Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01840)
| Name |
Transcription activator BRG1 (BRG1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Transcription activator BRG1; ATP-dependent helicase SMARCA4; BRG1-associated factor 190A; BAF190A; Mitotic growth and transcription activator; Protein BRG-1; Protein brahma homolog 1; SNF2-beta; SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 4
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SMARCA4
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr19:10,960,932-11,079,426[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSTPDPPLGGTPRPGPSPGPGPSPGAMLGPSPGPSPGSAHSMMGPSPGPPSAGHPIPTQG
PGGYPQDNMHQMHKPMESMHEKGMSDDPRYNQMKGMGMRSGGHAGMGPPPSPMDQHSQGY PSPLGGSEHASSPVPASGPSSGPQMSSGPGGAPLDGADPQALGQQNRGPTPFNQNQLHQL RAQIMAYKMLARGQPLPDHLQMAVQGKRPMPGMQQQMPTLPPPSVSATGPGPGPGPGPGP GPGPAPPNYSRPHGMGGPNMPPPGPSGVPPGMPGQPPGGPPKPWPEGPMANAAAPTSTPQ KLIPPQPTGRPSPAPPAVPPAASPVMPPQTQSPGQPAQPAPMVPLHQKQSRITPIQKPRG LDPVEILQEREYRLQARIAHRIQELENLPGSLAGDLRTKATIELKALRLLNFQRQLRQEV VVCMRRDTALETALNAKAYKRSKRQSLREARITEKLEKQQKIEQERKRRQKHQEYLNSIL QHAKDFKEYHRSVTGKIQKLTKAVATYHANTEREQKKENERIEKERMRRLMAEDEEGYRK LIDQKKDKRLAYLLQQTDEYVANLTELVRQHKAAQVAKEKKKKKKKKKAENAEGQTPAIG PDGEPLDETSQMSDLPVKVIHVESGKILTGTDAPKAGQLEAWLEMNPGYEVAPRSDSEES GSEEEEEEEEEEQPQAAQPPTLPVEEKKKIPDPDSDDVSEVDARHIIENAKQDVDDEYGV SQALARGLQSYYAVAHAVTERVDKQSALMVNGVLKQYQIKGLEWLVSLYNNNLNGILADE MGLGKTIQTIALITYLMEHKRINGPFLIIVPLSTLSNWAYEFDKWAPSVVKVSYKGSPAA RRAFVPQLRSGKFNVLLTTYEYIIKDKHILAKIRWKYMIVDEGHRMKNHHCKLTQVLNTH YVAPRRLLLTGTPLQNKLPELWALLNFLLPTIFKSCSTFEQWFNAPFAMTGEKVDLNEEE TILIIRRLHKVLRPFLLRRLKKEVEAQLPEKVEYVIKCDMSALQRVLYRHMQAKGVLLTD GSEKDKKGKGGTKTLMNTIMQLRKICNHPYMFQHIEESFSEHLGFTGGIVQGLDLYRASG KFELLDRILPKLRATNHKVLLFCQMTSLMTIMEDYFAYRGFKYLRLDGTTKAEDRGMLLK TFNEPGSEYFIFLLSTRAGGLGLNLQSADTVIIFDSDWNPHQDLQAQDRAHRIGQQNEVR VLRLCTVNSVEEKILAAAKYKLNVDQKVIQAGMFDQKSSSHERRAFLQAILEHEEQDESR HCSTGSGSASFAHTAPPPAGVNPDLEEPPLKEEDEVPDDETVNQMIARHEEEFDLFMRMD LDRRREEARNPKRKPRLMEEDELPSWIIKDDAEVERLTCEEEEEKMFGRGSRHRKEVDYS DSLTEKQWLKAIEEGTLEEIEEEVRQKKSSRKRKRDSDAGSSTPTTSTRSRDKDDESKKQ KKRGRPPAEKLSPNPPNLTKKMKKIVDAVIKYKDSSSGRQLSEVFIQLPSRKELPEYYEL IRKPVDFKKIKERIRNHKYRSLNDLEKDVMLLCQNAQTFNLEGSLIYEDSIVLQSVFTSV RQKIEKEDDSEGEESEEEEEGEEEGSESESRSVKVKIKLGRKEKAQDRLKGGRRRPSRGS RAKPVVSDDDSEEEQEEDRSGSGSEED Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Involved