Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00750) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Lidocaine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Lidocaine; 137-58-6; Lignocaine; Xylocaine; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; Lidoderm; Anestacon; Esracaine; Duncaine; Alphacaine; Cappicaine; Gravocain; Isicaina; L-Caine; Leostesin; Maricaine; Xylestesin; Xylocain; Xylocitin; Solcain; Isicaine; Rucaina; Xilina; Xycaine; Xylotox; Cito optadren; Lida-Mantle; Dalcaine; 2-(Diethylamino)-2',6'-acetoxylidide; Xyloneural (free base); Cuivasil; Jetocaine; Lidocainum; Remicaine; Xilocaina; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide; Acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-; Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide; ELA-Max; 2',6'-Acetoxylidide, 2-(diethylamino)-; alpha-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; Lidocaton; alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide; CHEBI:6456; UNII-98PI200987; Xylocaine (TN); CHEMBL79; MFCD00026733; LIDOPEN; N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide; MLS000069724; Dentipatch; Lignocainum; Xllina; NSC-40030; N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N(2),N(2)-diethylglycinamide; Lidocaine (VAN); .alpha.-Diethylaminoaceto-2,6-xylidide; NCGC00015611-10; Xilocaina [Italian]; Dilocaine; Lidocaina; SMR000058189; .alpha.-(Diethylamino)-2,6-acetoxylidide; Lidocaine Base; .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; .omega.-Diethylamino-2,6-dimethylacetanilide; 98PI200987; Lidocainum [INN-Latin]; DSSTox_CID_25166; DSSTox_RID_80716; DSSTox_GSID_45166; Lidocaina [INN-Spanish]; N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-Dimethylphenyl)ethanamide; EMBOLEX; Versatis; Ztilido; ZTlido; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-acetamide; Dentipatch (TN); CAS-137-58-6; LQZ; HSDB 3350; EINECS 205-302-8; NSC 40030; alfa-Dietilamino-2,6-dimetilacetanilide [Italian]; BRN 2215784; Qualigens; Xyline; Lignocaine base; LidocaineHClH2O; Lidocaine [USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Lidocaine, powder; N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N2,N2-diethylglycinamide; Zingo (Salt/Mix); CDS1_000283; Lidocaine (Alphacaine); Spectrum_001118; Lidothesin (Salt/Mix); Xyloneural (Salt/Mix); Opera_ID_385; Maybridge1_002571; Prestwick0_000050; Prestwick1_000050; Prestwick2_000050; Prestwick3_000050; Spectrum2_001343; Spectrum3_001392; Spectrum4_000070; Spectrum5_001549; Lopac-L-5647; Lidaform HC (Salt/Mix); Epitope ID:116205; Lidamantle HC (Salt/Mix); 2', 2-(diethylamino)-; Neosporin Plus (Salt/Mix); Lopac0_000669; SCHEMBL15689; BSPBio_000179; BSPBio_001359; BSPBio_003004; KBioGR_000079; KBioGR_000599; KBioSS_000079; KBioSS_001598; 2-Diethylamino-N-(2,6-dimethyl-phenyl)-acetamide; 4-12-00-02538 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS000758263; MLS001074177; MLS001423964; BIDD:GT0342; Diethylaminoacet-2,6-xylidide; DivK1c_000174; DivK1c_001323; Lidocaine, analytical standard; SPBio_001525; SPBio_002100; Lidocaine (JP17/USP/INN); ALGRX 3268; ALGRX-3268; BPBio1_000197; GTPL2623; DTXSID1045166; SCHEMBL17967359; HMS548M19; KBio1_000174; KBio2_000079; KBio2_001598; KBio2_002647; KBio2_004166; KBio2_005215; KBio2_006734; KBio3_000157; KBio3_000158; KBio3_002224; ZINC20237; Lidocaine 1.0 mg/ml in Methanol; NINDS_000174; Bio1_000379; Bio1_000868; Bio1_001357; Bio2_000079; Bio2_000559; HMS1791D21; HMS1989D21; HMS2051C21; HMS2089E15; HMS2235O14; HMS3371J04; HMS3393C21; HMS3428O07; HMS3651G09; AMY25560; BCP09081; HY-B0185; NSC40030; Tox21_110183; BDBM50017662; NSC789222; s1357; STK552033; AKOS001026768; Tox21_110183_1; CCG-100824; CS-2070; DB00281; MCULE-9294700940; NC00074; NSC-789222; SB19118; SDCCGSBI-0050648.P005; WLN: 2N2 & 1VMR B1 F1; .alpha.