Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00695)
| Name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase UFO (AXL)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AXL oncogene; UFO
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
AXL
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr19:41219223-41261766[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAWRCPRMGRVPLAWCLALCGWACMAPRGTQAEESPFVGNPGNITGARGLTGTLRCQLQV
QGEPPEVHWLRDGQILELADSTQTQVPLGEDEQDDWIVVSQLRITSLQLSDTGQYQCLVF LGHQTFVSQPGYVGLEGLPYFLEEPEDRTVAANTPFNLSCQAQGPPEPVDLLWLQDAVPL ATAPGHGPQRSLHVPGLNKTSSFSCEAHNAKGVTTSRTATITVLPQQPRNLHLVSRQPTE LEVAWTPGLSGIYPLTHCTLQAVLSDDGMGIQAGEPDPPEEPLTSQASVPPHQLRLGSLH PHTPYHIRVACTSSQGPSSWTHWLPVETPEGVPLGPPENISATRNGSQAFVHWQEPRAPL QGTLLGYRLAYQGQDTPEVLMDIGLRQEVTLELQGDGSVSNLTVCVAAYTAAGDGPWSLP VPLEAWRPGQAQPVHQLVKEPSTPAFSWPWWYVLLGAVVAAACVLILALFLVHRRKKETR YGEVFEPTVERGELVVRYRVRKSYSRRTTEATLNSLGISEELKEKLRDVMVDRHKVALGK TLGEGEFGAVMEGQLNQDDSILKVAVKTMKIAICTRSELEDFLSEAVCMKEFDHPNVMRL IGVCFQGSERESFPAPVVILPFMKHGDLHSFLLYSRLGDQPVYLPTQMLVKFMADIASGM EYLSTKRFIHRDLAARNCMLNENMSVCVADFGLSKKIYNGDYYRQGRIAKMPVKWIAIES LADRVYTSKSDVWSFGVTMWEIATRGQTPYPGVENSEIYDYLRQGNRLKQPADCLDGLYA LMSRCWELNPQDRPSFTELREDLENTLKALPPAQEPDEILYVNMDEGGGYPEPPGAAGGA DPPTQPDPKDSCSCLTAAEVHPAGRYVLCPSTTPSPAQPADRGSPAAPGQEDGA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor tyrosine kinase that transduces signals from the extracellular matrix into the cytoplasm by binding growth factor GAS6 and which is thus regulating many physiological processes including cell survival, cell proliferation, migration and differentiation. Ligand binding at the cell surface induces dimerization and autophosphorylation of AXL. Following activation by ligand, AXL binds and induces tyrosine phosphorylation of PI3-kinase subunits PIK3R1, PIK3R2 and PIK3R3; but also GRB2, PLCG1, LCK and PTPN11. Other downstream substrate candidates for AXL are CBL, NCK2, SOCS1 and TNS2. Recruitment of GRB2 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase regulatory subunits by AXL leads to the downstream activation of the AKT kinase. GAS6/AXL signaling plays a role in various processes such as endothelial cell survival during acidification by preventing apoptosis, optimal cytokine signaling during human natural killer cell development, hepatic regeneration, gonadotropin-releasing hormone neuron survival and migration, platelet activation, or regulation of thrombotic responses. Plays also an important role in inhibition of Toll-like receptors (TLRs)-mediated innate immune response.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
4 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Renal cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C90.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sunitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Kidney cancer [ICD-11: 2C90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Renal cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-02 Fold-change: 1.30E-01 Z-score: 3.05E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| ERK signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| STAT3/AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | 771R-luc cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Exosome-Transmitted lncARSR Promotes Sunitinib Resistance in Renal Cancer by Acting as a Competing Endogenous RNA. Here we identified an LncRNA, named lncARSR (LncRNA Activated in RCC with Sunitinib Resistance), which correlated with clinically poor sunitinib response. lncARSR promoted sunitinib resistance via competitively binding miR-34/miR-449 to facilitate AXL and c-MET expression in RCC cells. Furthermore, bioactive lncARSR could be incorporated into exosomes and transmitted to sensitive cells, thus disseminating sunitinib resistance. Treatment of sunitinib-resistant RCC with locked nucleic acids targeting lncARSR or an AXL/c-MET inhibitor restored sunitinib response. