Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01909)
| Name |
Retinoblastoma-like protein 1 (RBL1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
RBL1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
RBL1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr20:36,996,349-37,095,997[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MFEDKPHAEGAAVVAAAGEALQALCQELNLDEGSAAEALDDFTAIRGNYSLEGEVTHWLA
CSLYVACRKSIIPTVGKGIMEGNCVSLTRILRSAKLSLIQFFSKMKKWMDMSNLPQEFRE RIERLERNFEVSTVIFKKYEPIFLDIFQNPYEEPPKLPRSRKQRRIPCSVKDLFNFCWTL FVYTKGNFRMIGDDLVNSYHLLLCCLDLIFANAIMCPNRQDLLNPSFKGLPSDFHTADFT ASEEPPCIIAVLCELHDGLLVEAKGIKEHYFKPYISKLFDRKILKGECLLDLSSFTDNSK AVNKEYEEYVLTVGDFDERIFLGADAEEEIGTPRKFTRDTPLGKLTAQANVEYNLQQHFE KKRSFAPSTPLTGRRYLREKEAVITPVASATQSVSRLQSIVAGLKNAPSDQLINIFESCV RNPVENIMKILKGIGETFCQHYTQSTDEQPGSHIDFAVNRLKLAEILYYKILETVMVQET RRLHGMDMSVLLEQDIFHRSLMACCLEIVLFAYSSPRTFPWIIEVLNLQPFYFYKVIEVV IRSEEGLSRDMVKHLNSIEEQILESLAWSHDSALWEALQVSANKVPTCEEVIFPNNFETG NGGNVQGHLPLMPMSPLMHPRVKEVRTDSGSLRRDMQPLSPISVHERYSSPTAGSAKRRL FGEDPPKEMLMDKIITEGTKLKIAPSSSITAENVSILPGQTLLTMATAPVTGTTGHKVTI PLHGVANDAGEITLIPLSMNTNQESKVKSPVSLTAHSLIGASPKQTNLTKAQEVHSTGIN RPKRTGSLALFYRKVYHLASVRLRDLCLKLDVSNELRRKIWTCFEFTLVHCPDLMKDRHL DQLLLCAFYIMAKVTKEERTFQEIMKSYRNQPQANSHVYRSVLLKSIPREVVAYNKNIND DFEMIDCDLEDATKTPDCSSGPVKEERGDLIKFYNTIYVGRVKSFALKYDLANQDHMMDA PPLSPFPHIKQQPGSPRRISQQHSIYISPHKNGSGLTPRSALLYKFNGSPSKSLKDINNM IRQGEQRTKKRVIAIDSDAESPAKRVCQENDDVLLKRLQDVVSERANH Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Key regulator of entry into cell division. Directly involved in heterochromatin formation by maintaining overall chromatin structure and, in particular, that of constitutive heterochromatin