Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00632)
| Name |
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 (SMAD3)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MAD homolog 3; Mad3; Mothers against DPP homolog 3; hMAD-3; JV15-2; SMAD family member 3; SMAD 3; Smad3; hSMAD3; MADH3
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
SMAD3
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr15:67063763-67195173[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSSILPFTPPIVKRLLGWKKGEQNGQEEKWCEKAVKSLVKKLKKTGQLDELEKAITTQNV
NTKCITIPRSLDGRLQVSHRKGLPHVIYCRLWRWPDLHSHHELRAMELCEFAFNMKKDEV CVNPYHYQRVETPVLPPVLVPRHTEIPAEFPPLDDYSHSIPENTNFPAGIEPQSNIPETP PPGYLSEDGETSDHQMNHSMDAGSPNLSPNPMSPAHNNLDLQPVTYCEPAFWCSISYYEL NQRVGETFHASQPSMTVDGFTDPSNSERFCLGLLSNVNRNAAVELTRRHIGRGVRLYYIG GEVFAECLSDSAIFVQSPNCNQRYGWHPATVCKIPPGCNLKIFNNQEFAALLAQSVNQGF EAVYQLTRMCTIRMSFVKGWGAEYRRQTVTSTPCWIELHLNGPLQWLDKVLTQMGSPSIR CSSVS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Receptor-regulated SMAD (R-SMAD) that is an intracellular signal transducer and transcriptional modulator activated by TGF-beta (transforming growth factor) and activin type 1 receptor kinases. Binds the TRE element in the promoter region of many genes that are regulated by TGF-beta and, on formation of the SMAD3/SMAD4 complex, activates transcription. Also can form a SMAD3/SMAD4/JUN/FOS complex at the AP-1/SMAD site to regulate TGF-beta-mediated transcription. Has an inhibitory effect on wound healing probably by modulating both growth and migration of primary keratinocytes and by altering the TGF-mediated