Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG02001) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Bafetinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Bafetinib; 859212-16-1; INNO-406; NS-187; UNII-NVW4Z03I9B; CNS-9; NVW4Z03I9B; INNO406; CHEMBL206834; (S)-N-(3-([4,5'-bipyrimidin]-2-ylamino)-4-methylphenyl)-4-((3-(dimethylamino)pyrrolidin-1-yl)methyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)benzamide; 4-[[(3S)-3-DIMETHYLAMINOPYRROLIDIN-1-YL]METHYL]-N-[4-METHYL-3-[(4-PYRIMIDIN-5-YLPYRIMIDIN-2-YL)AMINO]PHENYL]-3-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)BENZAMIDE; INNO 406; NS 187; N-[3-(4,5'-Bipyrimidin-2-Ylamino)-4-Methylphenyl]-4-{[(3s)-3-(Dimethylamino)pyrrolidin-1-Yl]methyl}-3-(Trifluoromethyl)benzamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
Phase 2
|
||||
| Structure |
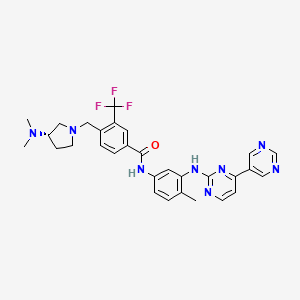
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Fusion protein Bcr-Abl (Bcr-Abl) | BCR_HUMAN-ABL1_HUMAN | |||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C30H31F3N8O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC(=C(C=C2)CN3CC[C@@H](C3)N(C)C)C(F)(F)F)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CN=C5
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C30H31F3N8O/c1-19-4-7-23(13-27(19)39-29-36-10-8-26(38-29)22-14-34-18-35-15-22)37-28(42)20-5-6-21(25(12-20)30(31,32)33)16-41-11-9-24(17-41)40(2)3/h4-8,10,12-15,18,24H,9,11,16-17H2,1-3H3,(H,37,42)(H,36,38,39)/t24-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
ZGBAJMQHJDFTQJ-DEOSSOPVSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Histone H3 | [1] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glucose metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Oral squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6E.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Lactylation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | OSCC samples | Homo Sapiens | ||
| Mechanism Description | We found that histone Kla-induced BCAM was overexpressed in OSCC, and a high BCAM level was related to a lower immune cell score and inhibition of immune response. On the other hand, BCAM induced EMT and angiogenesis, leading to OSCC malignant progression via activating the Notch signaling pathway. However, the difference of the BCAM function in Pan-cancers might be attributed to tumor heterogeneity. Taken together, BCAM played a vital role in OSCC chemotherapy resistance and prognosis and contributed to inhibition of the immune process, suggesting that it might be a novel therapeutic target for OSCC. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
