Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00737) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Fenofibrate
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Fenofibrate; 49562-28-9; Procetofen; Lipantil; Tricor; Lipanthyl; Fenobrate; Lipidil; Secalip; Antara; Finofibrate; Lipoclar; Lipofene; Proctofene; Triglide; Fenogal; Lipirex; Sedufen; Elasterin; Fenoglide; Fenotard; Protolipan; Ankebin; Lipidex; Lipifen; Lipofen; Liposit; Lipsin; Nolipax; Fenofibratum [INN-Latin]; propan-2-yl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate; Fenofibrato [INN-Spanish]; Lipantil (TN); Tricor (TN); LF-178; Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate; C20H21ClO4; Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionate; 2-(4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1-methylethyl ester; NSC 281319; UNII-U202363UOS; Isopropyl (4'-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-phenoxy-2-methyl)propionate; FNF; Elasterate; Procetofene; Luxacor; MFCD00133314; CHEMBL672; Propanoic acid, 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-, 1-methylethyl ester; MLS000028515; CHEBI:5001; isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate; Lofibra; U202363UOS; Propanoic acid, 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methyl-, 1-methylethyl ester; NSC-281319; NCGC00015437-10; Fenofibrato; Fenofibratum; Isopropyl 2-(p-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropionate; SMR000058299; Supralip; CAS-49562-28-9; DSSTox_CID_9874; propan-2-yl 2-{4-[(4-chlorophenyl)carbonyl]phenoxy}-2-methylpropanoate; DSSTox_RID_78828; DSSTox_GSID_29874; TRICOR (MICRONIZED); Antara (micronized); Fenomax; Isopropyl 2-[p-(p-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionate; Pharmavit; FENOFIBRATE (MICRONIZED); Fulcro; 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid isopropyl ester; 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionic Acid Isopropyl Ester; CIP-Fenofibrate; 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid 1-methylethyl ester; LCP-FenoChol; LCP-Feno; Triglide (TN); Fenofibrate IDD-P; Lipofen (TN); Antara (TN); CCRIS 7282; SR-01000000091; EINECS 256-376-3; LF 178; BRN 2062462; Procetoken; Isopropyl 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropionate; HSDB 7736; Fenofibrate,(S); GRS-027; Fenofibrate [USAN:USP:INN:BAN]; Prestwick_217; Fenofibrate micronized; Spectrum_001250; Opera_ID_328; Prestwick0_000275; Prestwick1_000275; Prestwick2_000275; Prestwick3_000275; Spectrum2_001390; Spectrum3_001431; Spectrum4_000413; Spectrum5_001479; Lopac-F-6020; Fenofibrate delayed release; EC 256-376-3; F 6020; SCHEMBL4670; Lopac0_000486; BSPBio_000150; BSPBio_003162; KBioGR_000706; KBioSS_001730; MLS001148191; MLS002548878; BIDD:GT0574; DivK1c_000557; Fenofibrate (JAN/USP/INN); SPECTRUM1501010; SPBio_001380; SPBio_002369; Fenofibrate, >=99%, powder; BPBio1_000166; Fenofibrate (Tricor, Trilipix); GTPL7186; DTXSID2029874; HMS501L19; KBio1_000557; KBio2_001730; KBio2_004298; KBio2_006866; KBio3_002382; NINDS_000557; HMS1568H12; HMS1921B17; HMS2090G20; HMS2092B05; HMS2095H12; HMS2231B14; HMS3259K03; HMS3261B13; HMS3369M13; HMS3649D20; HMS3655K12; HMS3712H12; isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoate; Pharmakon1600-01501010; ZINC584092; ALBB-028958; BCP21243; Tox21_110147; Tox21_300151; Tox21_500486; BDBM50085042; CCG-38996; NSC281319; NSC757822; s1794; AKOS005107777; Tox21_110147_1; AB03716; AC-4227; CS-0892; DB01039; LP00486; MCULE-9460650238; MS-2223; NC00452; NSC-757822; SDCCGSBI-0050470.P004; IDI1_000557; NCGC00015437-01; NCGC00015437-02; NCGC00015437-03; NCGC00015437-04; NCGC00015437-05; NCGC00015437-06; NCGC00015437-07; NCGC00015437-08; NCGC00015437-09; NCGC00015437-11; NCGC00015437-12; NCGC00015437-13; NCGC00015437-14; NCGC00015437-16; NCGC00015437-17; NCGC00015437-31; NCGC00021475-03; NCGC00021475-04; NCGC00021475-05; NCGC00021475-06; NCGC00021475-07; NCGC00021475-08; NCGC00253945-01; NCGC00261171-01; FENOFIBRATE (MICRONIZED) (fenofibrate; Fenofibrate, analytical reference