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Alectinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Crizotinib-resistant PDX mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AXL phosphorylation was increased in CR mice | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Crizotinib-resistant PDX mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AXL phosphorylation was increased in CR mice | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Axl signalling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | MOLM-13/sor cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Apoptosis assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sorafenib-resistant MOLM-13/sor cells have increased protein levels of FLT3 and Axl signaling pathways. These results suggest that activated FLT3-ITD signaling, Axl signaling, and protein translation contribute to sorafenib resistance. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lazertinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | HCC4011 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| NCI-H1975 EGFR-T790M/C797S/L858R cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_UE30 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| HCC4006 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1269 | |
| PC-9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; RT-PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | This study aimed to elucidate the adaptive resistance to lazertinib and advocate novel combination treatments that demonstrate efficacy in preventing resistance as a first-line treatment for EGFR mutation-positive NSCLC. We found that AXL knockdown significantly inhibited lung cancer cell viability in the presence of lazertinib, indicating that AXL activation contributes to lazertinib resistance. However, long-term culture with a combination of lazertinib and AXL inhibitors led to residual cell proliferation and increased the MCL-1 expression level, which was mediated by the nuclear translocation of the transcription factor YAP. Triple therapy with an MCL-1 or YAP inhibitor in combination with lazertinib and an AXL inhibitor significantly reduced cell viability and increased the apoptosis rate. These results demonstrate that AXL and YAP/MCL-1 signals contribute to adaptive lazertinib resistance in EGFR-mutant lung cancer cells, suggesting that the initial dual inhibition of AXL and YAP/MCL-1 might be a highly effective strategy in eliminating lazertinib-resistant cells. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | ASP3026 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Crizotinib-resistant PDX mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AXL phosphorylation was increased in CR mice | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Kidney | |
| The Specified Disease | Kidney cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.15E-02; Fold-change: 5.17E-01; Z-score: 7.01E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.22E-37; Fold-change: 9.25E-01; Z-score: 3.04E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

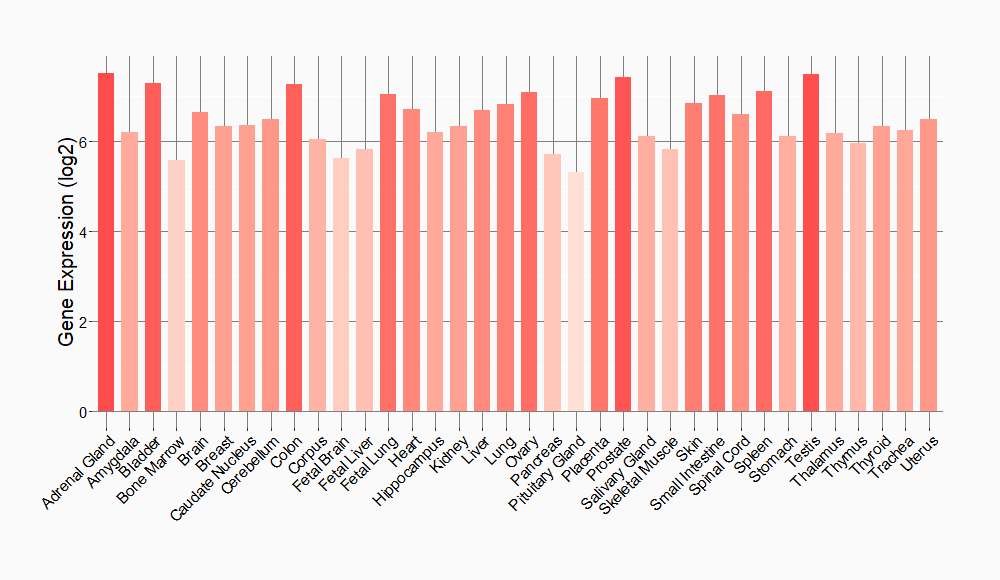
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
