Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00527)
| Name |
Neurofibromin (NF1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Neurofibromatosis-related protein NF-1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NF1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr17:31094927-31382116[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAAHRPVEWVQAVVSRFDEQLPIKTGQQNTHTKVSTEHNKECLINISKYKFSLVISGLTT
ILKNVNNMRIFGEAAEKNLYLSQLIILDTLEKCLAGQPKDTMRLDETMLVKQLLPEICHF LHTCREGNQHAAELRNSASGVLFSLSCNNFNAVFSRISTRLQELTVCSEDNVDVHDIELL QYINVDCAKLKRLLKETAFKFKALKKVAQLAVINSLEKAFWNWVENYPDEFTKLYQIPQT DMAECAEKLFDLVDGFAESTKRKAAVWPLQIILLILCPEIIQDISKDVVDENNMNKKLFL DSLRKALAGHGGSRQLTESAAIACVKLCKASTYINWEDNSVIFLLVQSMVVDLKNLLFNP SKPFSRGSQPADVDLMIDCLVSCFRISPHNNQHFKICLAQNSPSTFHYVLVNSLHRIITN SALDWWPKIDAVYCHSVELRNMFGETLHKAVQGCGAHPAIRMAPSLTFKEKVTSLKFKEK PTDLETRSYKYLLLSMVKLIHADPKLLLCNPRKQGPETQGSTAELITGLVQLVPQSHMPE IAQEAMEALLVLHQLDSIDLWNPDAPVETFWEISSQMLFYICKKLTSHQMLSSTEILKWL REILICRNKFLLKNKQADRSSCHFLLFYGVGCDIPSSGNTSQMSMDHEELLRTPGASLRK GKGNSSMDSAAGCSGTPPICRQAQTKLEVALYMFLWNPDTEAVLVAMSCFRHLCEEADIR CGVDEVSVHNLLPNYNTFMEFASVSNMMSTGRAALQKRVMALLRRIEHPTAGNTEAWEDT HAKWEQATKLILNYPKAKMEDGQAAESLHKTIVKRRMSHVSGGGSIDLSDTDSLQEWINM TGFLCALGGVCLQQRSNSGLATYSPPMGPVSERKGSMISVMSSEGNADTPVSKFMDRLLS LMVCNHEKVGLQIRTNVKDLVGLELSPALYPMLFNKLKNTISKFFDSQGQVLLTDTNTQF VEQTIAIMKNLLDNHTEGSSEHLGQASIETMMLNLVRYVRVLGNMVHAIQIKTKLCQLVE