in transcriptional activation and repression of select genes by chromatin remodeling (alteration of DNA-nucleosome topology). Component of SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complexes that carry out key enzymatic activities, changing chromatin structure by altering DNA-histone contacts within a nucleosome in an ATP-dependent manner. Component of the CREST-BRG1 complex, a multiprotein complex that regulates promoter activation by orchestrating the calcium-dependent release of a repressor complex and the recruitment of an activator complex. In resting neurons, transcription of the c-FOS promoter is inhibited by SMARCA4-dependent recruitment of a phospho-RB1-HDAC repressor complex. Upon calcium influx, RB1 is dephosphorylated by calcineurin, which leads to release of the repressor complex. At the same time, there is increased recruitment of CREBBP to the promoter by a CREST-dependent mechanism, which leads to transcriptional activation. The CREST-BRG1 complex also binds to the NR2B promoter, and activity-dependent induction of NR2B expression involves the release of HDAC1 and recruitment of CREBBP. Belongs to the neural progenitors-specific chromatin remodeling complex (npBAF complex) and the neuron-specific chromatin remodeling complex (nBAF complex). During neural development, a switch from a stem/progenitor to a postmitotic chromatin remodeling mechanism occurs as neurons exit the cell cycle and become committed to their adult state. The transition from proliferating neural stem/progenitor cells to postmitotic neurons requires a switch in subunit composition of the npBAF and nBAF complexes. As neural progenitors exit mitosis and differentiate into neurons, npBAF complexes which contain ACTL6A/BAF53A and PHF10/BAF45A, are exchanged for homologous alternative ACTL6B/BAF53B and DPF1/BAF45B or DPF3/BAF45C subunits in neuron-specific complexes (nBAF). The npBAF complex is essential for the self-renewal/proliferative capacity of the multipotent neural stem cells. The nBAF complex along with CREST plays a role regulating the activity of genes essential for dendrite growth. SMARCA4/BAF190A may promote neural stem cell self-renewal/proliferation by enhancing Notch-dependent proliferative signals, while concurrently making the neural stem cell insensitive to SHH-dependent