material; HY-17356; SY052561; SBI-0050470.P003; DB-051642; AB00052196; EU-0100486; F0674; FT-0626400; FT-0654669; SW196525-4; C07586; D00565; J10318; AB00052196-15; AB00052196-16; AB00052196_17; AB00052196_18; 562F289; A827746; Q419724; Q-201111; SR-01000000091-2; SR-01000000091-5; SR-01000000091-6; SR-01000000091-8; BRD-K50388907-001-05-6; BRD-K50388907-001-18-9; BRD-K50388907-001-20-5; SR-01000000091-16; Z2768724415; Fenofibrate, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Isopropyl 2-(4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoate; 1-methylethyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoate; 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoicacidisopropylester; Fenofibrate, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Isopropyl (4''-(p-chlorobenzoyl)-2-phenoxy-2-methyl)propionate; 2-[4-(4-Chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methylpropanoic acid 1-methyl-ethyl ester; Fenofibrate, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material; isopropyl 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-propanoate;Fenofibrate; Propanoic acid, 2-[4-(4-chlorobenzoyl)phenoxy]-2-methyl-, 1-methylethylester
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
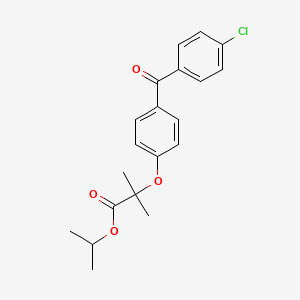
|
||||
| Target | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARA) | PPARA_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C20H21ClO4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC(C)OC(=O)C(C)(C)OC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C20H21ClO4/c1-13(2)24-19(23)20(3,4)25-17-11-7-15(8-12-17)18(22)14-5-9-16(21)10-6-14/h5-13H,1-4H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YMTINGFKWWXKFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-05: Endocrine/nutritional/metabolic diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Protein phosphatase 3 catalytic subunit alpha (PPP3CA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Insulin-resistance syndrome [ICD-11: 5A44.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Intracellular calcium flux signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05207 | |
| TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation | Activation | hsa04137 | ||
| Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| CaMKKbeta-AMPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04152 | ||
| In Vivo Model | HFD-fed mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | Administration of fenofibrate effectively ameliorated glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. In this study, fenofibrate treatment appeared to increase intracellular calcium flux and TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation and autophagy through two different mechanisms. One is the aforementioned calcium-mediated upregulation of the CaMKKbeta-AMPK pathway and the other is the activation of the calcium-dependent dephosphatase calcineurin subunit PPP3CA. | |||
ICD-13: Digestive system diseases
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Protein phosphatase 3 catalytic subunit alpha (PPP3CA) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [ICD-11: DB92.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Intracellular calcium flux signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05207 | |
| TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation | Activation | hsa04137 | ||
| Cell autophagy | Activation | hsa04140 | ||
| CaMKKbeta-AMPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04152 | ||
| In Vivo Model | HFD-fed mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Mechanism Description | Administration of fenofibrate effectively ameliorated glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in HFD-fed mice. In this study, fenofibrate treatment appeared to increase intracellular calcium flux and TFEB/TFE3 nuclear translocation and autophagy through two different mechanisms. One is the aforementioned calcium-mediated upregulation of the CaMKKbeta-AMPK pathway and the other is the activation of the calcium-dependent dephosphatase calcineurin subunit PPP3CA. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
