Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01905)
| Name |
Protein phosphatase 3 catalytic subunit alpha (PPP3CA)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PPP3R1; CNA2; CNB
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
PPP3CA
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:68,178,857-68,256,237[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MGNEASYPLEMCSHFDADEIKRLGKRFKKLDLDNSGSLSVEEFMSLPELQQNPLVQRVID
IFDTDGNGEVDFKEFIEGVSQFSVKGDKEQKLRFAFRIYDMDKDGYISNGELFQVLKMMV GNNLKDTQLQQIVDKTIINADKDGDGRISFEEFCAVVGGLDIHKKMVVDV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Regulatory subunit of calcineurin, a calcium-dependent, calmodulin stimulated protein phosphatase. Confers calcium sensitivity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fenofibrate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Intracellular calcium flux signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05207 | |
| TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation | Activation | hsa04137 | ||
| Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| CaMKKbeta-AMPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04152 | ||
| In Vivo Model | HFD-fed mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | Administration of fenofibrate effectively ameliorated glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. In this study, fenofibrate treatment appeared to increase intracellular calcium flux and TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation and autophagy through two different mechanisms. One is the aforementioned calcium-mediated upregulation of the CaMKKbeta-AMPK pathway and the other is the activation of the calcium-dependent dephosphatase calcineurin subunit PPP3CA. | |||
