Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01884)
| Name |
Interleukin 6 receptor (IL6R)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
IL6R
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
IL6R
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:154,405,193-154,469,450[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MLAVGCALLAALLAAPGAALAPRRCPAQEVARGVLTSLPGDSVTLTCPGVEPEDNATVHW
VLRKPAAGSHPSRWAGMGRRLLLRSVQLHDSGNYSCYRAGRPAGTVHLLVDVPPEEPQLS CFRKSPLSNVVCEWGPRSTPSLTTKAVLLVRKFQNSPAEDFQEPCQYSQESQKFSCQLAV PEGDSSFYIVSMCVASSVGSKFSKTQTFQGCGILQPDPPANITVTAVARNPRWLSVTWQD PHSWNSSFYRLRFELRYRAERSKTFTTWMVKDLQHHCVIHDAWSGLRHVVQLRAQEEFGQ GEWSEWSPEAMGTPWTESRSPPAENEVSTPMQALTTNKDDDNILFRDSANATSLPVQDSS SVPLPTFLVAGGSLAFGTLLCIAIVLRFKKTWKLRALKEGKTSMHPPYSLGQLVPERPRP TPVLVPLISPPVSPSSLGSDNTSSHNRPDARDPRSPYDISNTDYFFPR Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Part of the receptor for interleukin 6. Binds to IL6 with low affinity, but does not transduce a signal. Signal activation necessitate an association with IL6ST. Activation leads to the regulation of the immune response, acute-phase reactions and hematopoiesis. The interaction with membrane-bound IL6R and IL6ST stimulates 'classic signaling', the restricted expression of the IL6R limits classic IL6 signaling to only a few tissues such as the liver and some cells of the immune system. Whereas the binding of IL6 and soluble IL6R to IL6ST stimulates 'trans-signaling'. Alternatively, 'cluster signaling' occurs when membrane-bound IL6:IL6R complexes on transmitter cells activate IL6ST receptors on neighboring receiver cells (Probable).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer bone metastasis [ICD-11: 2E03.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer bone metastasis [ICD-11: 2E03.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Metastatic bone cancer [ICD-11: 2E03] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer bone metastasis | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Blood | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.37E-03 Fold-change: 4.18E-01 Z-score: 3.52E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometric | |||
| Mechanism Description | Interleukin-6 (IL-6), a pro-inflammatory cytokine produced in the tumor microenvironment by stromal cells, fibroblasts, and cancer cells. Binding of IL-6 to its receptor IL-6R on the cell membrane activates Janus Kinase 2 (JAK2) kinases. Activated JAK2 mediates phosphorylation, dimerization, and nuclear translocation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3). STAT3 signaling mediates the expression of various genes, including p53, Bcl-2, MRP1, and ABCG2. Bcl-2 and p53 are associated with regulation of apoptosis while overexpression of drug transporters MRP1, ABCG2 has been shown to mediate efflux of drugs from cancer cells, thus decreasing intracellular drug concentration leading to drug-resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Our findings in the fallopian tube cancer and ovarian cancer cell lines showed that SKOV3 cells displayed 10-fold greater resistance to cisplatin and 5.8 times more resistance to carboplatin than A2780 cells. SKOV3 cells displayed platinum-induced IL-6 and IL-8 overproduction whereas wild type A2780 displayed no detectable cytokine production. