Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00722) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Eflornithine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
EFLORNITHINE; 70052-12-9; Ornidyl; 2-(Difluoromethyl)ornithine; dfmo; 2,5-diamino-2-(difluoromethyl)pentanoic acid; Difluoromethylornithine; Vaniqa; alpha-Difluoromethylornithine; 2-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine; Eflornithine free base; alpha-(Difluoromethyl)-DL-ornithine; Difluromethylornithine; RMI 71782; 67037-37-0; DL-.alpha.-Difluoromethylornithine; CHEMBL830; DFMO HCl; CHEBI:41948; 70052-12-9 (free base); NSC337250; Eflornithinum; Eflornitina; Eflornithinum [Latin]; Eflornitina [Spanish]; 2,5-diamino-2-(difluoromethyl)pentanoic acid.; .alpha.-DFMO HCl; DFMO (growth regulator); Eflornithine [INN:BAN]; 70050-56-5; L-DFMO;L-RMI71782;L-alpha-difluoromethylornithine; DL-alpha-(Difluoromethyl)ornithine; DL-Ornithine, monohydrochloride; MDL 71782; Eflornithine (INN); CCRIS 3295; Ornithine, 2-(difluoromethyl)-; NSC-337250; DL-Ornithine, 2-(difluoromethyl)-; (-)-2-Difluoromethylornithine; BRN 2250529; alpha,delta-Diamino-alpha-(difluoromethyl)valeric acid; SR-01000076229; C6H12F2N2O2; HSDB 7923; alpha-DFMO; (RS)-eflornithine; RFI 7178; Lopac0_000429; SCHEMBL26327; GTPL5176; 2-(difluoromethyl)-L-ornithine; alpha-difluoromethyl-dl-ornithine; DTXSID3020467; H-DL-(a-Difluoromethyl)Orn-OH; BCP10516; HY-B0744; 2-(difluoromethyl)ornithine (DMFO); BDBM50028197; HSCI1_000267; MFCD00221766; AKOS006281180; CCG-204521; DB06243; SDCCGSBI-0050414.P002; NCGC00015316-02; NCGC00015316-03; NCGC00015316-06; NCGC00015316-15; NCGC00162152-01; K100; 2-difluoromethyl-2,5-diaminopentanoic acid; DB-055371; FT-0630795; FT-0720946; FT-0775156; 2-(difluoromethyl)-2,5-diaminopentanoic acid;; C07997; D07883; 020E916; A936641; Q424751; (RS)-2,5-diamino-2-(difluoromethyl)pentanoic acid; DFMO;MDL71782;RMI71782;; A-difluoromethylornithine; SR-01000076229-10
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
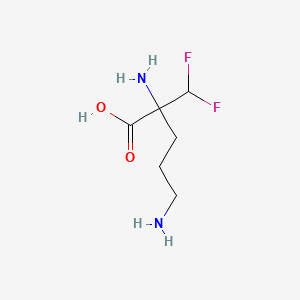
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C6H12F2N2O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C(CC(C(F)F)(C(=O)O)N)CN
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C6H12F2N2O2/c7-4(8)6(10,5(11)12)2-1-3-9/h4H,1-3,9-10H2,(H,11,12)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
VLCYCQAOQCDTCN-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1) | [2] | |||
| Metabolic Type | Glutamine metabolism | |||
| Resistant Disease | Osteosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B51.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | 6-8-week-old female nude mice, with osteosarcoma cells | Mice | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DFMO treatment curbs the phosphorylation of YAP1 protein in OS cells, promoting nuclear entry and initiating the YAP1-mediated glutamine metabolic pathway. This reduces intracellular ROS levels, countering DFMO's anticancer effect. The therapeutic efficacy of DFMO can be amplified both in vivo and in vitro by combining it with the YAP1 inhibitor CIL56 or the glutaminase inhibitor CB-839. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