by stabilizing histone methylation. Recruits and targets histone methyltransferases KMT5B and KMT5C, leading to epigenetic transcriptional repression. Controls histone H4 'Lys-20' trimethylation. Probably acts as a transcription repressor by recruiting chromatin-modifying enzymes to promoters. Potent inhibitor of E2F-mediated trans-activation. May act as a tumor suppressor.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A193T |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A193T |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A193T |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | The tumor suppressor RB is the aforementioned key checkpoint in the cell cycle. As the primary target of CDK4/6 inhibitors, RB was considered to be one of the most important biomarkers of sensitivity to therapy. In this scenario, loss of RB is the evident cause of resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors, and various preclinical studies have supported this hypothesis. In addition, some preclinical and clinical studies have also reported that mutations in RB are responsible for the resistance. A study using glioblastoma xenograft cells, a missense mutation in exon 2 of RB(A193T) resulted in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.03E-53; Fold-change: 1.58E-01; Z-score: 8.91E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.02E-14; Fold-change: 9.11E-02; Z-score: 6.65E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
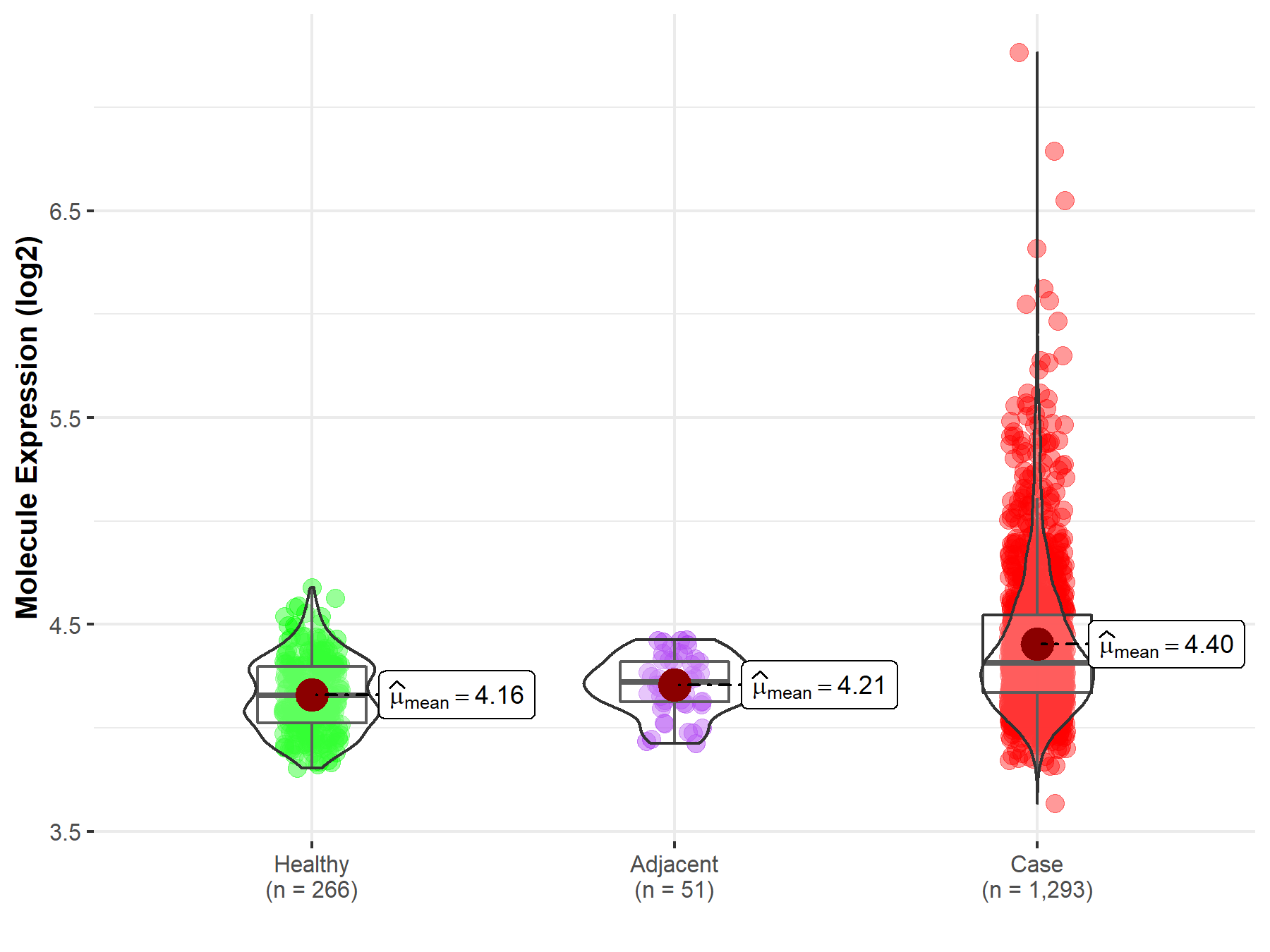
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

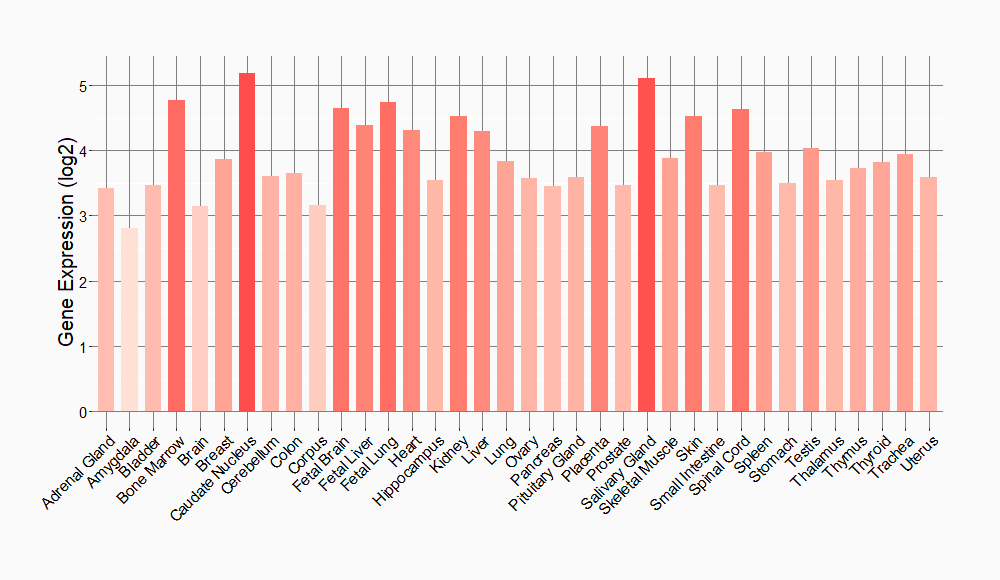
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