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ovarian cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Our findings in the fallopian tube cancer and ovarian cancer cell lines showed that SKOV3 cells displayed 10-fold greater resistance to cisplatin and 5.8 times more resistance to carboplatin than A2780 cells. SKOV3 cells displayed platinum-induced IL-6 and IL-8 overproduction whereas wild type A2780 displayed no detectable cytokine production. | |||
| Disease Class: Fallopian tube cancer [ICD-11: 2C74.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Fallopian tube cancer [ICD-11: 2C74.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Fallopian tube cancer tissue | N.A. | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
ELISA assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Our findings in the fallopian tube cancer and ovarian cancer cell lines showed that SKOV3 cells displayed 10-fold greater resistance to cisplatin and 5.8 times more resistance to carboplatin than A2780 cells. SKOV3 cells displayed platinum-induced IL-6 and IL-8 overproduction whereas wild type A2780 displayed no detectable cytokine production. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Copanlisib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | RWPE-1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3791 |
| SW1116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0544 | |
| HCT15 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0292 | |
| LS174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | |
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | |
| SW948 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0632 | |
| C4-2B cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4784 | |
| OCI-Ly1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1879 | |
| Riva cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| SU-DHL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9550 | |
| U2932 (ABC-DLBCL) cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1896 | |
| BJAB cells | Groin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5711 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cytokine arrays revealed upregulation of interleukin (IL)-6 in both copanlisib- and duvelisib-resistant cell lines. Phosphorylated STAT5, AKT, p70S6K and MAPK were increased in copanlisib-resistant B-cell lymphoma cells, whereas phosphorylated STAT3 and NF-kappaB were increased in duvelisib-resistant T cell lymphoma cells. Conversely, depletion of IL-6 sensitized both resistant cell lines, and led to downregulation of phosphorylated STAT3 and STAT5 in copanlisib- and duvelisib-resistant cells, respectively. Moreover, combined treatment with a JAK inhibitor (BSK805) and