Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00492)
| Name |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Mdm2 (MDM2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Double minute 2 protein; Hdm2; Oncoprotein Mdm2; RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase Mdm2; p53-binding protein Mdm2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MDM2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr12:68808177-68845544[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MCNTNMSVPTDGAVTTSQIPASEQETLVRPKPLLLKLLKSVGAQKDTYTMKEVLFYLGQY
IMTKRLYDEKQQHIVYCSNDLLGDLFGVPSFSVKEHRKIYTMIYRNLVVVNQQESSDSGT SVSENRCHLEGGSDQKDLVQELQEEKPSSSHLVSRPSTSSRRRAISETEENSDELSGERQ RKRHKSDSISLSFDESLALCVIREICCERSSSSESTGTPSNPDLDAGVSEHSGDWLDQDS VSDQFSVEFEVESLDSEDYSLSEEGQELSDEDDEVYQVTVYQAGESDTDSFEEDPEISLA DYWKCTSCNEMNPPLPSHCNRCWALRENWLPEDKGKDKGEISEKAKLENSTQAEEGFDVP DCKKTIVNDSRESCVEENDDKITQASQSQESEDYSQPSTSSSIIYSSQEDVKEFEREETQ DKEESVESSLPLNAIEPCVICQGRPKNGCIVHGKTGHLMACFTCAKKLKKRNKPCPVCRQ PIQMIVLTYFP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase that mediates ubiquitination of p53/TP53, leading to its degradation by the proteasome. Inhibits p53/TP53- and p73/TP73-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by binding its transcriptional activation domain. Also acts as a ubiquitin ligase E3 toward itself and ARRB1. Permits the nuclear export of p53/TP53. Promotes proteasome-dependent ubiquitin-independent