| Disease Class: Insulin-resistance syndrome [ICD-11: 5A44.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Insulin-resistance syndrome [ICD-11: 5A44.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fenofibrate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Intracellular calcium flux signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05207 | |
| TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation | Activation | hsa04137 | ||
| Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| CaMKKbeta-AMPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04152 | ||
| In Vivo Model | HFD-fed mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | Administration of fenofibrate effectively ameliorated glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. In this study, fenofibrate treatment appeared to increase intracellular calcium flux and TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation and autophagy through two different mechanisms. One is the aforementioned calcium-mediated upregulation of the CaMKKbeta-AMPK pathway and the other is the activation of the calcium-dependent dephosphatase calcineurin subunit PPP3CA. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 13

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.51E-01; Fold-change: 3.81E-01; Z-score: 8.35E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
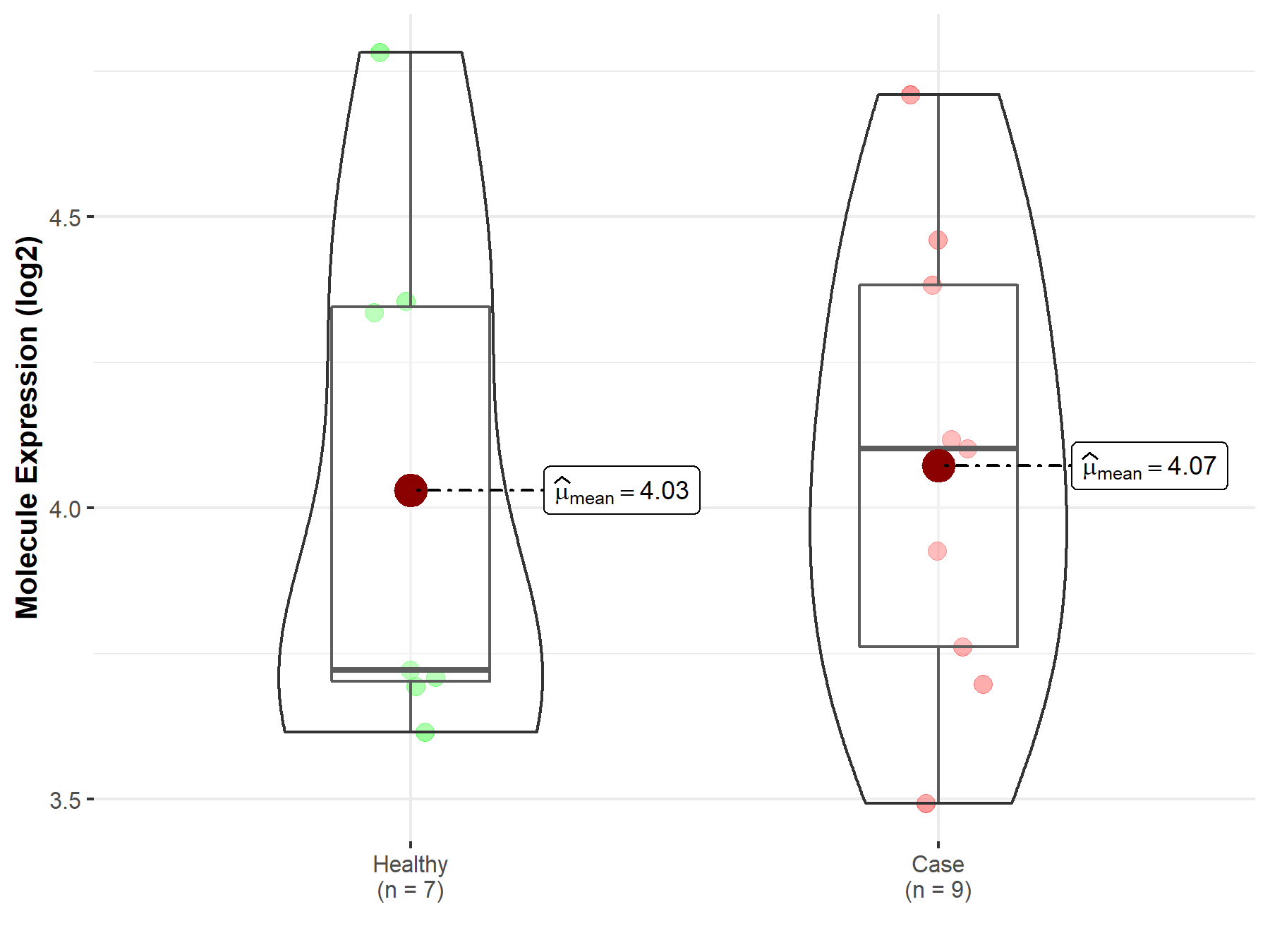
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

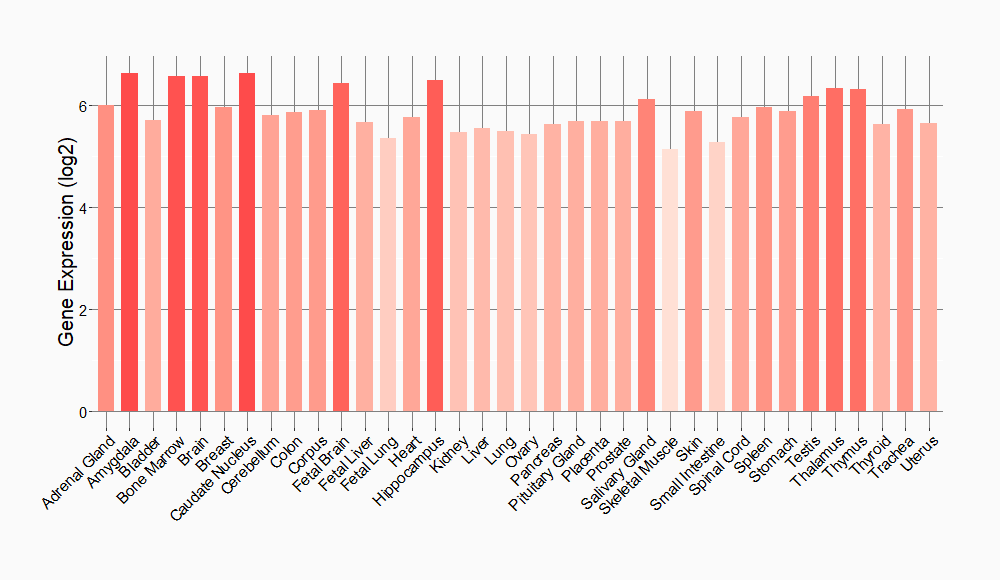
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
