Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01238) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ivacaftor
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ivacaftor; 873054-44-5; VX-770; Kalydeco; Ivacaftor (VX-770); N-(2,4-di-tert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide; VX 770; VX770; UNII-1Y740ILL1Z; N-[2,4-Bis(tert-butyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxamide; CHEBI:66901; 1Y740ILL1Z; N-(2,4-ditert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1H-quinoline-3-carboxamide; 3-Quinolinecarboxamide, N-(2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl)-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-; 1413431-05-6; 3-Quinolinecarboxamide, N-[2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-; Kalydeco (TN); Ivacaftor [USAN:INN]; ivacaftorum; Ivacaftor D18; VX7; Ivacaftor (USAN/INN); VX-770 - Ivacaftor; MLS006011119; SCHEMBL351373; GTPL4342; VX-770, Ivacaftor, Kalydeco; CHEMBL2010601; DTXSID00236281; EX-A441; QCR-155; BCPP000199; HMS3654E10; HMS3744K05; AOB31714; BCP19794; BDBM50032693; MFCD17171361; s1144; ZINC52509463; AKOS015994762; AKOS032950001; BCP9000799; CCG-268562; CS-0497; DB08820; EX-7211; LE-0002; SB16815; N-(2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide; NCGC00242480-01; NCGC00242480-03; AC-28324; HY-13017; SMR004702900; FT-0696681; SW219620-1; X7565; EC-000.2478; A25626; D09916; AB01565806_02; Q6095693; CTP-656; CTP-656; CTP-656; d9-ivacaftor;VX-561; Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator Potentiator; N-(5-hydroxy-2,4-ditert-butyl-phenyl)-4-oxo-1H-quinoline-3-carboxamide; N-(2,4-ditert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide; N-(5-Hydroxy-2,4-bis(2-methyl-2-propanyl)phenyl]-4-oxo-1,4-dihydro-3-quinolinecarboxamide; N-[2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxamide; 1134822-00-6; Ivacaftor;N-(2,4-di-tert-butyl-5-hydroxyphenyl)-4-oxo-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carboxamide;Ivacaftor; Kalydeco; ; ; N-[2,4-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-hydroxyphenyl]-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
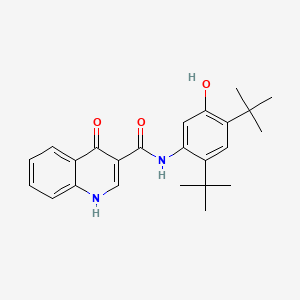
|
||||
| Target | cAMP-dependent chloride channel (CFTR) | CFTR_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C24H28N2O3
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)(C)C1=CC(=C(C=C1NC(=O)C2=CNC3=CC=CC=C3C2=O)O)C(C)(C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C24H28N2O3/c1-23(2,3)16-11-17(24(4,5)6)20(27)12-19(16)26-22(29)15-13-25-18-10-8-7-9-14(18)21(15)28/h7-13,27H,1-6H3,(H,25,28)(H,26,29)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PURKAOJPTOLRMP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| HEK293 FT cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6911 | |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c female nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; Immunofluorescence staining assay; Immunohistochemistry; RNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Colony formation assay; EdU incorporation assay; Cell apoptosis assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Osimertinib, a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI), has demonstrated significant clinical benefits in the treatment of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, inevitable acquired resistance to osimertinib limits its clinical utility, and there is a lack of effective countermeasures. Here, we established osimertinib-resistant cell lines and performed drug library screening. This screening identified ivacaftor, a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiator, as a synergistic enhancer of osimertinib-induced anti-tumor activity both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ivacaftor facilitated the colocalization of CFTR and PTEN on the plasma membrane to promote the function of PTEN, subsequently inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and suppressing tumor growth. In summary, our study suggests that activating CFTR enhances osimertinib-induced anti-tumor activity by regulating the PTEN-AKT axis. Furthermore, ivacaftor and osimertinib constitute a potential combination strategy for treating osimertinib-resistant EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients. | |||
| Key Molecule: Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC-9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 |
| HEK293 FT cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6911 | |
| NCI-H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c female nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; Immunofluorescence staining assay; Immunohistochemistry; RNA sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay; Colony formation assay; EdU incorporation assay; Cell apoptosis assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Osimertinib, a third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI), has demonstrated significant clinical benefits in the treatment of EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). However, inevitable acquired resistance to osimertinib limits its clinical utility, and there is a lack of effective countermeasures. Here, we established osimertinib-resistant cell lines and performed drug library screening. This screening identified ivacaftor, a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiator, as a synergistic enhancer of osimertinib-induced anti-tumor activity both in vitro and in vivo. Mechanistically, ivacaftor facilitated the colocalization of CFTR and PTEN on the plasma membrane to promote the function of PTEN, subsequently inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and suppressing tumor growth. In summary, our study suggests that activating CFTR enhances osimertinib-induced anti-tumor activity by regulating the PTEN-AKT axis. Furthermore, ivacaftor and osimertinib constitute a potential combination strategy for treating osimertinib-resistant EGFR-mutated NSCLC patients. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