degradation of retinoblastoma RB1 protein. Inhibits DAXX-mediated apoptosis by inducing its ubiquitination and degradation. Component of the TRIM28/KAP1-MDM2-p53/TP53 complex involved in stabilizing p53/TP53. Also component of the TRIM28/KAP1-ERBB4-MDM2 complex which links growth factor and DNA damage response pathways. Mediates ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation of DYRK2 in nucleus. Ubiquitinates IGF1R and SNAI1 and promotes them to proteasomal degradation. Ubiquitinates DCX, leading to DCX degradation and reduction of the dendritic spine density of olfactory bulb granule cells. Ubiquitinates DLG4, leading to proteasomal degradation of DLG4 which is required for AMPA receptor endocytosis. Negatively regulates NDUFS1, leading to decreased mitochondrial respiration, marked oxidative stress, and commitment to the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis. Binds NDUFS1 leading to its cytosolic retention rather than mitochondrial localization resulting in decreased supercomplex assembly (interactions between complex I and complex III), decreased complex I activity, ROS production, and apoptosis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
8 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.50E-04 Fold-change: 7.14E-02 Z-score: 4.02E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 |
| Hep3B cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0326 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-221 can activate the p53/mdm2 axis by inhibiting MDM2 and, in turn, p53 activation contributes to miR-221 enhanced expression. Moreover, by modulating the p53 axis, miR-221 impacts cell-cycle progression and apoptotic response to doxorubicin in hepatocellular carcinoma-derived cell lines. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.3] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.31E-13 Fold-change: 5.68E-02 Z-score: 7.37E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Sk-MES-1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0630 |
| H157 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2458 | |
| NCl-H226 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1544 | |
| NCI-H522 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1567 | |
| NCl-H1437 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1472 | |
| NCl-H1792 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1495 | |
| NCl-H1944 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1508 | |
| NCl-H596 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1571 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoprecipitation assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | piR-L-138 directly interacted with p60-MDM2 and inhibited CDDP-activated apoptosis in p53-mutated LSCC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.54E-23 Fold-change: 