Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00270) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Alectinib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1256580-46-7; CH5424802; CH 5424802; AF-802; Alecensa; UNII-LIJ4CT1Z3Y; AF 802; LIJ4CT1Z3Y; Alectinib (CH5424802); 9-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-8-(4-morpholinopiperidin-1-yl)-11-oxo-6,11-dihydro-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile; CHEMBL1738797; AF802; 9-Ethyl-6,6-Dimethyl-8-[4-(Morpholin-4-Yl)piperidin-1-Yl]-11-Oxo-6,11-Dihydro-5h-Benzo[b]carbazole-3-Carbonitrile; 9-Ethyl-6,11-dihydro-6,6-dimethyl-8-[4-(4-morpholinyl)-1-piperidinyl]-11-oxo-5H-benzo[b]carbazole-3-carbonitrile; AK170451; C30H34N4O2; Alectinib; 9-ethyl-6,6-dimethyl-
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
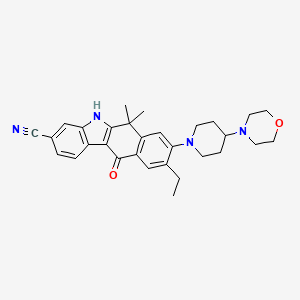
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[2]
[3]
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[4]
[5]
|
||||
| Target | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | ALK_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C30H34N4O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCC1=CC2=C(C=C1N3CCC(CC3)N4CCOCC4)C(C5=C(C2=O)C6=C(N5)C=C(C=C6)C#N)(C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C30H34N4O2/c1-4-20-16-23-24(17-26(20)34-9-7-21(8-10-34)33-11-13-36-14-12-33)30(2,3)29-27(28(23)35)22-6-5-19(18-31)15-25(22)32-29/h5-6,15-17,21,32H,4,7-14H2,1-3H3
|
||||
| InChIKey |
KDGFLJKFZUIJMX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NBLW cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ90 | |||||||||
| NBLW-R cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ91 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sangersequencing assay; Targeted deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Array CGH assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the sensitivity of NBLW and NBLW-R cells to a panel of ALk inhibitors (TAE-684, Crizotinib, Alectinib and Lorlatinib) revealed differences between the paired cell lines, and overall NBLW-R cells with the F1174L mutation were more resistant to ALk inhibitor induced apoptosis compared with NBLW cells. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger C3HC-type containing 1 (ZC3HC1) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | NPM-ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 |
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For KARPAS-299-derived cell lines, we observed oncogene overexpression as the main resistance mechanism, whereas in SUP-M2-derived cell lines, we identified several point mutations located within the NPM-ALK kinase domain, which could explain drug resistance. | |||
| Key Molecule: Zinc finger C3HC-type containing 1 (ZC3HC1) | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | NPM-ALK-Positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.8] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | p.L1122V+p.F1174V+p.L1196M+p.L1198F+p.S1206C+p.L1122V+p.L1196M+p.F1174V+p.L1198F+p.L1196M+p.D1203N |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 |
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | For KARPAS-299-derived cell lines, we observed oncogene overexpression as the main resistance mechanism, whereas in SUP-M2-derived cell lines, we identified several point mutations located within the NPM-ALK kinase domain, which could explain drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [6], [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171S |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography assay; Computed tomography assay; Analysis of progression-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Here, we report a patient with NSCLC harboring a novel HIP1-ALk fusion variant (H30; A20). This patient and another patient with EML4-ALk variant 3a/b initially responded sequentially to crizotinib and then alectinib, a next-generation ALk inhibitor, but developed acquired resistance to alectinib with the presence of a mutation in amino acid residue 1171 (I1171N and I1171S respectively) located in the hydrophobic regulatory spine (R-spine) of the ALk kinase in both the cases. | |||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Some acquired ALk mutations may cause co-resistance to other ALk inhibitors. Re-biopsy for ALk mutation analysis might be suggested prior to choosing a second-line ALk inhibitor treatment. A special mutation, G1202R, was resistant to crizotinib as well as to alectinib and ceritinib. | |||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [9] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171N |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR assay; Direct sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Although an in vitro mutagenesis screen identified I1171T in the ALk gene, mutations at codon 1171, which is located in the vicinity of the kinase DFG (Asp-Phe-Gly) motif of the activation loop, have yet to be identified in patients with ALk-rearranged NSCLC who have acquired resistance to ALk inhibitors. In addition, in vitro analyses howed that I1171T and I1171N confer resistance to crizotinib. In addition to the novel finding of mutations at I1171 in ALk-rearranged patients, it is intriguing that mutations at I1171 confer resistance to both crizotinib and alectinib, which is a representative second-generation ALk inhibitor. | |||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1180L |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We identified a novel V1180L gatekeeper mutation from the cell line model and a second novel I1171T mutation from the patient who developed resistance to alectinib. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Cystine/glutamate transporter (SLC7A11) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ALK1903 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| DTP cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo 3D cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DTP cells evade ALK-TKI-induced ROS-mediated cell death through GPX4 activity. From these data showing elevated levels of ROS that arise through decreased levels of various antioxidant factors and decreased GSH synthesis, it might be expected that ROS-mediated cell death should occur in alectinib-induced DTP cells. However, DTP cells concurrently upregulated GPX4 protein, suggesting that ALK1903 DTP cells are able to evade ROS-mediated cell death by reducing ROS level in a GPX4-dependent manner. | |||
| Key Molecule: Glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ALK1903 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| DTP cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo 3D cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DTP cells evade ALK-TKI-induced ROS-mediated cell death through GPX4 activity. From these data showing elevated levels of ROS that arise through decreased levels of various antioxidant factors and decreased GSH synthesis, it might be expected that ROS-mediated cell death should occur in alectinib-induced DTP cells. However, DTP cells concurrently upregulated GPX4 protein, suggesting that ALK1903 DTP cells are able to evade ROS-mediated cell death by reducing ROS level in a GPX4-dependent manner. | |||
| Key Molecule: Ferritin heavy chain (FTH1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | ALK1903 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| DTP cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo 3D cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DTP cells evade ALK-TKI-induced ROS-mediated cell death through GPX4 activity. From these data showing elevated levels of ROS that arise through decreased levels of various antioxidant factors and decreased GSH synthesis, it might be expected that ROS-mediated cell death should occur in alectinib-induced DTP cells. However, DTP cells concurrently upregulated GPX4 protein, suggesting that ALK1903 DTP cells are able to evade ROS-mediated cell death by reducing ROS level in a GPX4-dependent manner. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Pro-neuregulin-1, membrane-bound isoform (NRG1) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa01521 | |
| HER3 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | ALK1903 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| DTP cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay; qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo 3D cell viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DTP cells evade ALK-TKI-induced cell death through activation of EGFR and HER3 signaling. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: SHC-transforming protein 1 (SHC1) | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Crizotinib-resistant PDX mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | SHC1 phosphorylation was increased in CR mice | |||
| Key Molecule: Tyrosine-protein kinase UFO (AXL) | [10] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vivo Model | Crizotinib-resistant PDX mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | AXL phosphorylation was increased in CR mice | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | A novel, secondary mutation in ALK exon 23 (L1196Q) was identified in patient 1 after alectinib resistance developed. | |||
| Key Molecule: ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196Q |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Mechanism Description | A novel, secondary mutation in ALK exon 23 (L1196Q) was identified in patient 1 after alectinib resistance developed. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
