Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol03010)
| Name |
Cyclin dependent kinase 7 (CDK7)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CDK7; CAK; CAK1; CDKN7; MO15; STK1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDK7
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr5:69,234,795-69,277,430[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MALDVKSRAKRYEKLDFLGEGQFATVYKARDKNTNQIVAIKKIKLGHRSEAKDGINRTAL
REIKLLQELSHPNIIGLLDAFGHKSNISLVFDFMETDLEVIIKDNSLVLTPSHIKAYMLM TLQGLEYLHQHWILHRDLKPNNLLLDENGVLKLADFGLAKSFGSPNRAYTHQVVTRWYRA PELLFGARMYGVGVDMWAVGCILAELLLRVPFLPGDSDLDQLTRIFETLGTPTEEQWPDM CSLPDYVTFKSFPGIPLHHIFSAAGDDLLDLIQGLFLFNPCARITATQALKMKYFSNRPG PTPGCQLPRPNCPVETLKEQSNPALAIKRKRTEALEQGGLPKKLIF Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine kinase involved in cell cycle control and in RNA polymerase II-mediated RNA transcription. Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are activated by the binding to a cyclin and mediate the progression through the cell cycle. Each different complex controls a specific transition between 2 subsequent phases in the cell cycle. Required for both activation and complex formation of CDK1/cyclin-B during G2-M transition, and for activation of CDK2/cyclins during G1-S transition (but not complex formation). CDK7 is the catalytic subunit of the CDK-activating kinase (CAK) complex. Phosphorylates SPT5/SUPT5H, SF1/NR5A1, POLR2A, p53/TP53, CDK1, CDK2, CDK4, CDK6 and CDK11B/CDK11. CAK activates the cyclin-associated kinases CDK1, CDK2, CDK4 and CDK6 by threonine phosphorylation, thus regulating cell cycle progression. CAK complexed to the core-TFIIH basal transcription factor activates RNA polymerase II by serine phosphorylation of the repetitive C-terminal domain (CTD) of its large subunit (POLR2A), allowing its escape from the promoter and elongation of the transcripts. Phosphorylation of POLR2A in complex with DNA promotes transcription initiation by triggering dissociation from DNA. Its expression and activity are constant throughout the cell cycle. Upon