010759)|4-methanesulfonyl-1-{3-[(5-methyl-3-{3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl}-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}piperidine|4-Methanesulfonyl-1-{3-[(5-methyl-3-{3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl}-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methyl]phenyl}piperi dine
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
.
|
||||
| Structure |
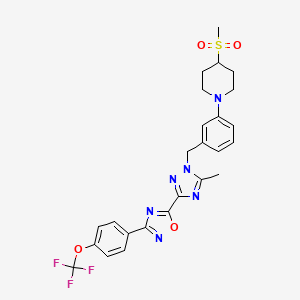
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C25H25F3N6O4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=NC(=NN1CC2=CC(=CC=C2)N3CCC(CC3)S(=O)(=O)C)C4=NC(=NO4)C5=CC=C(C=C5)OC(F)(F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C25H25F3N6O4S/c1-16-29-23(24-30-22(32-38-24)18-6-8-20(9-7-18)37-25(26,27)28)31-34(16)15-17-4-3-5-19(14-17)33-12-10-21(11-13-33)39(2,35)36/h3-9,14,21H,10-13,15H2,1-2H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
HWJWNWZJUYCGKV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cyclin-dependent kinase 12 (CDK12) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | Nude (nu/nu) mice, with PC3 VEC or PC3 CDK12KO | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Tumor volume assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | CDK12-deficient prostate cancers reprogramme cellular energy metabolism to support their aggressive progression. In particular, CDK12 deficiency enhanced the mitochondrial respiratory chain for electronic transfer and ATP synthesis to create a ferroptosis potential in CRPC cells. However, CDK12 deficiency downregulated ACSL4 expression, which counteracts the lipid oxidation stress, leading to the escape of CRPC cells from ferroptosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | . | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | PNT1A cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2163 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recently, we have demonstrated that an inhibitor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I IACS-010759 ('IACS') acts synergistically with ARN in reducing PCa cell growth [25]. In this study, we investigated the effects of ARN and IACS on the mitochondrial network architecture and dynamics in PCa cells. Additionally, we explored the effect of androgen in regulating the mitochondrial network dynamics and metabolic modulations of respiratory pathways. | |||
| Key Molecule: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | . | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recently, we have demonstrated that an inhibitor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I IACS-010759 ('IACS') acts synergistically with ARN in reducing PCa cell growth [26]. In this study, we investigated the effects of ARN and IACS on the mitochondrial network architecture and dynamics in PCa cells. Additionally, we explored the effect of androgen in regulating the mitochondrial network dynamics and metabolic modulations of respiratory pathways. | |||
| Key Molecule: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | . | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | PC-3 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recently, we have demonstrated that an inhibitor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I IACS-010759 ('IACS') acts synergistically with ARN in reducing PCa cell growth [27]. In this study, we investigated the effects of ARN and IACS on the mitochondrial network architecture and dynamics in PCa cells. Additionally, we explored the effect of androgen in regulating the mitochondrial network dynamics and metabolic modulations of respiratory pathways. | |||
| Key Molecule: Homeodomain-interacting protein kinase 3 (HIPK3) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Mitochondrial metabolism | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | . | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | C4-2 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4782 |
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis rate assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Recently, we have demonstrated that an inhibitor of the mitochondrial electron transport chain complex I IACS-010759 ('IACS') acts synergistically with ARN in reducing PCa cell growth [28]. In this study, we investigated the effects of ARN and IACS on the mitochondrial network architecture and dynamics in PCa cells. Additionally, we explored the effect of androgen in regulating the mitochondrial network dynamics and metabolic modulations of respiratory pathways. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