VMMARRDDLSFCQEMKFRNKMVEYLTDWVMGTSNQAADDDVKCLTRDLDQASMEAVVSLL AGLPLQPEEGDGVELMEAKSQLFLKYFTLFMNLLNDCSEVEDESAQTGGRKRGMSRRLAS LRHCTVLAMSNLLNANVDSGLMHSIGLGYHKDLQTRATFMEVLTKILQQGTEFDTLAETV LADRFERLVELVTMMGDQGELPIAMALANVVPCSQWDELARVLVTLFDSRHLLYQLLWNM FSKEVELADSMQTLFRGNSLASKIMTFCFKVYGATYLQKLLDPLLRIVITSSDWQHVSFE VDPTRLEPSESLEENQRNLLQMTEKFFHAIISSSSEFPPQLRSVCHCLYQATCHSLLNKA TVKEKKENKKSVVSQRFPQNSIGAVGSAMFLRFINPAIVSPYEAGILDKKPPPRIERGLK LMSKILQSIANHVLFTKEEHMRPFNDFVKSNFDAARRFFLDIASDCPTSDAVNHSLSFIS DGNVLALHRLLWNNQEKIGQYLSSNRDHKAVGRRPFDKMATLLAYLGPPEHKPVADTHWS SLNLTSSKFEEFMTRHQVHEKEEFKALKTLSIFYQAGTSKAGNPIFYYVARRFKTGQING DLLIYHVLLTLKPYYAKPYEIVVDLTHTGPSNRFKTDFLSKWFVVFPGFAYDNVSAVYIY NCNSWVREYTKYHERLLTGLKGSKRLVFIDCPGKLAEHIEHEQQKLPAATLALEEDLKVF HNALKLAHKDTKVSIKVGSTAVQVTSAERTKVLGQSVFLNDIYYASEIEEICLVDENQFT LTIANQGTPLTFMHQECEAIVQSIIHIRTRWELSQPDSIPQHTKIRPKDVPGTLLNIALL NLGSSDPSLRSAAYNLLCALTCTFNLKIEGQLLETSGLCIPANNTLFIVSISKTLAANEP HLTLEFLEECISGFSKSSIELKHLCLEYMTPWLSNLVRFCKHNDDAKRQRVTAILDKLIT MTINEKQMYPSIQAKIWGSLGQITDLLDVVLDSFIKTSATGGLGSIKAEVMADTAVALAS GNVKLVSSKVIGRMCKIIDKTCLSPTPTLEQHLMWDDIAILARYMLMLSFNNSLDVAAHL PYLFHVVTFLVATGPLSLRASTHGLVINIIHSLCTCSQLHFSEETKQVLRLSLTEFSLPK FYLLFGISKVKSAAVIAFRSSYRDRSFSPGSYERETFALTSLETVTEALLEIMEACMRDI PTCKWLDQWTELAQRFAFQYNPSLQPRALVVFGCISKRVSHGQIKQIIRILSKALESCLK GPDTYNSQVLIEATVIALTKLQPLLNKDSPLHKALFWVAVAVLQLDEVNLYSAGTALLEQ NLHTLDSLRIFNDKSPEEVFMAIRNPLEWHCKQMDHFVGLNFNSNFNFALVGHLLKGYRH PSPAIVARTVRILHTLLTLVNKHRNCDKFEVNTQSVAYLAALLTVSEEVRSRCSLKHRKS LLLTDISMENVPMDTYPIHHGDPSYRTLKETQPWSSPKGSEGYLAATYPTVGQTSPRARK SMSLDMGQPSQANTKKLLGTRKSFDHLISDTKAPKRQEMESGITTPPKMRRVAETDYEME TQRISSSQQHPHLRKVSVSESNVLLDEEVLTDPKIQALLLTVLATLVKYTTDEFDQRILY EYLAEASVVFPKVFPVVHNLLDSKINTLLSLCQDPNLLNPIHGIVQSVVYHEESPPQYQT SYLQSFGFNGLWRFAGPFSKQTQIPDYAELIVKFLDALIDTYLPGIDEETSEESLLTPTS PYPPALQSQLSITANLNLSNSMTSLATSQHSPGIDKENVELSPTTGHCNSGRTRHGSASQ VQKQRSAGSFKRNSIKKIV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Stimulates the GTPase activity of Ras. NF1 shows greater affinity for Ras GAP, but lower specific activity. May be a regulator of Ras activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04014 | |
| In Vitro Model | sNF02.2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_K280 |
| Hs 53.T cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0786 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ez-Cytox assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High expression of Bcl-xL in the MPNST cells was caused by a decreased transcriptional expression of the NF1 gene. Down-regulation of the NF1 gene by RNA interference (RNAi) induced an increase in Bcl-xL expression and a decrease in its sensitivity to apoptosis in the benign neurofibroma cell line and primary normal cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04014 | |
