Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol01210)
| Name |
Very low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
VLDLR
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
LncRNA
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDA11
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr9:2621182-2660056[+]
|
||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Bile duct | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.58E-05 Fold-change: 3.24E+00 Z-score: 5.00E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| PLC/PRF-5 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LincRNA-VLDLR (linc-VLDLR) was significantly up-regulated in malignant hepatocytes. Exposure of HCC cells to diverse anti-cancer agents such as sorafenib, camptothecin, and doxorubicin increased linc-VLDLR expression in cells as well as within EVs released from these cells. Incubation with EVs reduced chemotherapy-induced cell death and also increased linc-VLDLR expression in recipient cells. RNAi-mediated knockdown of linc-VLDLR decreased cell viability and abrogated cell cycle progression. Moreover, knockdown of VLDLR reduced expression of ABCG2 (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G member 2), whereas over-expression of this protein reduced the effects of VLDLR knockdown on sorafenib-induced cell death. Here, linc-VLDLR is identified as an extracellular vesicle enriched LncRNA that contributes to cellular stress responses. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| PLC/PRF-5 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LincRNA-VLDLR (linc-VLDLR) was significantly up-regulated in malignant hepatocytes. Exposure of HCC cells to diverse anti-cancer agents such as sorafenib, camptothecin, and doxorubicin increased linc-VLDLR expression in cells as well as within EVs released from these cells. Incubation with EVs reduced chemotherapy-induced cell death and also increased linc-VLDLR expression in recipient cells. RNAi-mediated knockdown of linc-VLDLR decreased cell viability and abrogated cell cycle progression. Moreover, knockdown of VLDLR reduced expression of ABCG2 (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G member 2), whereas over-expression of this protein reduced the effects of VLDLR knockdown on sorafenib-induced cell death. Here, linc-VLDLR is identified as an extracellular vesicle enriched LncRNA that contributes to cellular stress responses. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal cancer [ICD-11: 2B70.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | ECA-109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Extracellular vesicles released by drug-resistant cells were proved that they could upregulate the expression of ABCG2 in esophageal cancer cells and thus regulate the drug resistance of esophageal cancer cells, which was related to the linc-VLDLR carried by EVs. | |||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| PLC/PRF-5 