5.01E-02 Z-score: 1.02E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Approximately 20%-30% of breast cancer patients show overexpression of MDM2, and this overexpression contributes particularly to the progression of HR-positive breast cancer. It is reported that CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells have disrupted senescence pathways and insensitivity to the induction of senescence. Therefore, interruption of the senescence pathway by MDM2 in a p53-dependent manner may cause resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Paclitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.89E-01 Fold-change: 2.25E-02 Z-score: 9.05E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hey A8 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_8878 |
| SkVO3ip1 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0C84 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Down-regulation of miR-194-5p induces paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells by altering MDM2 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Approximately 20%-30% of breast cancer patients show overexpression of MDM2, and this overexpression contributes particularly to the progression of HR-positive breast cancer. It is reported that CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells have disrupted senescence pathways and insensitivity to the induction of senescence. Therefore, interruption of the senescence pathway by MDM2 in a p53-dependent manner may cause resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Approximately 20%-30% of breast cancer patients show overexpression of MDM2, and this overexpression contributes particularly to the progression of HR-positive breast cancer. It is reported that CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells have disrupted senescence pathways and insensitivity to the induction of senescence. Therefore, interruption of the senescence pathway by MDM2 in a p53-dependent manner may cause resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Sorafenib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MDM2/AR-FkBP5/PHLPP signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| AKT/ERK signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| HepG2 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0027 | |
| SNU398 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0077 | |
| Skhep1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| HA22T cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7046 | |
| SNU423 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0366 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