| In Vitro Model | sNF02.2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_K280 |
| Hs 53.T cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0786 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ez-Cytox assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High expression of Bcl-xL in the MPNST cells was caused by a decreased transcriptional expression of the NF1 gene. Down-regulation of the NF1 gene by RNA interference (RNAi) induced an increase in Bcl-xL expression and a decrease in its sensitivity to apoptosis in the benign neurofibroma cell line and primary normal cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Peripheral nerve sheath tumor [ICD-11: 2F3Y.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Etoposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04014 | |
| In Vitro Model | sNF02.2 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_K280 |
| Hs 53.T cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0786 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Ez-Cytox assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | High expression of Bcl-xL in the MPNST cells was caused by a decreased transcriptional expression of the NF1 gene. Down-regulation of the NF1 gene by RNA interference (RNAi) induced an increase in Bcl-xL expression and a decrease in its sensitivity to apoptosis in the benign neurofibroma cell line and primary normal cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Lenvatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | |
| MAPK/ERK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| FOXO3 signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04068 | ||
| In Vivo Model | Xenograft-nude mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Quantitative RT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Transwell invasion assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | With RNAi knockdown and CRISPR/Cas9 knockout models, we further clarified the mechanisms by which NF1 loss reactivates the PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways, while DUSP9 loss activates the MAPK/ERK signaling pathways, thereby inactivating FOXO3, followed by degradation of FOXO3, finally induced lenvatinib resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [3], [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tretinoin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Alteration | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | Kelly cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2092 |
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | |
| IMR-5 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1306 | |