DNA damage, triggers p53/TP53 activation by phosphorylation, but is inactivated in turn by p53/TP53; this feedback loop may lead to an arrest of the cell cycle and of the transcription, helping in cell recovery, or to apoptosis. Required for DNA-bound peptides-mediated transcription and cellular growth inhibition.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.85E-35 Fold-change: 9.86E-02 Z-score: 1.38E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CDK7 is a cell cycle regulator. In addition, it also acts as a transcription factor, after complexation with cyclin H and MAT1. Increased expression of CDK7 is reported to confer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. It acts as a CDK-activating kinase (CAK) and is involved in the G2/M phase by maintaining CDK1 and CDK2 activity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CDK7 is a cell cycle regulator. In addition, it also acts as a transcription factor, after complexation with cyclin H and MAT1. Increased expression of CDK7 is reported to confer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. It acts as a CDK-activating kinase (CAK) and is involved in the G2/M phase by maintaining CDK1 and CDK2 activity. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | CDK7 is a cell cycle regulator. In addition, it also acts as a transcription factor, after complexation with cyclin H and MAT1. Increased expression of CDK7 is reported to confer resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. It acts as a CDK-activating kinase (CAK) and is involved in the G2/M phase by maintaining CDK1 and CDK2 activity. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.85E-35; Fold-change: 4.89E-01; Z-score: 7.71E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-03; Fold-change: 2.54E-01; Z-score: 4.08E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
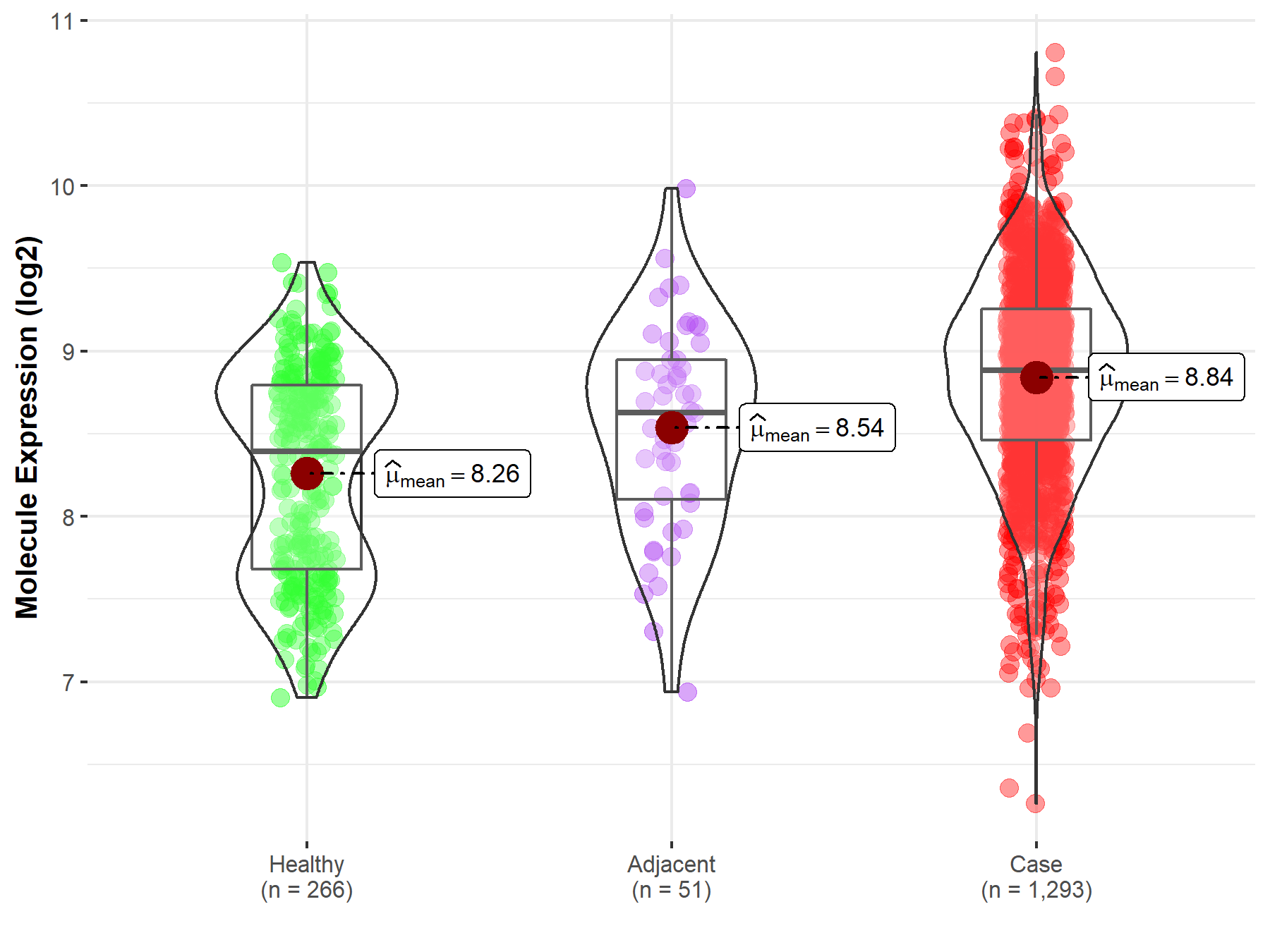
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

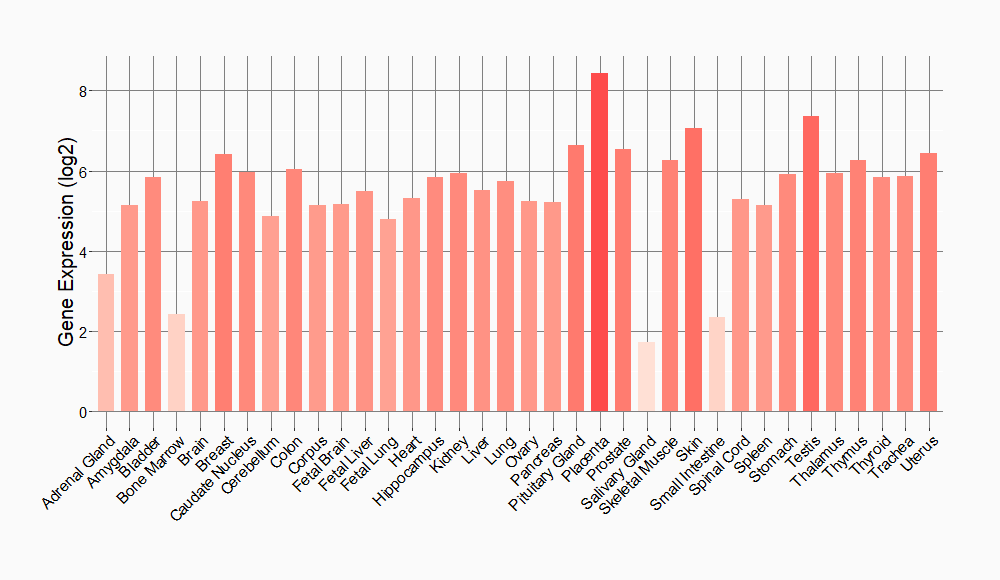
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