3D Invasion Assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR367-3p could increase AR expression via directly targeting the 3'UTR of MDM2 to decrease MDM2 protein expression. The resultant increase of AR expression might then promote the expression of FkBP5 and PHLPP, thus dephosphorylating and inactivating AkT and ERk, to suppress the HCC cell invasion. miR367-3p may function as an AR enhancer to increase Sorafenib chemotherapy efficacy via altering the MDM2/AR/FkBP5/PHLPP/(pAkT and pERk) signals to better suppress HCC metastasis. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Teniposide | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | U87 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0022 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MDM2 is a candidate target of miR-181b. MDM2 knockdown mimicked the sensitization effect of miR-181b. Further study revealed that miR-181b binds to the 3'-UTR region of MDM2 leading to the decrease in MDM2 levels and subsequent increase in teniposide sensitivity. Partial restoration of MDM2 attenuated the sensitivity enhancement by miR-181b. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.59E-23; Fold-change: 7.37E-02; Z-score: 3.63E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
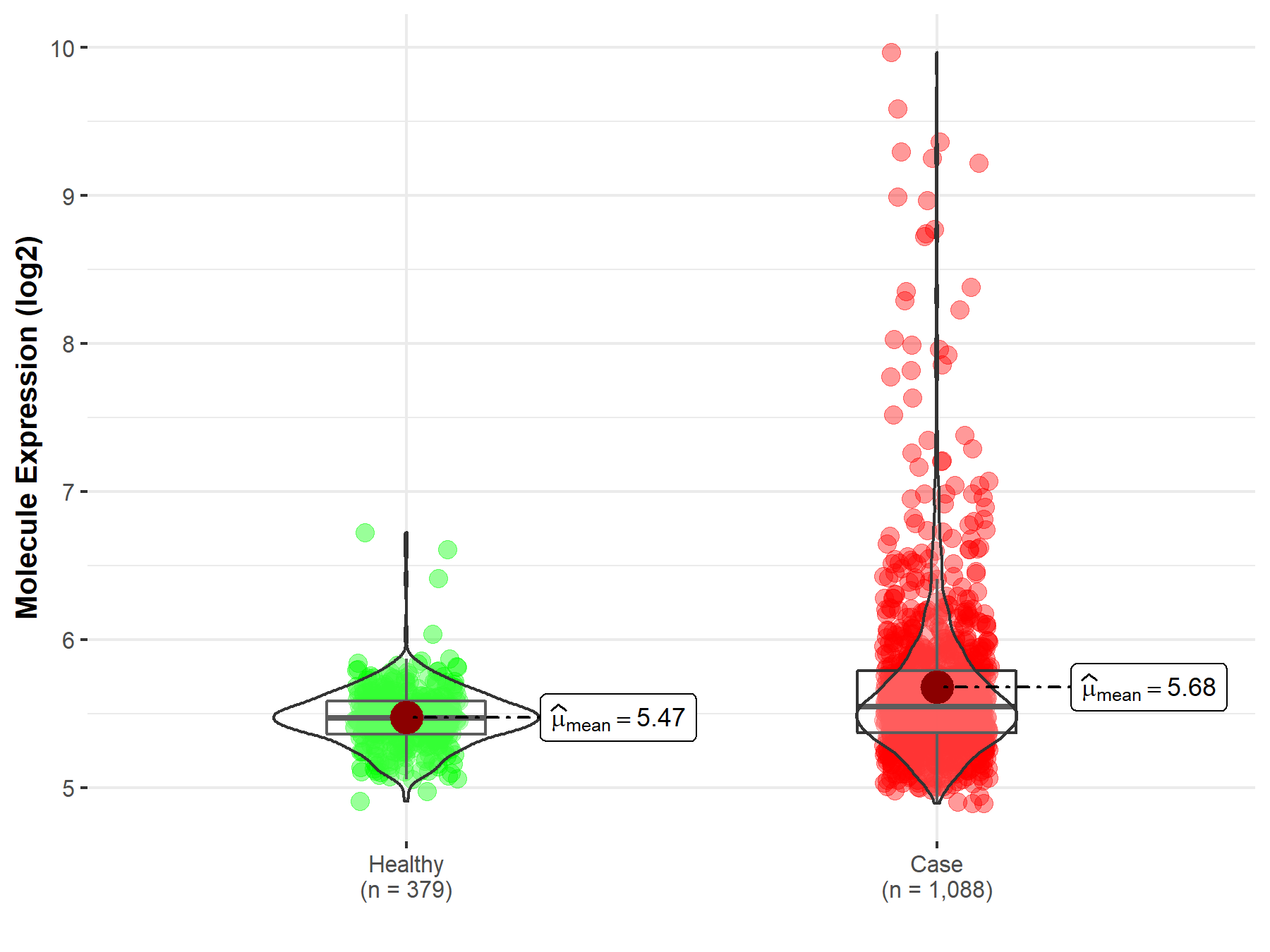
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.17E-01; Fold-change: 3.47E-01; Z-score: 1.21E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.62E-04; Fold-change: 7.64E-01; Z-score: 1.66E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.25E-02; Fold-change: -8.00E-03; Z-score: -3.55E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