-Diethylamino-2,6-acetoxylidide; CAS-73-78-9; IDI1_000174; IDI1_033829; NCGC00015611-01; NCGC00015611-02; NCGC00015611-03; NCGC00015611-04; NCGC00015611-05; NCGC00015611-06; NCGC00015611-07; NCGC00015611-08; NCGC00015611-09; NCGC00015611-11; NCGC00015611-12; NCGC00015611-13; NCGC00015611-14; NCGC00015611-15; NCGC00015611-16; NCGC00015611-18; NCGC00015611-31; NCGC00022176-05; NCGC00022176-06; NCGC00022176-07; NCGC00022176-08; NCGC00022176-09; AC-10282; AS-13718; M620; SY052029; 2-(Diethylamino)-2'',6''-acetoxylidide; SBI-0050648.P004; AB00053581; L0156; SW196598-4; A18187; C07073; D00358; J10173; M06299; AB00053581-27; AB00053581-28; AB00053581_29; AB00053581_30; A833036; Q216935; (2,6-dimethylphenyl)carbamoylmethyl-diethyl-azanium; N1-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-2-(diethylamino)acetamide; W-108233; 2-(Diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide #; BRD-K52662033-001-02-6; BRD-K52662033-003-05-5; BRD-K52662033-003-14-7; Z55135799; Lidocaine, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Lidocaine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; N~1~-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-N~2~,N~2~-diethylglycinamide; Lidocaine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide hydrate hydrochloride; Lidocaine, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; Lidocaine solution, 1.0 mg/mL in methanol, ampule of 1 mL, certified reference material; 91484-71-8
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
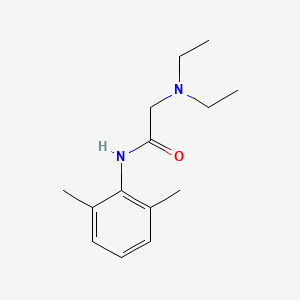
|
||||
| Target | Voltage-gated sodium channel alpha Nav1.9 (SCN11A) | SCNBA_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C14H22N2O
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCN(CC)CC(=O)NC1=C(C=CC=C1C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C14H22N2O/c1-5-16(6-2)10-13(17)15-14-11(3)8-7-9-12(14)4/h7-9H,5-6,10H2,1-4H3,(H,15,17)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
NNJVILVZKWQKPM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Hepatocyte growth factor receptor (MET) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | HGF/MET signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | ||||
| DBTRG-05MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1169 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay; Cell cytotoxicity assay; Colony formation assay; Cell proliferation assay; Wound-healing assay; Transwell assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | In the present study, the clinical importance of the HGF/MET pathway was analyzed using bioinformatics. By establishing TMZ?resistant cell lines, the impact of combined treatment with lidocaine and TMZ was investigated. Additionally, the effects of lidocaine on cellular function were also examined and confirmed using knockdown techniques. The current findings revealed that the HGF/MET pathway played a key role in brain cancer, and its activation in GBM was associated with increased malignancy and poorer patient outcomes. Elevated HGF levels and activation of its receptor were found to be associated with TMZ resistance in GBM cells. Lidocaine effectively suppressed the HGF/MET pathway, thereby restoring TMZ sensitivity in TMZ?resistant cells. Furthermore, lidocaine also inhibited cell migration. Overall, these results indicated that inhibiting the HGF/MET pathway using lidocaine can enhance the sensitivity of GBM cells to TMZ and reduce cell migration, providing a potential basis for developing novel therapeutic strategies for GBM. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