differentiating cues (By similarity). Acts as a corepressor of ZEB1 to regulate E-cadherin transcription and is required for induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by ZEB1. Binds via DLX1 to enhancers located in the intergenic region between DLX5 and DLX6 and this binding is stabilized by the long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) Evf2 (By similarity). Binds to RNA in a promiscuous manner (By similarity). Binding to RNAs including lncRNA Evf2 leads to inhibition of SMARCA4 ATPase and chromatin remodeling activities (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number loss | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1703 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1490 |
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female YFP/SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-blue assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SMARCA4/2 loss reduces cyclin D1 expression by a combination of restricting CCND1 chromatin accessibility and suppressing c-Jun, a transcription activator of CCND1. Reduced cyclin D1 in SMARCA4-deficient NSCLC causes sensitivities to CDK4/6 inhibitors, abemaciclib or palbociclib. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Copy number loss | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H1703 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1490 |
| NCI-H1299 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| In Vivo Model | Female YFP/SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-blue assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SMARCA4/2 loss reduces cyclin D1 expression by a combination of restricting CCND1 chromatin accessibility and suppressing c-Jun, a transcription activator of CCND1. Reduced cyclin D1 in SMARCA4-deficient NSCLC causes sensitivities to CDK4/6 inhibitors, abemaciclib or palbociclib. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.16E-16; Fold-change: 2.68E-01; Z-score: 7.04E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.68E-09; Fold-change: 2.56E-01; Z-score: 6.48E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
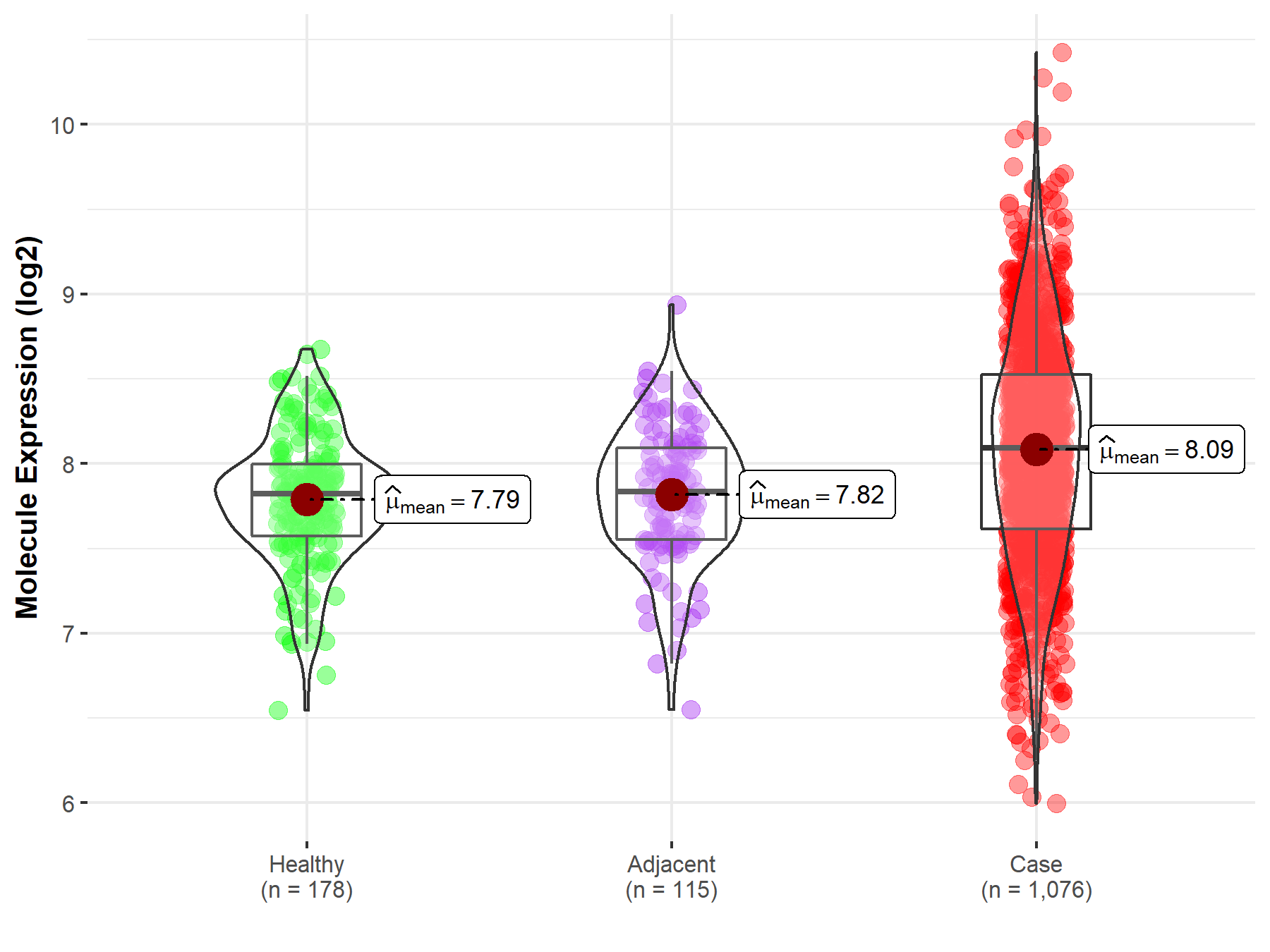
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

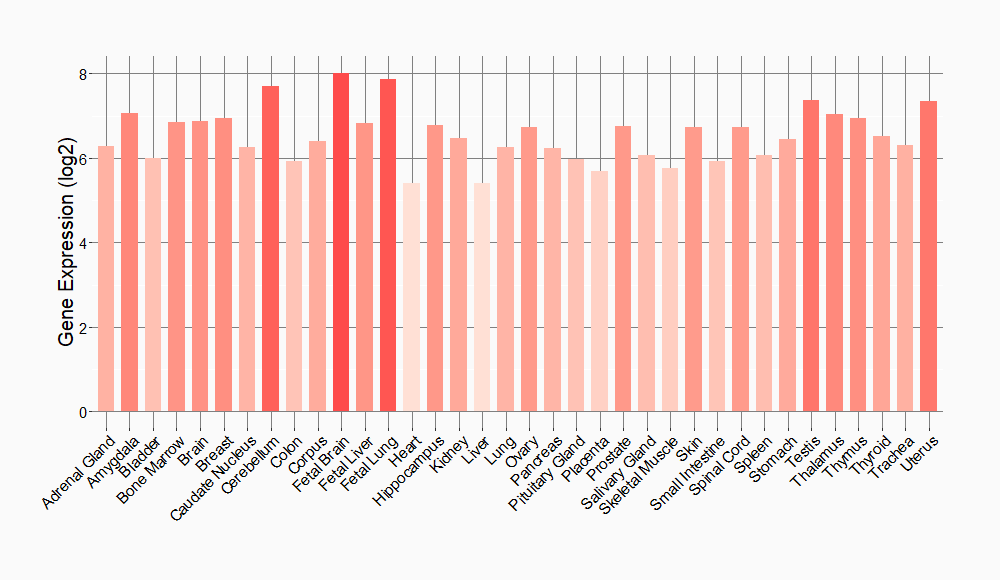
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