| NBL-S cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2136 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | NF1 i.ctivation has been reported in neuroblastoma and confers activation of RAS-MAPk signalling and resistance to retinoic acid. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.07E-09; Fold-change: -1.45E-01; Z-score: -3.48E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
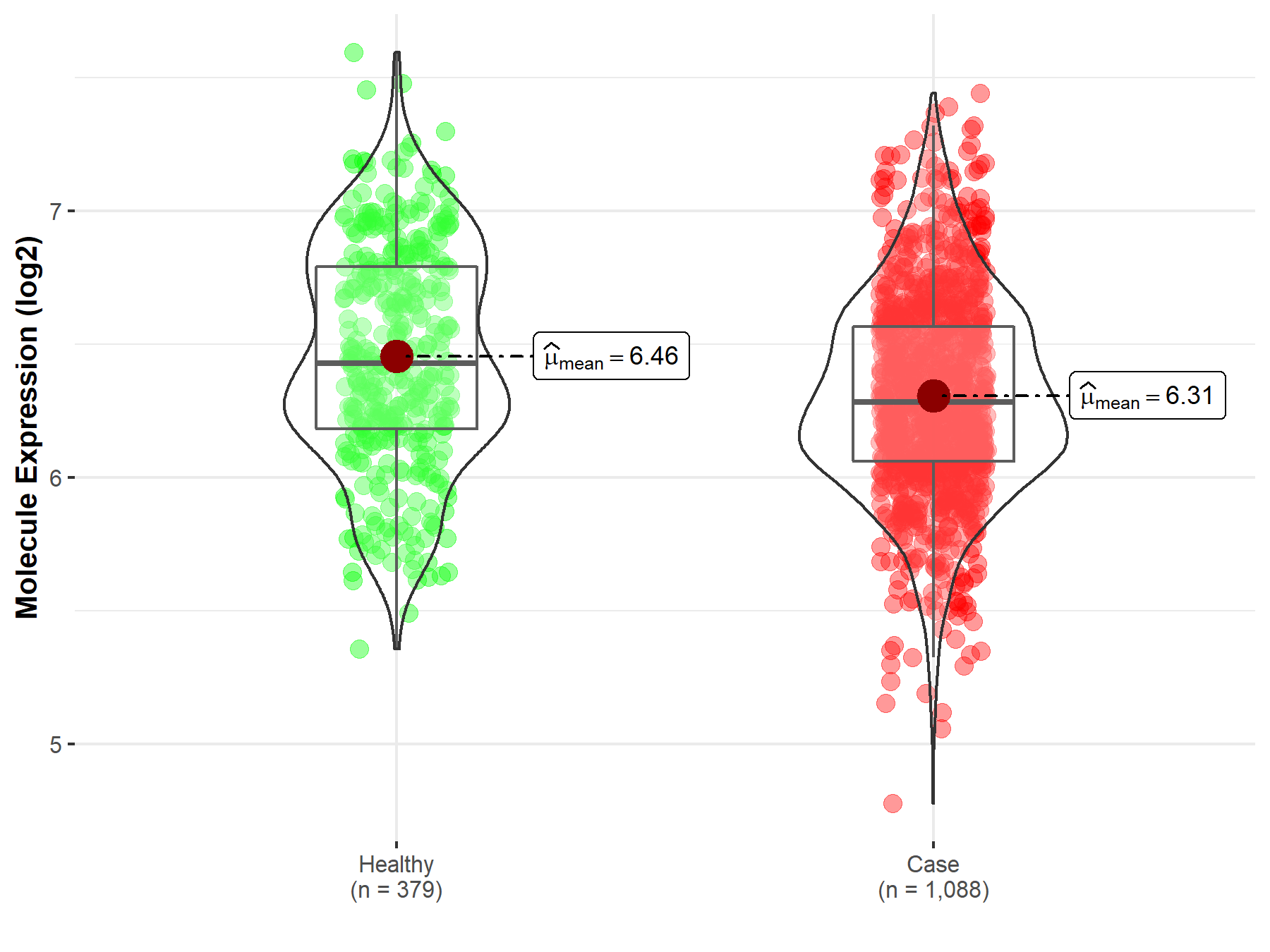
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.00E-01; Fold-change: 1.54E-01; Z-score: 5.88E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.31E-03; Fold-change: 4.23E-01; Z-score: 1.47E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
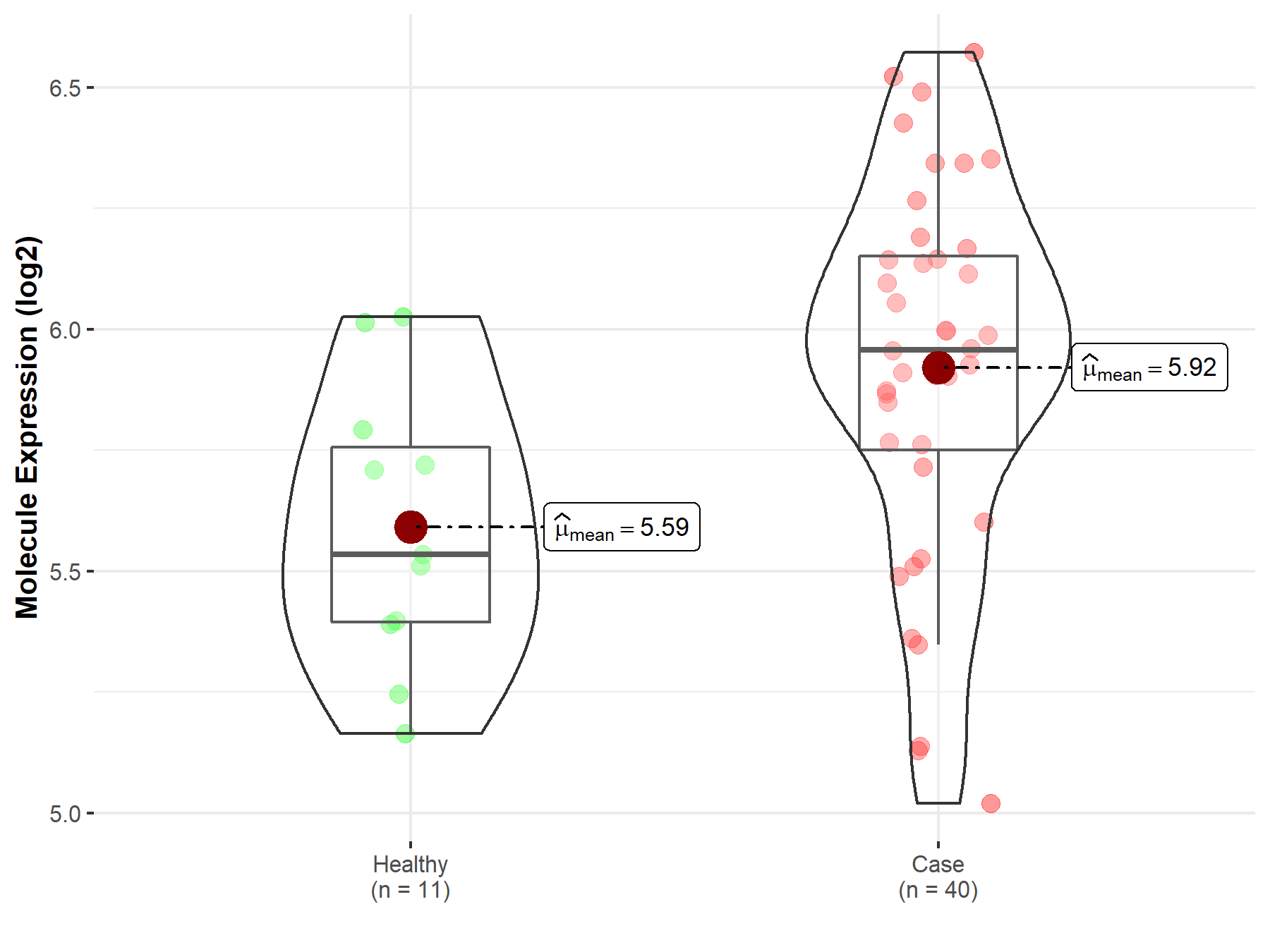
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.18E-02; Fold-change: -1.67E-01; Z-score: -8.65E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
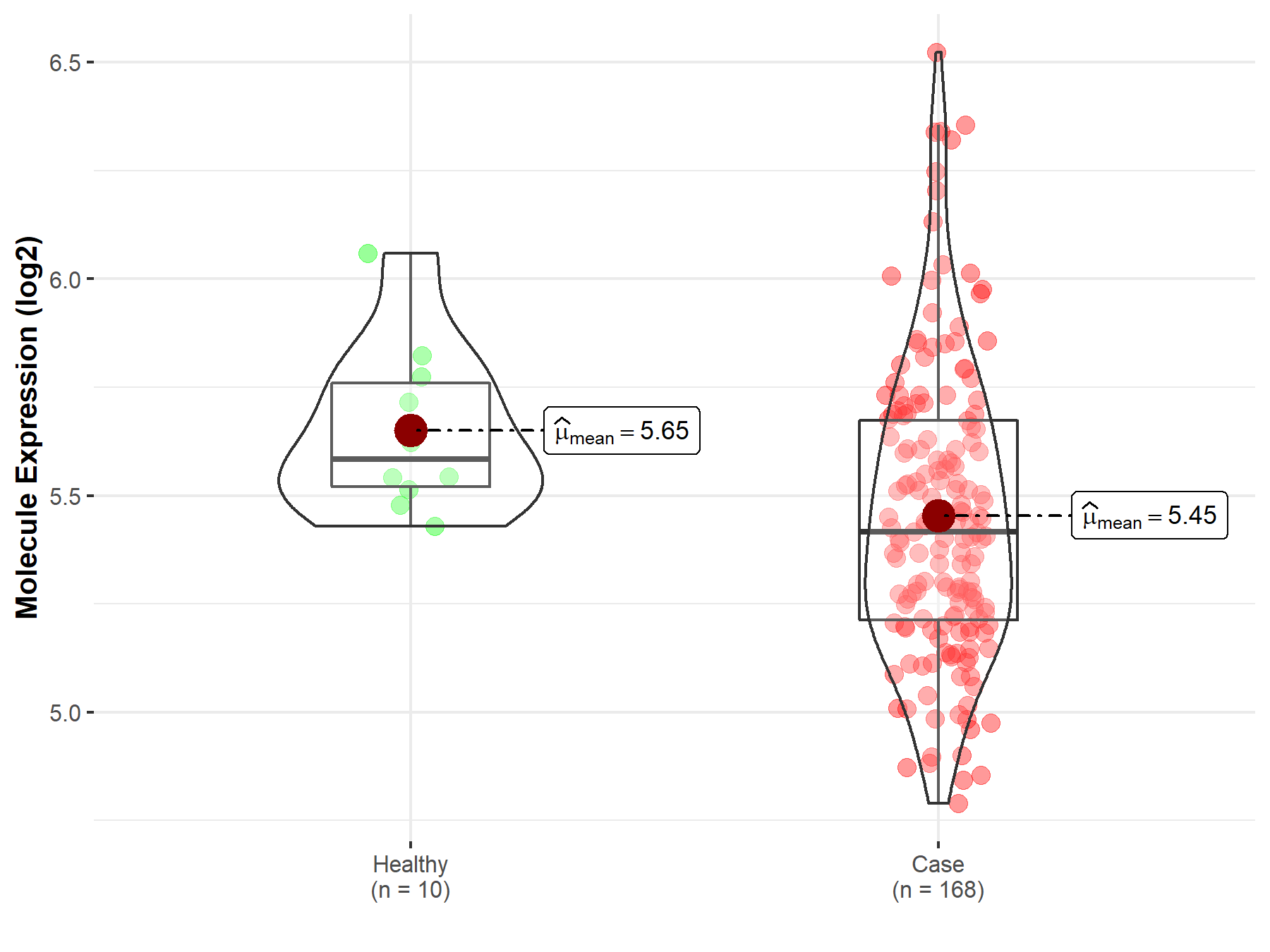
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.54E-09; Fold-change: 2.24E-01; Z-score: 1.05E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.02E-32; Fold-change: 2.63E-01; Z-score: 1.24E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 1.75E-01; Fold-change: 2.91E-01; Z-score: 9.18E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
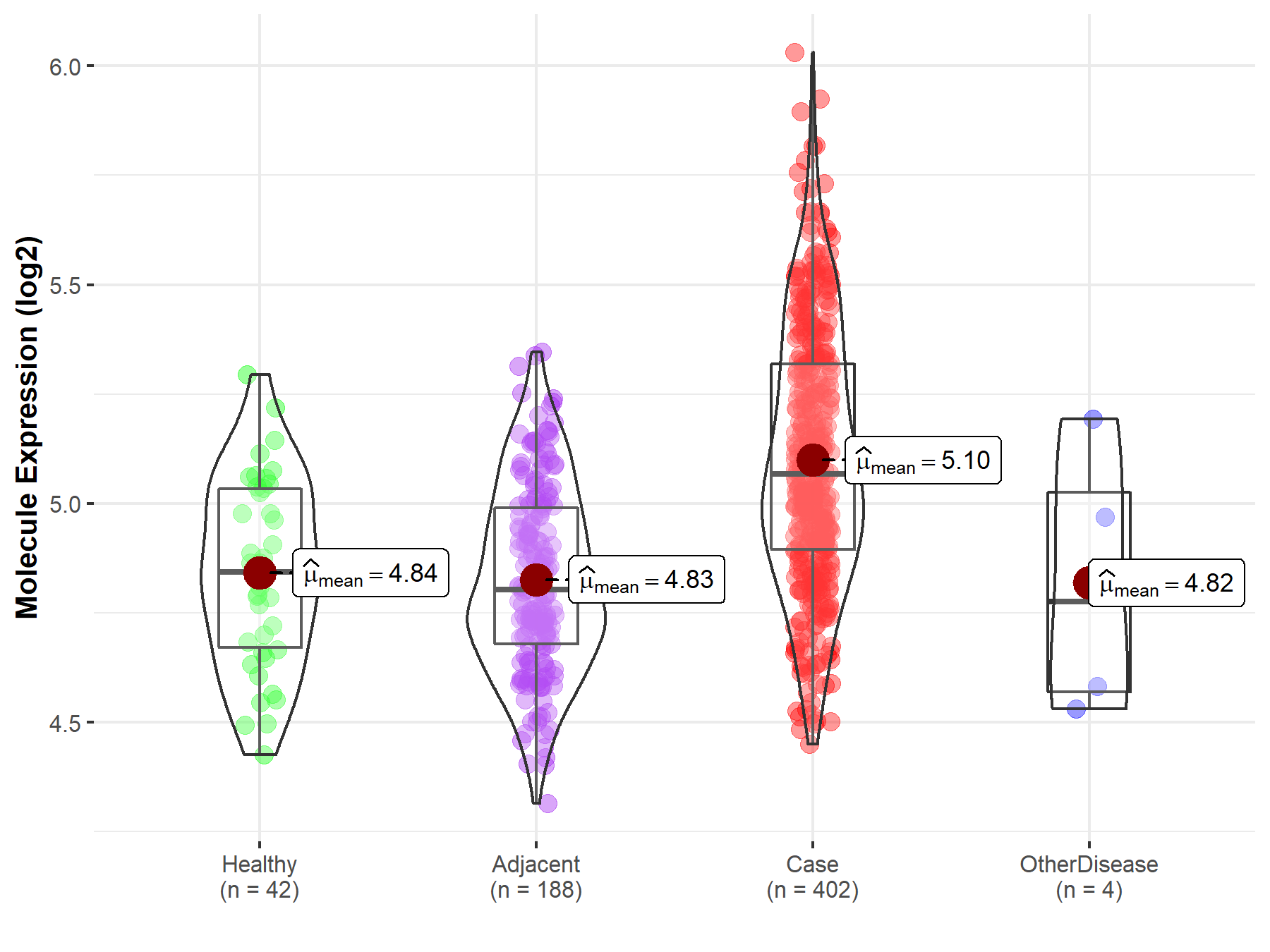
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
