Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02006) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
CB839
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Phase 2
|
||||
| Structure |
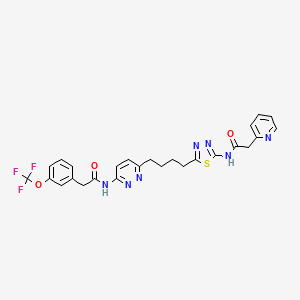
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Glutaminase (GLS) |
GLSK_HUMAN
; GLSL_HUMAN |
|||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C26H24F3N7O3S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=CC=NC(=C1)CC(=O)NC2=NN=C(S2)CCCCC3=NN=C(C=C3)NC(=O)CC4=CC(=CC=C4)OC(F)(F)F
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C26H24F3N7O3S/c27-26(28,29)39-20-9-5-6-17(14-20)15-22(37)31-21-12-11-18(33-34-21)7-1-2-10-24-35-36-25(40-24)32-23(38)16-19-8-3-4-13-30-19/h3-6,8-9,11-14H,1-2,7,10,15-16H2,(H,31,34,37)(H,32,36,38)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PRAAPINBUWJLGA-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | PDAC patients | Homo Sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | Metabolic pressures like glutamine deficiency lead to the emergence of an aggressive and poor prognostic reverse Warburg phenotype in PDAC. As the major fuel of this phenotype, lactate taken up by MCT1 maintains cellular redox homeostasis and thereby cell viability during critical shortages of glutamine supply. This also manifests in resistance against inhibitors of glutamine metabolism, thus limiting their usage in the clinic. | |||
| Key Molecule: Monocarboxylate transporter 1 (MCT1) | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A818-6 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3893 |
| T3M4 cells | Pancreas | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4056 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Metabolic pressures like glutamine deficiency lead to the emergence of an aggressive and poor prognostic reverse Warburg phenotype in PDAC. As the major fuel of this phenotype, lactate taken up by MCT1 maintains cellular redox homeostasis and thereby cell viability during critical shortages of glutamine supply. This also manifests in resistance against inhibitors of glutamine metabolism, thus limiting their usage in the clinic. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