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LincRNA-VLDLR (linc-VLDLR) was significantly up-regulated in malignant hepatocytes. Exposure of HCC cells to diverse anti-cancer agents such as sorafenib, camptothecin, and doxorubicin increased linc-VLDLR expression in cells as well as within EVs released from these cells. Incubation with EVs reduced chemotherapy-induced cell death and also increased linc-VLDLR expression in recipient cells. RNAi-mediated knockdown of linc-VLDLR decreased cell viability and abrogated cell cycle progression. Moreover, knockdown of VLDLR reduced expression of ABCG2 (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G member 2), whereas over-expression of this protein reduced the effects of VLDLR knockdown on sorafenib-induced cell death. Here, linc-VLDLR is identified as an extracellular vesicle enriched LncRNA that contributes to cellular stress responses. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular cancer [ICD-11: 2C12.4] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Camptothecin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| PLC/PRF-5 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0485 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | LincRNA-VLDLR (linc-VLDLR) was significantly up-regulated in malignant hepatocytes. Exposure of HCC cells to diverse anti-cancer agents such as sorafenib, camptothecin, and doxorubicin increased linc-VLDLR expression in cells as well as within EVs released from these cells. Incubation with EVs reduced chemotherapy-induced cell death and also increased linc-VLDLR expression in recipient cells. RNAi-mediated knockdown of linc-VLDLR decreased cell viability and abrogated cell cycle progression. Moreover, knockdown of VLDLR reduced expression of ABCG2 (ATP-binding cassette, sub-family G member 2), whereas over-expression of this protein reduced the effects of VLDLR knockdown on sorafenib-induced cell death. Here, linc-VLDLR is identified as an extracellular vesicle enriched LncRNA that contributes to cellular stress responses. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal carcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.39E-51; Fold-change: 1.59E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
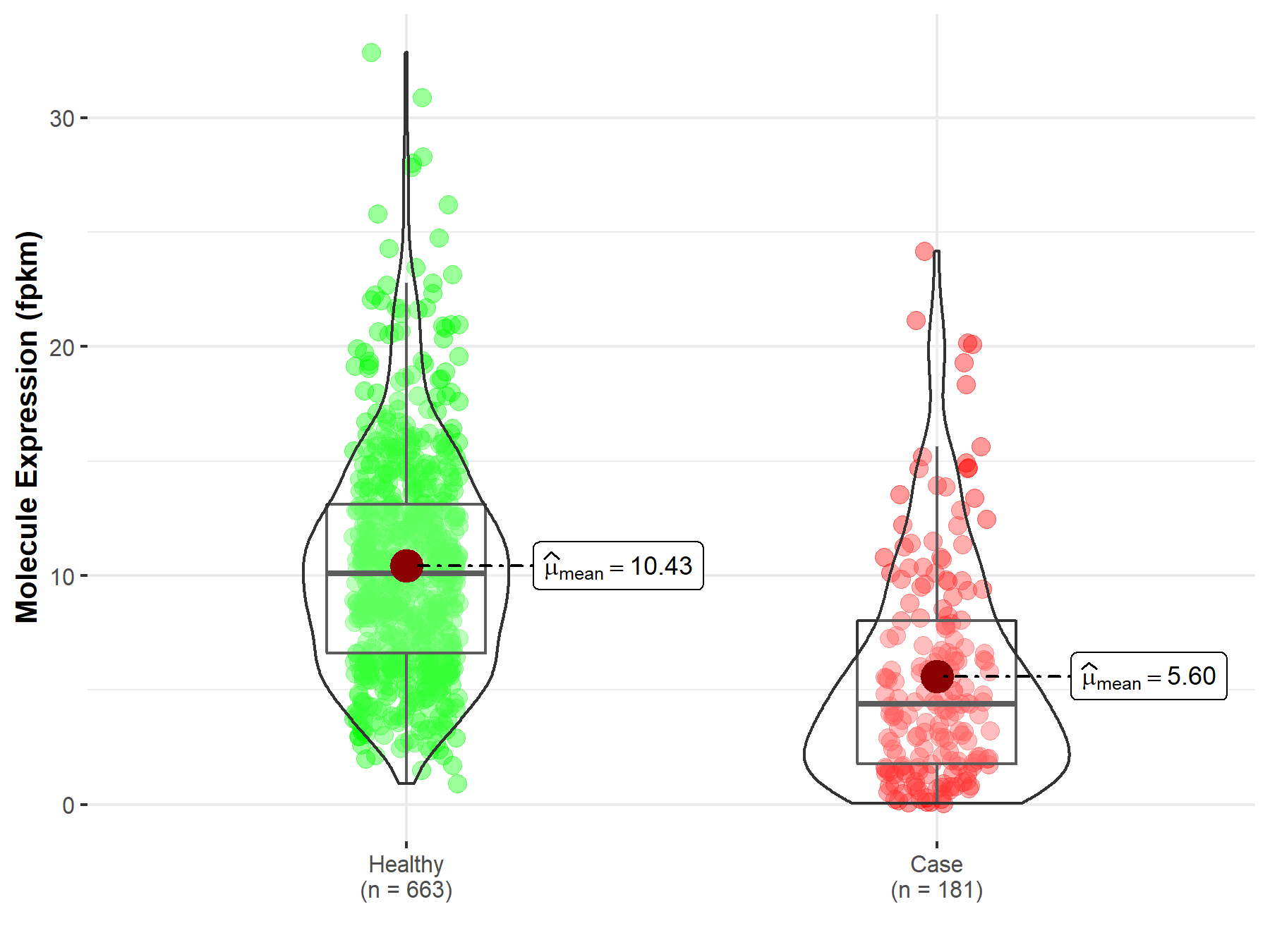
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bile duct | |
| The Specified Disease | Cholangiocarcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.03E-03; Fold-change: -5.87E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
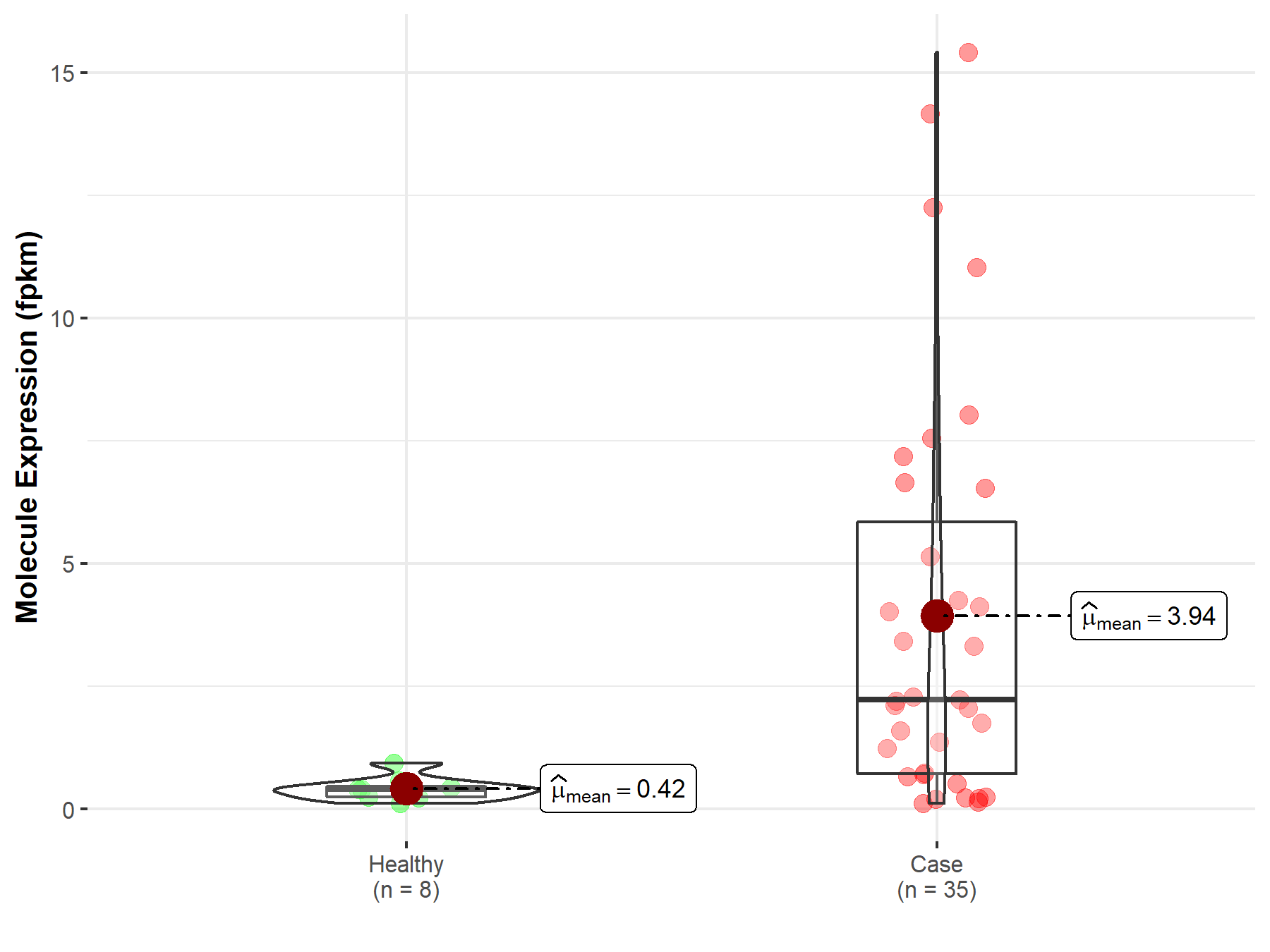
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver hepatocellular carcinoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.23E-02; Fold-change: -7.41E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
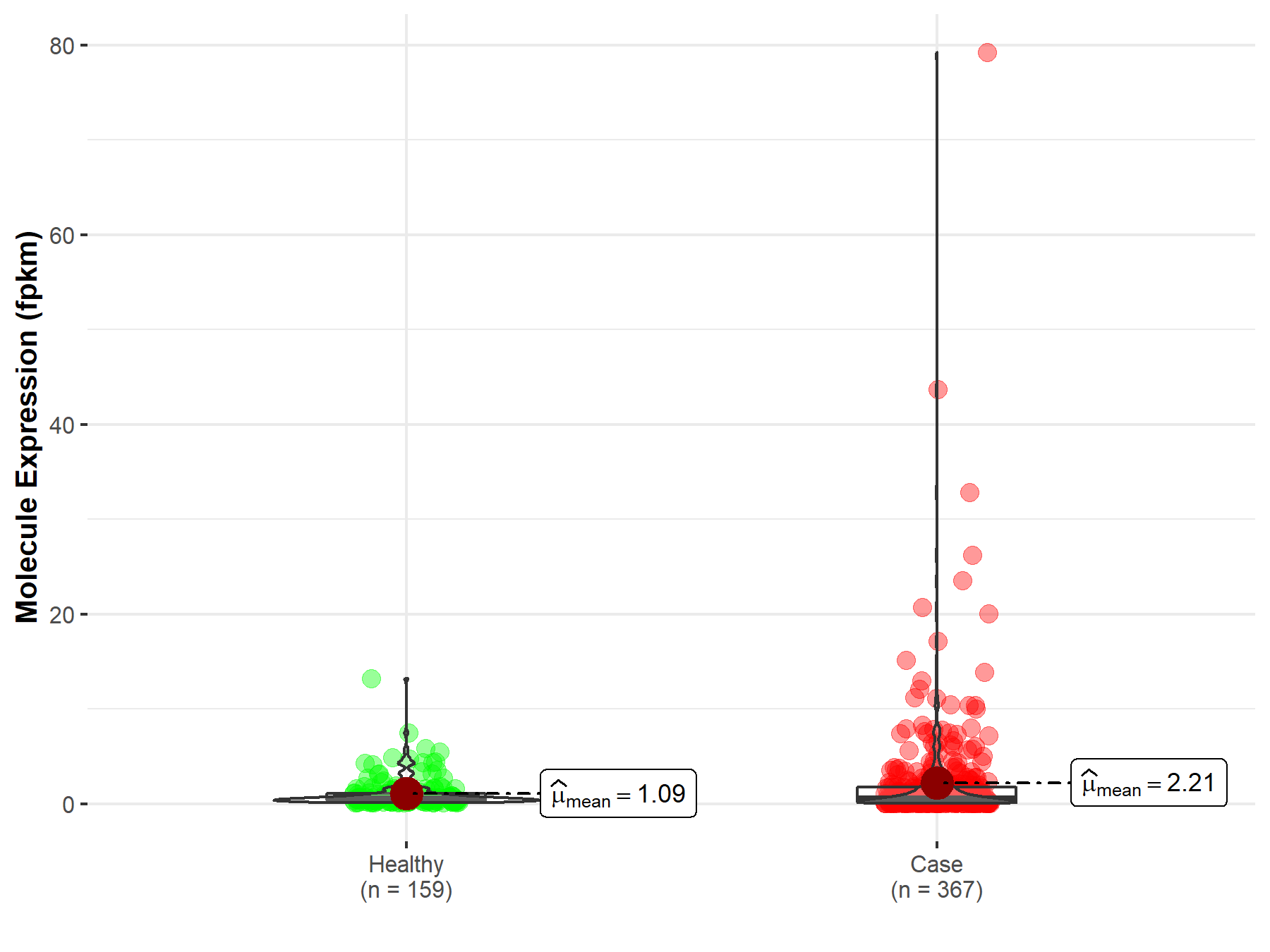
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

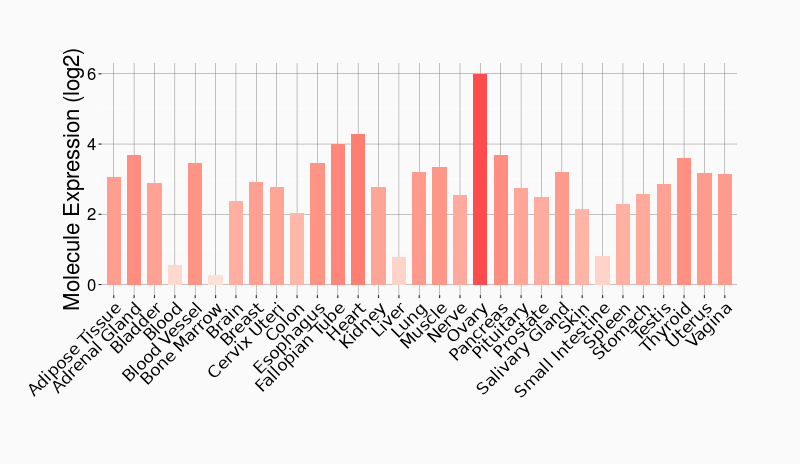
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