chemotaxis of monocytes. This effect on wound healing appears to be hormone-sensitive. Regulator of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis and inhibits early healing of bone fractures. Positively regulates PDPK1 kinase activity by stimulating its dissociation from the 14-3-3 protein YWHAQ which acts as a negative regulator.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.40E-28 Fold-change: -6.82E-02 Z-score: -1.18E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Inhibition | hsa04670 | |
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-489 was significantly suppressed in MCF-7/ADM cells compared with chemosensitive parental control MCF-7/WT cells. Forced-expression of miR-489 reversed chemoresistance. Furthermore, Smad3 was identified as the target of miR-489 and is highly expressed in MCF-7/ADM cells. Forced expression of miR-489 both inhibited Smad3 expression and Smad3 related EMT properties. Finally, the interactions between Smad3, miR-489 and EMT were confirmed in chemoresistant tumor xenografts and clinical samples, indicating their potential implication for treatment of chemoresistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prolactinomas [ICD-11: 2F37.2] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prolactinomas [ICD-11: 2F37.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bromocriptine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | TGF-beta 1/Smad3 pathway | Activation | hsa04350 | |
| In Vitro Model | HS27 cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0E34 |
| MMQ cells | Pituitary gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_2117 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | TGF-beta1 promotes the synthesis and secretion of collagen fibers in fibroblasts and that the TGF-beta1/Smad3 pathway is involved in the mechanism of prolactinoma resistance by increasing fibrosis through interactions with fibroblasts. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Smad3 is a component of the TGF-beta signaling pathway, having antiproliferative effects that contribute to G1 cell cycle arrest. From this perspective, it was demonstrated that the suppression of Smad3 was involved in mechanisms responsible for resistance to certain anticancer drugs, such as trastzumab. Furthermore, some evidences suggested that Smad3 may be correlated with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Mechanistically, Smad3 was reported to be suppressed through phosphorylation by the cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D1-CDK4/6 complexes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Smad3 is a component of the TGF-beta signaling pathway, having antiproliferative effects that contribute to G1 cell cycle arrest. From this perspective, it was demonstrated that the suppression of Smad3 was involved in mechanisms responsible for resistance to certain anticancer drugs, such as trastzumab. Furthermore, some evidences suggested that Smad3 may be correlated with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Mechanistically, Smad3 was reported to be suppressed through phosphorylation by the cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D1-CDK4/6 complexes. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Smad3 is a component of the TGF-beta signaling pathway, having antiproliferative effects that contribute to G1 cell cycle arrest. From this perspective, it was demonstrated that the suppression of Smad3 was involved in mechanisms responsible for resistance to certain anticancer drugs, such as trastzumab. Furthermore, some evidences suggested that Smad3 may be correlated with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Mechanistically, Smad3 was reported to be suppressed through phosphorylation by the cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D1-CDK4/6 complexes. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.40E-28; Fold-change: -3.59E-01; Z-score: -9.53E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.65E-06; Fold-change: -3.84E-01; Z-score: -9.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
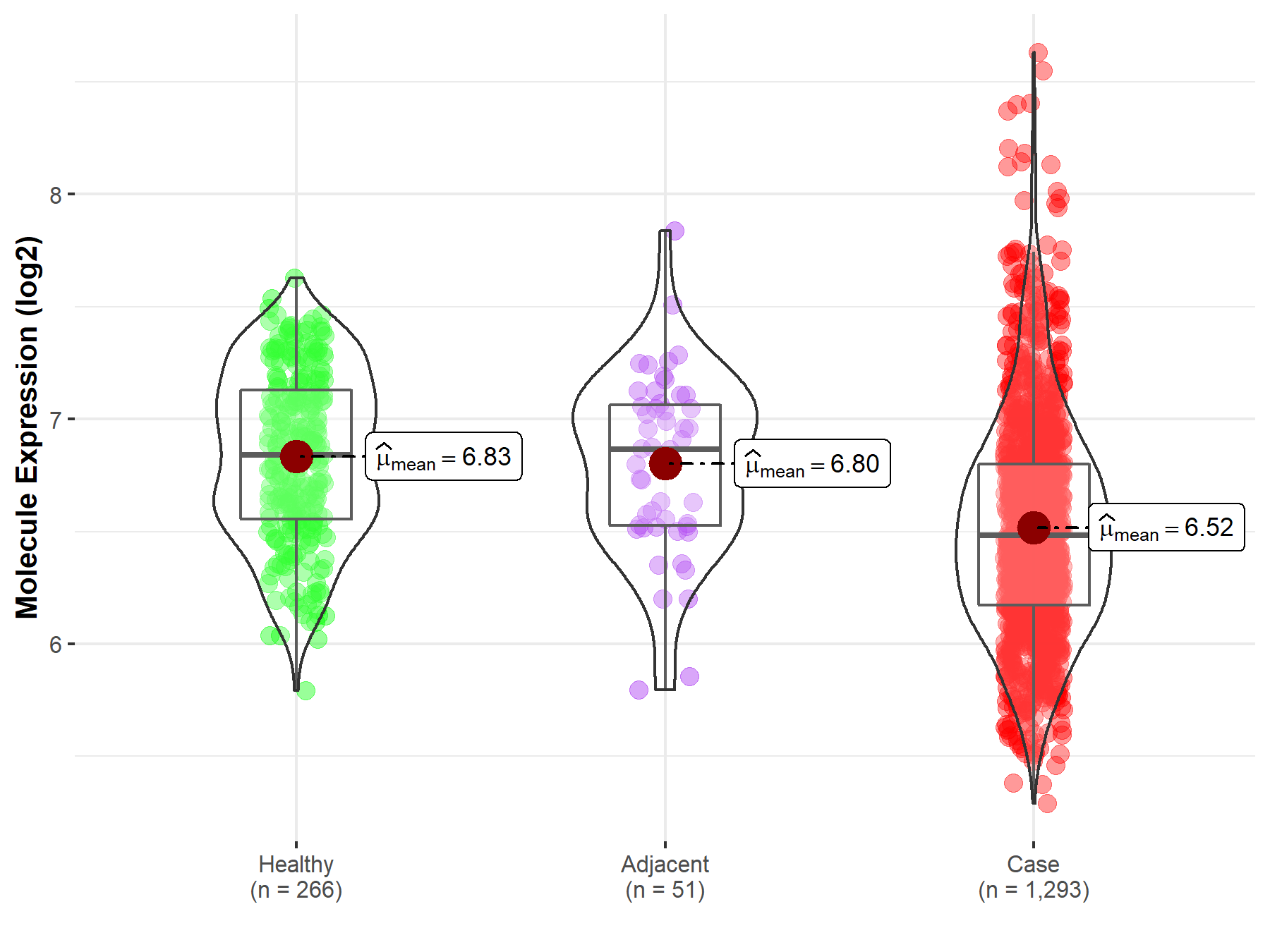
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.72E-03; Fold-change: -3.51E-01; Z-score: -1.18E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
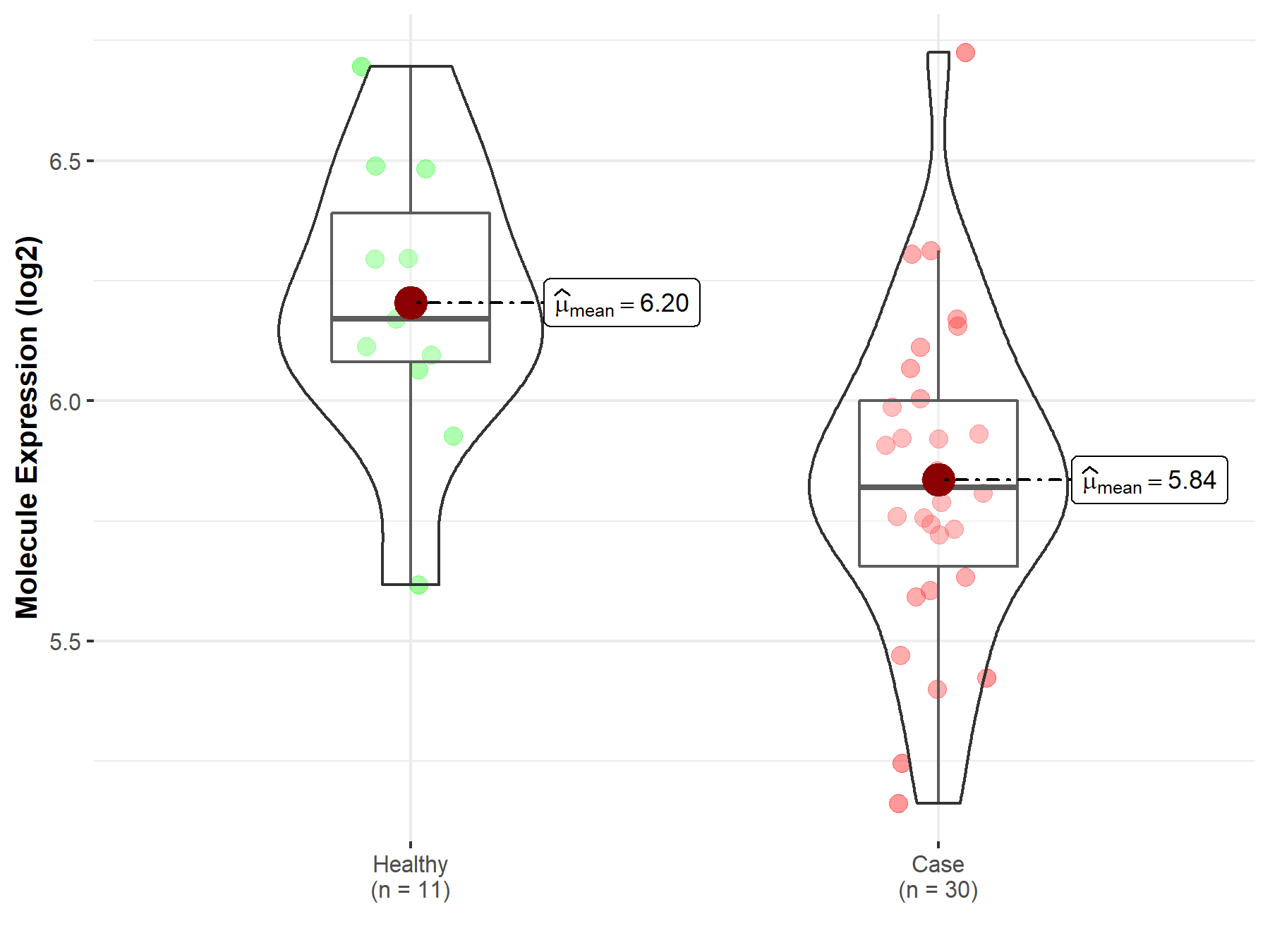
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary gonadotrope tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.57E-02; Fold-change: -5.17E-01; Z-score: -1.41E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
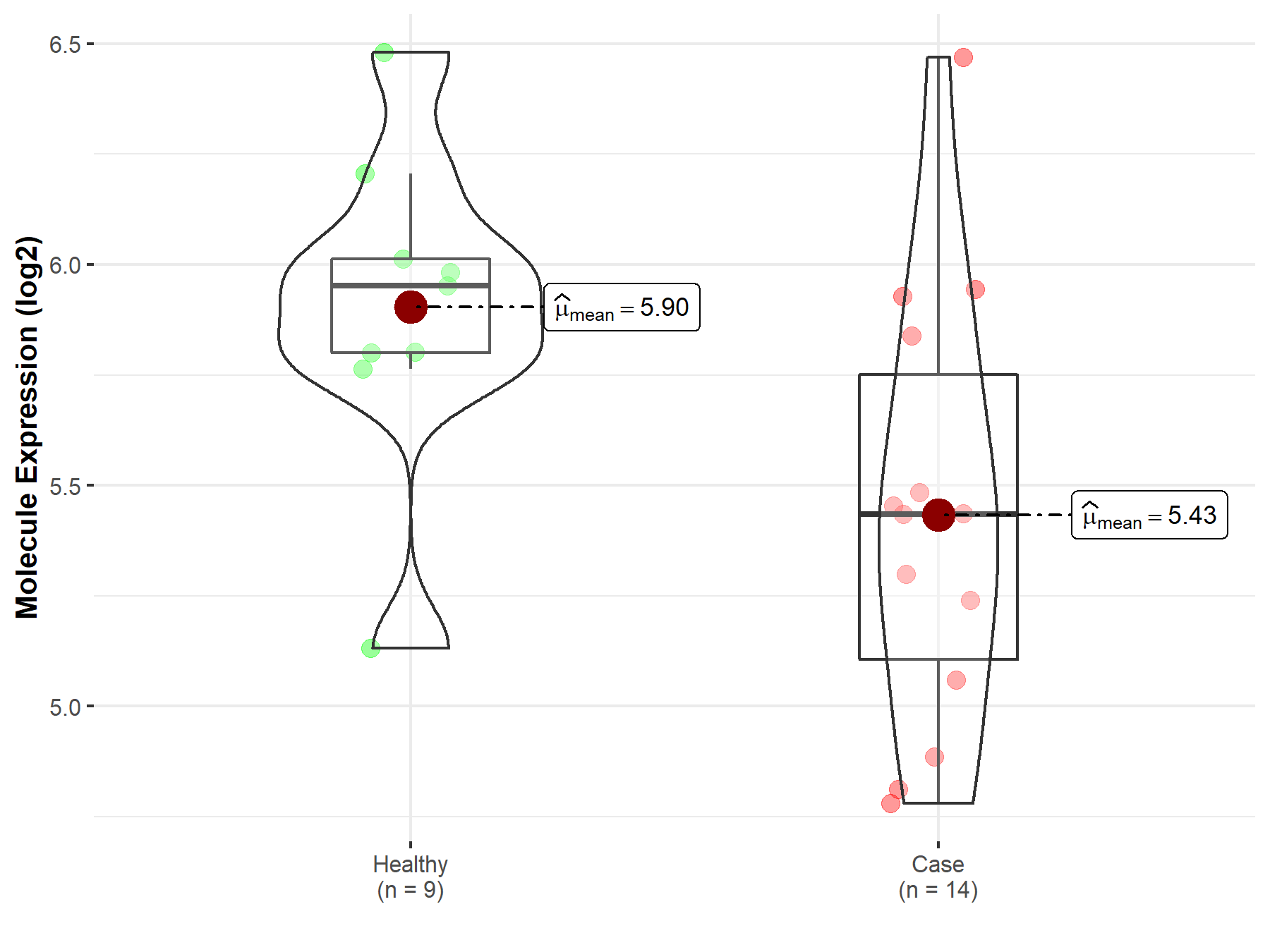
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

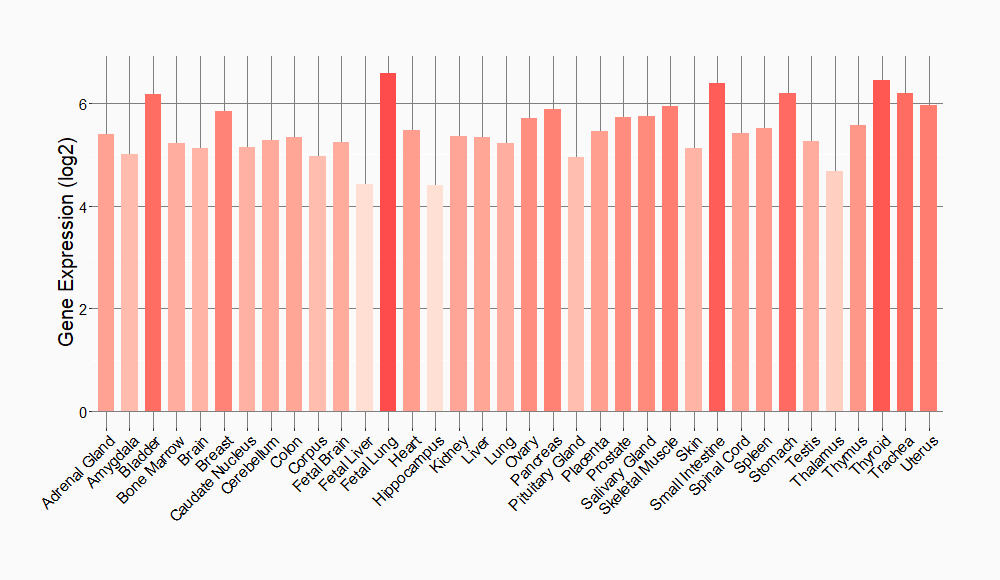
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
