Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00678) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Ethambutol
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ethambutol; 74-55-5; Ethambutolum; Aethambutolum; D-Ethambutol; (+)-S,S-Ethambutol; Ethambutol Hydrochloride; (+)-ethambutol; (S,S)-ethambutol; Myambutol; (2S,2'S)-2,2'-(Ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanediyl))bis(butan-1-ol); Etambutolo [DCIT]; Tibutol; Etambutol [INN-Spanish]; Ethambutolum [INN-Latin]; S,S-Ethambutol; Diambutol; Ebutol; CHEBI:4877; UNII-8G167061QZ; (+)-2,2'-(Ethylenediimino)di-1-butanol; Purderal; (+)-N,N'-Bis(1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl)ethylenediamine; EMB; (2S)-2-[2-[[(2S)-1-hydroxybutan-2-yl]amino]ethylamino]butan-1-ol; 8G167061QZ; (2R)-2-[2-(1-hydroxybutan-2-ylamino)ethylamino]butan-1-ol; 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis-, (2S,2'S)-; 1-Butanol,2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis-, (2S,2'S)-; (2S,7S)-2,7-diethyl-3,6-diazaoctane-1,8-diol; (2S,2'S)-2,2'-(ethane-1,2-diyldiimino)dibutan-1-ol; Etambutolo; C10H24N2O2; D-2,2'-(Ethylenediimino)di-1-butanol; D-2,2'-(Ethylenediimino)bis(1-butanol); 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis-, (S-(R*,R*))-; Ethambutol, racemic mixture; 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(ethylenediimino)di-, (+)-; d,N,N'-Bis(1-hydroxymethylpropyl)ethylenediamine; D-N,N'-Bis(1-hydroxymethylpropyl)ethylenediamine; Ethambutol [INN:BAN]; (R)-2,2'-(1,2-Ethanediyldiimino)bis-1-butanol; NCGC00178864-03; 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis-, (R-(R*,R*))-; HSDB 3078; Servambutol (TN); 95E; Ethambutol (INN); EINECS 200-810-6; Spectrum_001058; Spectrum2_001014; Spectrum3_000426; Spectrum4_000545; Spectrum5_000702; 1-Butanol, 2,2'-(1,2-ethanediyldiimino)bis-, (R)-; Myambutol (dihydrochloride); SCHEMBL3399; BSPBio_002012; KBioGR_001209; KBioSS_001538; CHEMBL44884; DivK1c_000561; SPBio_001167; CL 40881 (dihydrochloride); DTXSID8023006; KBio1_000561; KBio2_001538; KBio2_004106; KBio2_006674; KBio3_001232; NINDS_000561; HY-B0535; 2860AH; BDBM50448407; ZINC19364219; DB00330; MCULE-9663372083; IDI1_000561; NCGC00178864-01; NCGC00178864-04; SBI-0051375.P003; C06984; D07925; D94801; E-3950; AB00053473_04; AB00053473_05; Q412318; (S,S)-2,2'-(1,2-Ethanediyldiimino)bis-1-butanol; BRD-K93231391-300-03-1; (+)-(S,S)-2,2'-(1,2-Ethylenediimino)-di-1-butanol; Ethambutol dihydrochloride, Antibiotic for Culture Media Use Only; (2S)-2-[(2-{[(2S)-1-hydroxybutan-2-yl]amino}ethyl)amino]butan-1-ol; (2S)-2-[2-[[(1S)-1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]amino]ethylamino]butan-1-ol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
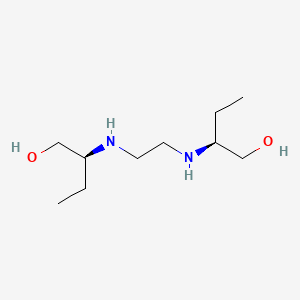
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[2]
[3]
[5]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[4]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Mycobacterium Arabinosyltransferase C (MycB embC) | EMBC_MYCTU | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C10H24N2O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H](CO)NCCN[C@@H](CC)CO
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C10H24N2O2/c1-3-9(7-13)11-5-6-12-10(4-2)8-14/h9-14H,3-8H2,1-2H3/t9-,10-/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
AEUTYOVWOVBAKS-UWVGGRQHSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Probable arabinosyltransferase A (EMBA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Mechanism Description | Ethambutol (EMB) is one of the first-line drugs regimens for TB treatment. Arabinosyl transferases are established targets of EMB, which is involved in the biosynthesis of arabinogalactan (AG) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM). Mutations among embCAB operon are responsible for around 70% clinical EMB resistant M. tuberculosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable arabinosyltransferase B (EMBB) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Mechanism Description | Ethambutol (EMB) is one of the first-line drugs regimens for TB treatment. Arabinosyl transferases are established targets of EMB, which is involved in the biosynthesis of arabinogalactan (AG) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM). Mutations among embCAB operon are responsible for around 70% clinical EMB resistant M. tuberculosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Probable arabinosyltransferase C (EMBC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | STK11 KO cells | Fetal kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B3IE |
| Mechanism Description | Ethambutol (EMB) is one of the first-line drugs regimens for TB treatment. Arabinosyl transferases are established targets of EMB, which is involved in the biosynthesis of arabinogalactan (AG) and lipoarabinomannan (LAM). Mutations among embCAB operon are responsible for around 70% clinical EMB resistant M. tuberculosis. | |||
| Key Molecule: Outer membrane protein A (OmpA) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expressiom | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | 1773 | ||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | These results support the model that the roles of OmpA as a porin protein overexpressing in mycobacteria can increase the hydrophilic ability of the cell wall which can facilitate the streptomycin uptakes and increase the mycobacteria's sensitivity to aminoglycosides. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Probable arabinosyltransferase B (EMBB) | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Tuberculosis [ICD-11: 1B10.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | R173C |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
GeneSeq assay; Bioinformatics assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Out of total 112 mycobacterial positive cultures, five?M. bovis?were isolated and underwent WGS. All sequenced strains belonged to?Mycobacterium tuberculosis var bovis, spoligotype BOV_1; BOV_11. Resistance gene mutations were determined in 100% of strains to pyrazinamide (pncA?and?rpsA), isoniazid (KatG?and?ahpC), ethambutol (embB,?embC,?embR?and?ubiA), streptomycin (rpsl) and fluoroquinolones (gyrA?and?gyrB). Rifampin (rpoB?and?rpoC) and delamanid (fbiC) resistance genes were found in 80% of strains. The major represented virulence classes were the secretion system, cell surface components and regulation system. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