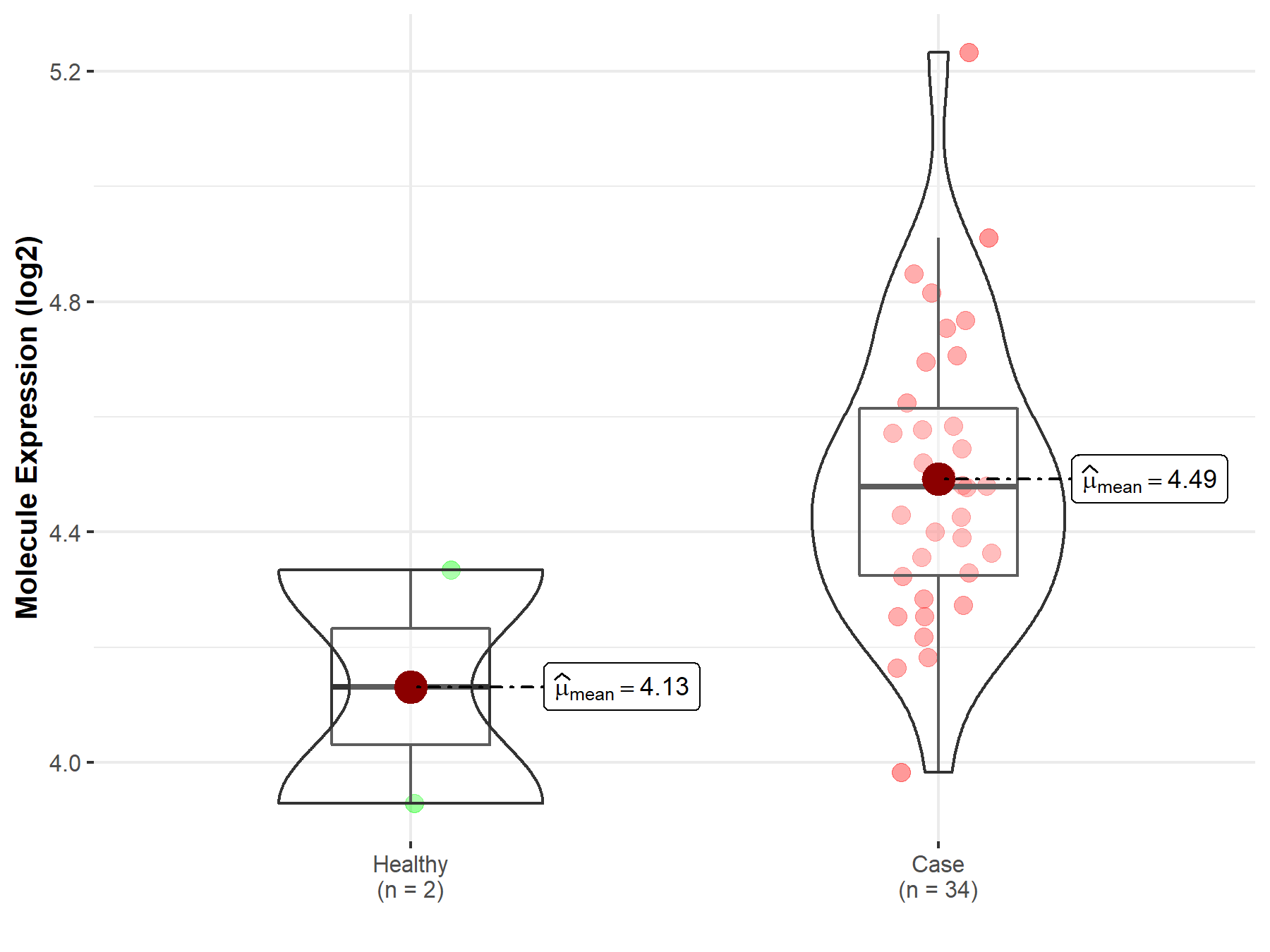
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.50E-04; Fold-change: 1.93E-01; Z-score: 5.64E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.41E-01; Fold-change: -1.42E-01; Z-score: -4.48E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 4.96E-01; Fold-change: 2.42E-02; Z-score: 1.06E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
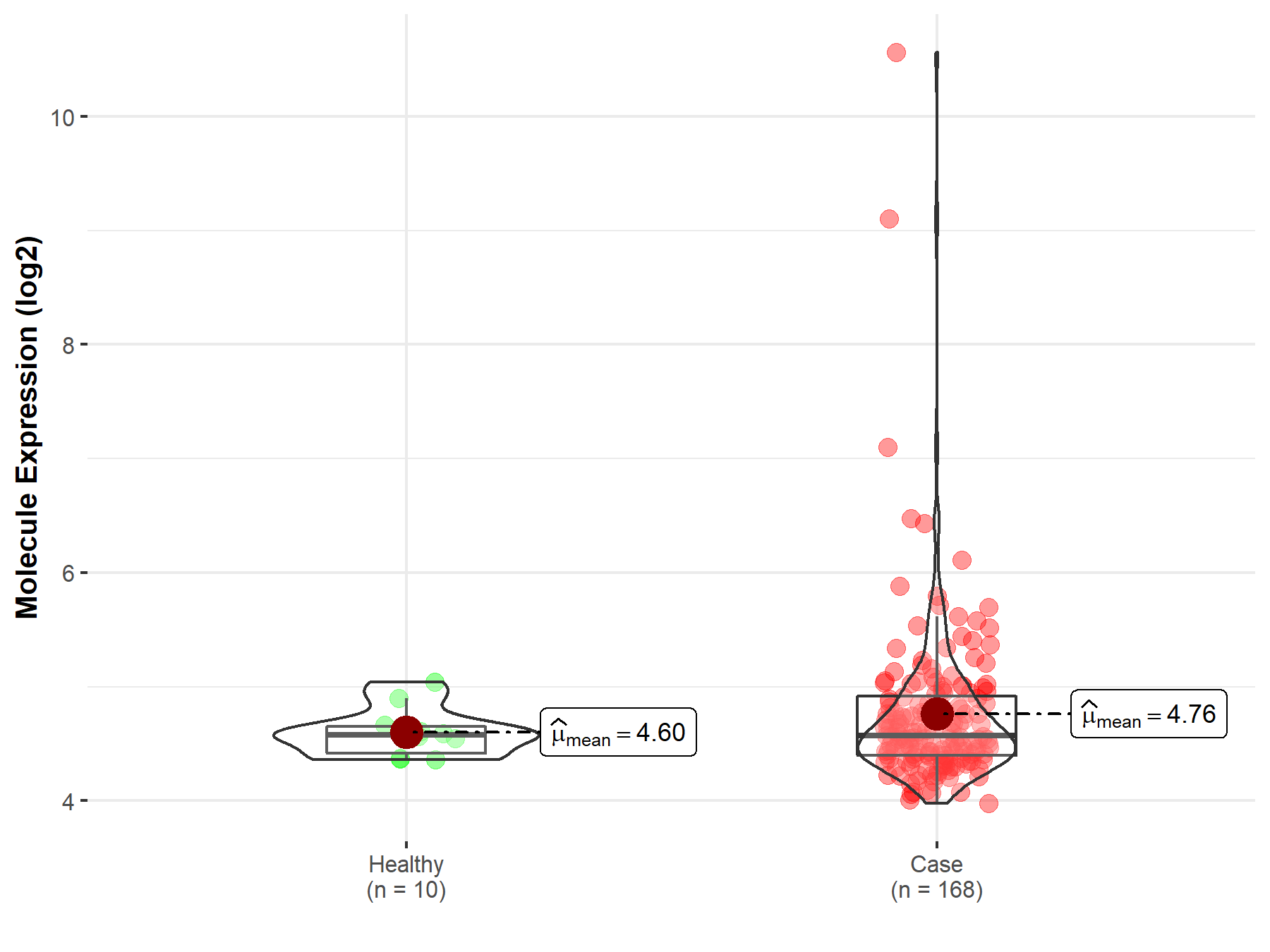
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 8.31E-13; Fold-change: 1.15E-01; Z-score: 4.36E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 9.70E-11; Fold-change: 1.87E-01; Z-score: 5.20E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
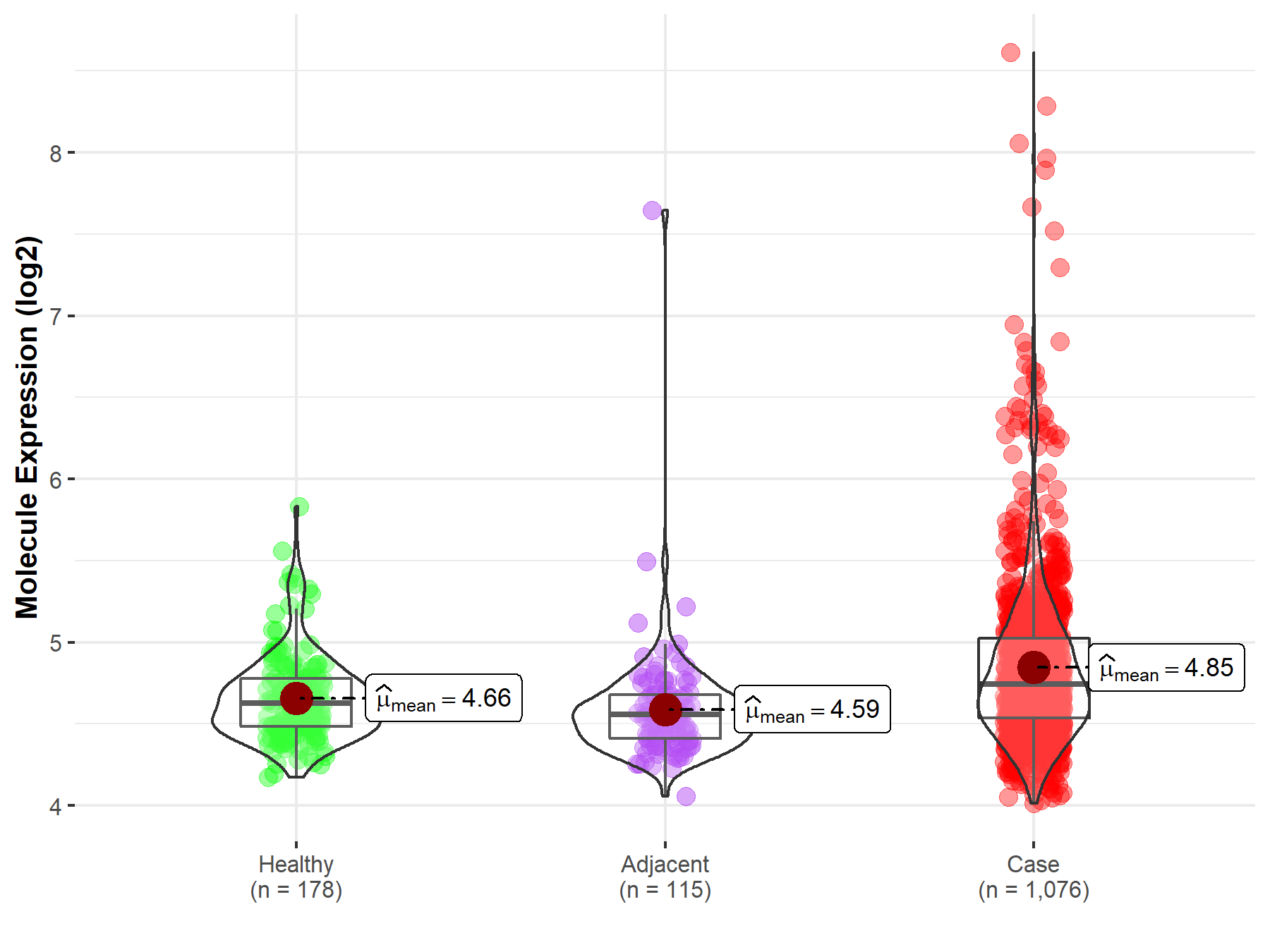
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
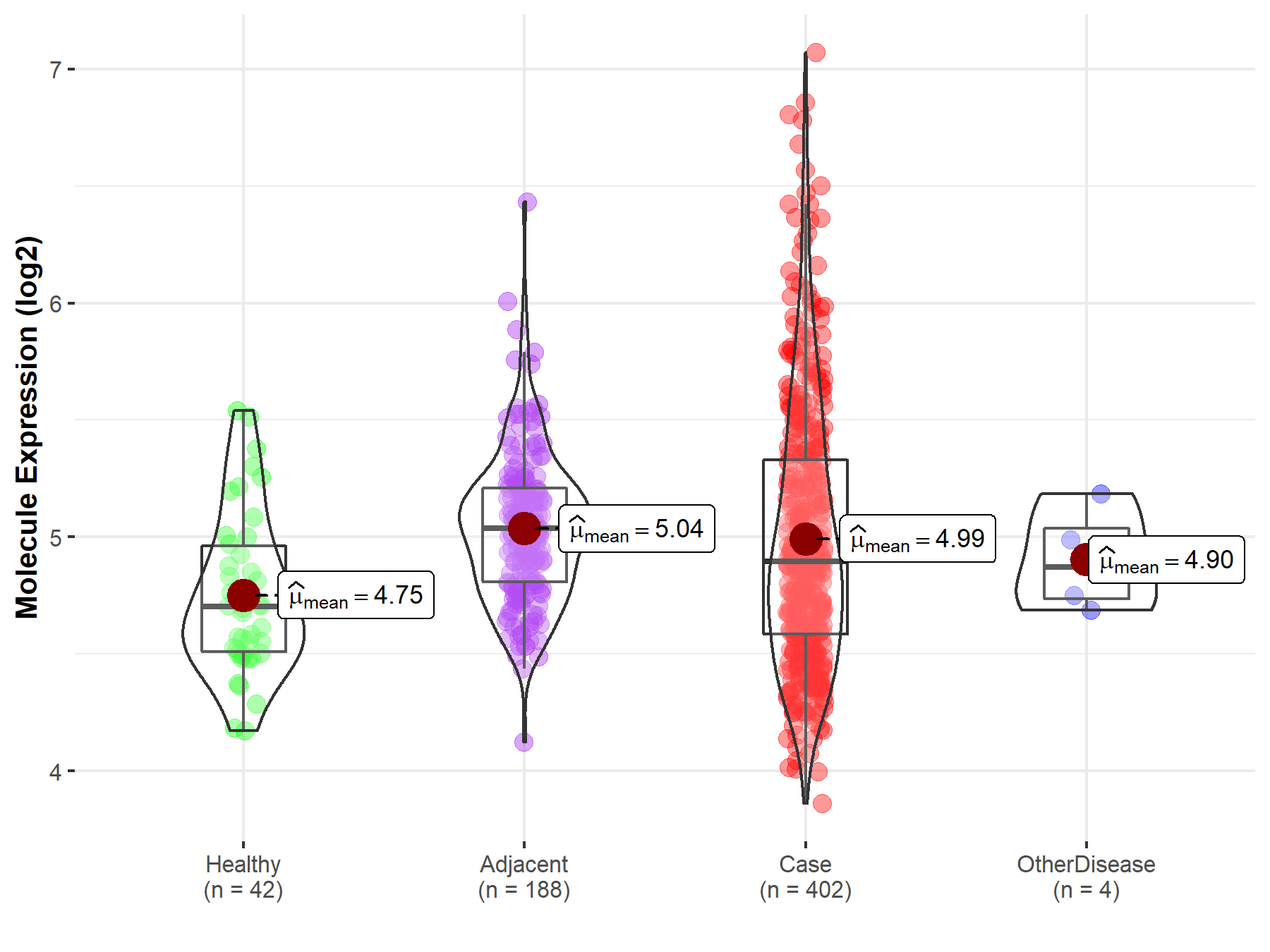
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.54E-23; Fold-change: 1.05E-01; Z-score: 5.51E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.48E-03; Fold-change: 8.91E-02; Z-score: 3.33E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.89E-01; Fold-change: -6.93E-02; Z-score: -2.80E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.37E-01; Fold-change: -2.40E-01; Z-score: -4.79E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

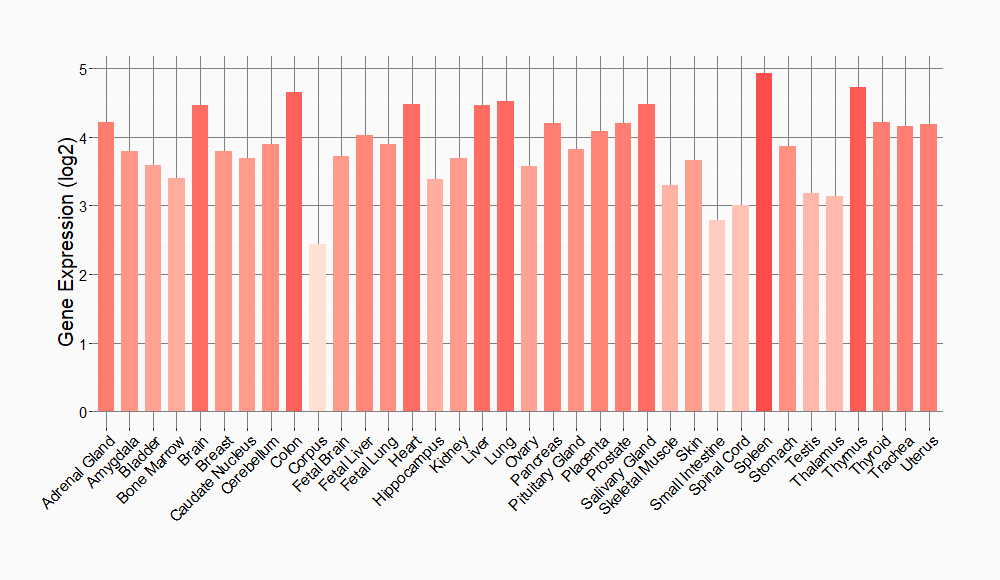
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