a PI3K inhibitor circumvented the acquired resistance to PI3K inhibitors in lymphoma, and concurrent inhibition of the activated pathways produced combined effects.IL-6-induced STAT3 or STAT5 activation is a critical mechanism underlying PI3K inhibitor resistance in lymphoma, supporting the utility of IL-6 as an effective biomarker to predict therapeutic response to PI3K inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-Hodgkin lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.5] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-Hodgkin lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A85.5] | |||
| Resistant Drug | IPI-145 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | RWPE-1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3791 |
| SW1116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0544 | |
| HCT15 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0292 | |
| LS174T cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1384 | |
| NCI-H716 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1581 | |
| SW948 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0632 | |
| C4-2B cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4784 | |
| OCI-Ly1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1879 | |
| Riva cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| SU-DHL2 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9550 | |
| U2932 (ABC-DLBCL) cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1896 | |
| BJAB cells | Groin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5711 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cytokine arrays revealed upregulation of interleukin (IL)-6 in both copanlisib- and duvelisib-resistant cell lines. Phosphorylated STAT5, AKT, p70S6K and MAPK were increased in copanlisib-resistant B-cell lymphoma cells, whereas phosphorylated STAT3 and NF-kappaB were increased in duvelisib-resistant T cell lymphoma cells. Conversely, depletion of IL-6 sensitized both resistant cell lines, and led to downregulation of phosphorylated STAT3 and STAT5 in copanlisib- and duvelisib-resistant cells, respectively. Moreover, combined treatment with a JAK inhibitor (BSK805) and a PI3K inhibitor circumvented the acquired resistance to PI3K inhibitors in lymphoma, and concurrent inhibition of the activated pathways produced combined effects.IL-6-induced STAT3 or STAT5 activation is a critical mechanism underlying PI3K inhibitor resistance in lymphoma, supporting the utility of IL-6 as an effective biomarker to predict therapeutic response to PI3K inhibitors. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.76E-01; Fold-change: -5.27E-01; Z-score: -4.82E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.58E-01; Fold-change: -1.76E-01; Z-score: -1.02E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
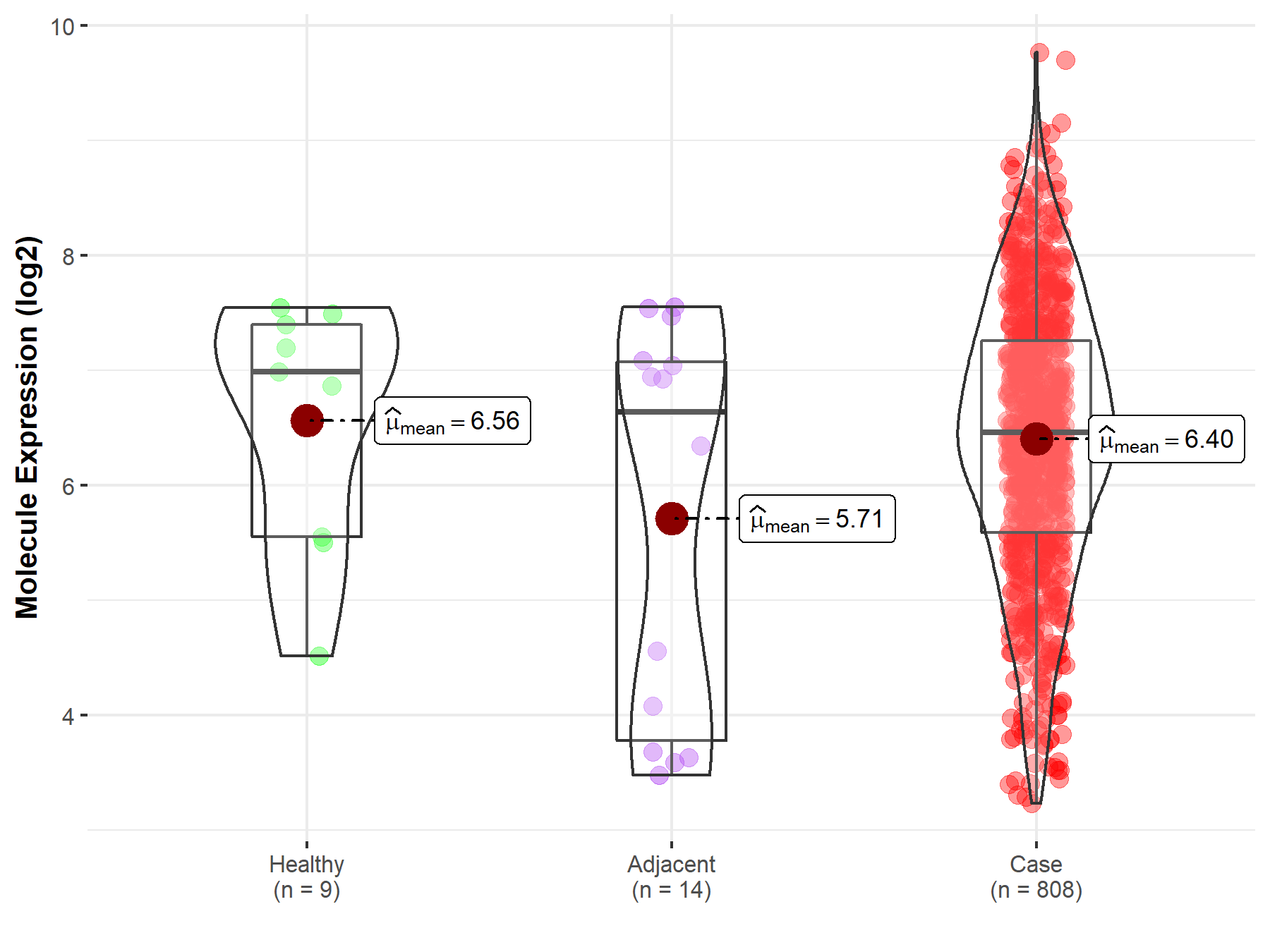
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

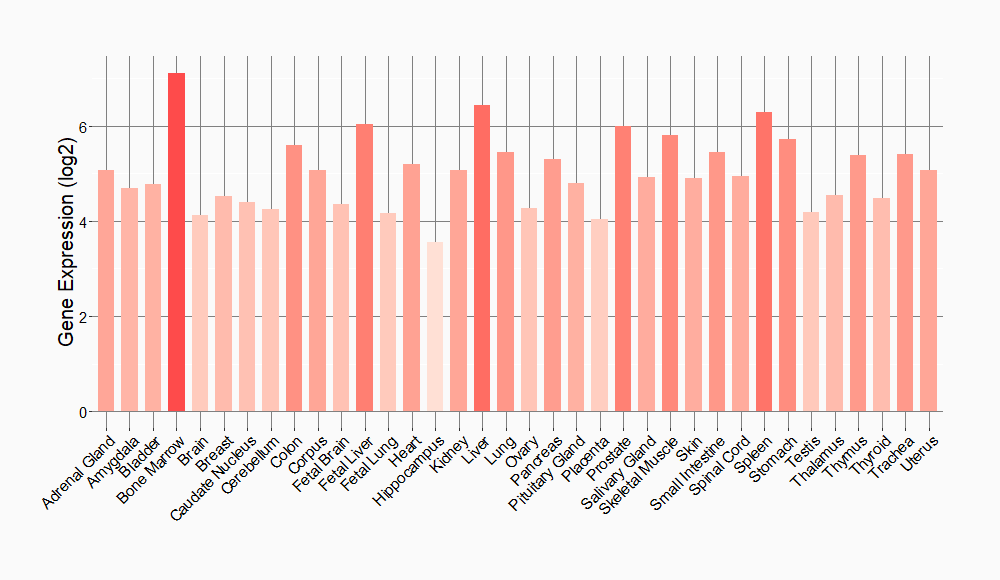
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
