Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00463)
| Name |
Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-3 (RPS6KA3)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
S6K-alpha-3; 90 kDa ribosomal protein S6 kinase 3; p90-RSK 3; p90RSK3; Insulin-stimulated protein kinase 1; ISPK-1; MAP kinase-activated protein kinase 1b; MAPK-activated protein kinase 1b; MAPKAP kinase 1b; MAPKAPK-1b; Ribosomal S6 kinase 2; RSK-2; pp90RSK2; ISPK1; MAPKAPK1B; RSK2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
RPS6KA3
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chrX:20149911-20267519[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPLAQLADPWQKMAVESPSDSAENGQQIMDEPMGEEEINPQTEEVSIKEIAITHHVKEGH
EKADPSQFELLKVLGQGSFGKVFLVKKISGSDARQLYAMKVLKKATLKVRDRVRTKMERD ILVEVNHPFIVKLHYAFQTEGKLYLILDFLRGGDLFTRLSKEVMFTEEDVKFYLAELALA LDHLHSLGIIYRDLKPENILLDEEGHIKLTDFGLSKESIDHEKKAYSFCGTVEYMAPEVV NRRGHTQSADWWSFGVLMFEMLTGTLPFQGKDRKETMTMILKAKLGMPQFLSPEAQSLLR MLFKRNPANRLGAGPDGVEEIKRHSFFSTIDWNKLYRREIHPPFKPATGRPEDTFYFDPE FTAKTPKDSPGIPPSANAHQLFRGFSFVAITSDDESQAMQTVGVHSIVQQLHRNSIQFTD GYEVKEDIGVGSYSVCKRCIHKATNMEFAVKIIDKSKRDPTEEIEILLRYGQHPNIITLK DVYDDGKYVYVVTELMKGGELLDKILRQKFFSEREASAVLFTITKTVEYLHAQGVVHRDL KPSNILYVDESGNPESIRICDFGFAKQLRAENGLLMTPCYTANFVAPEVLKRQGYDAACD IWSLGVLLYTMLTGYTPFANGPDDTPEEILARIGSGKFSLSGGYWNSVSDTAKDLVSKML HVDPHQRLTAALVLRHPWIVHWDQLPQYQLNRQDAPHLVKGAMAATYSALNRNQSPVLEP VGRSTLAQRRGIKKITSTAL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase that acts downstream of ERK (MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1) signaling and mediates mitogenic and stress-induced activation of the transcription factors CREB1, ETV1/ER81 and NR4A1/NUR77, regulates translation through RPS6 and EIF4B phosphorylation, and mediates cellular proliferation, survival, and differentiation by modulating mTOR signaling and repressing pro-apoptotic function of BAD and DAPK1. In fibroblast, is required for EGF-stimulated phosphorylation of CREB1 and histone H3 at 'Ser-10', which results in the subsequent transcriptional activation of several immediate-early genes. In response to mitogenic stimulation (EGF and PMA), phosphorylates and activates NR4A1/NUR77 and ETV1/ER81 transcription factors and the cofactor CREBBP. Upon insulin-derived signal, acts indirectly on the transcription regulation of several genes by phosphorylating GSK3B at 'Ser-9' and inhibiting its activity. Phosphorylates RPS6 in response to serum or EGF via an mTOR-independent mechanism and promotes translation initiation by facilitating assembly of the preinitiation complex. In response to insulin, phosphorylates EIF4B, enhancing EIF4B affinity for the EIF3 complex and stimulating cap-dependent translation. Is involved in the mTOR nutrient-sensing pathway by directly phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-1798', which potently inhibits TSC2 ability to suppress mTOR signaling, and mediates phosphorylation of RPTOR, which regulates mTORC1 activity and may promote rapamycin-sensitive signaling independently of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Mediates cell survival by phosphorylating the pro-apoptotic proteins BAD and DAPK1 and suppressing their pro-apoptotic function. Promotes the survival of hepatic stellate cells by phosphorylating CEBPB in response to the hepatotoxin carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). Is involved in cell cycle regulation by phosphorylating the CDK inhibitor CDKN1B, which promotes CDKN1B association with 14-3-3 proteins and prevents its translocation to the nucleus and inhibition of G1 progression. In LPS-stimulated dendritic cells, is involved in TLR4-induced macropinocytosis, and in myeloma cells, acts as effector of FGFR3-mediated transformation signaling, after direct phosphorylation at Tyr-529 by FGFR3. Negatively regulates EGF-induced MAPK1/3 phosphorylation via phosphorylation of SOS1. Phosphorylates SOS1 at 'Ser-1134' and 'Ser-1161' that create YWHAB and YWHAE binding sites and which contribute to the negative regulation of MAPK1/3 phosphorylation. Phosphorylates EPHA2 at 'Ser-897', the RPS6KA-EPHA2 signaling pathway controls cell migration. Acts as a regulator of osteoblast differentiation by mediating phosphorylation of ATF4, thereby promoting ATF4 transactivation activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.14E-02; Fold-change: 5.08E-01; Z-score: 1.07E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.78E-03; Fold-change: -6.85E-01; Z-score: -1.26E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
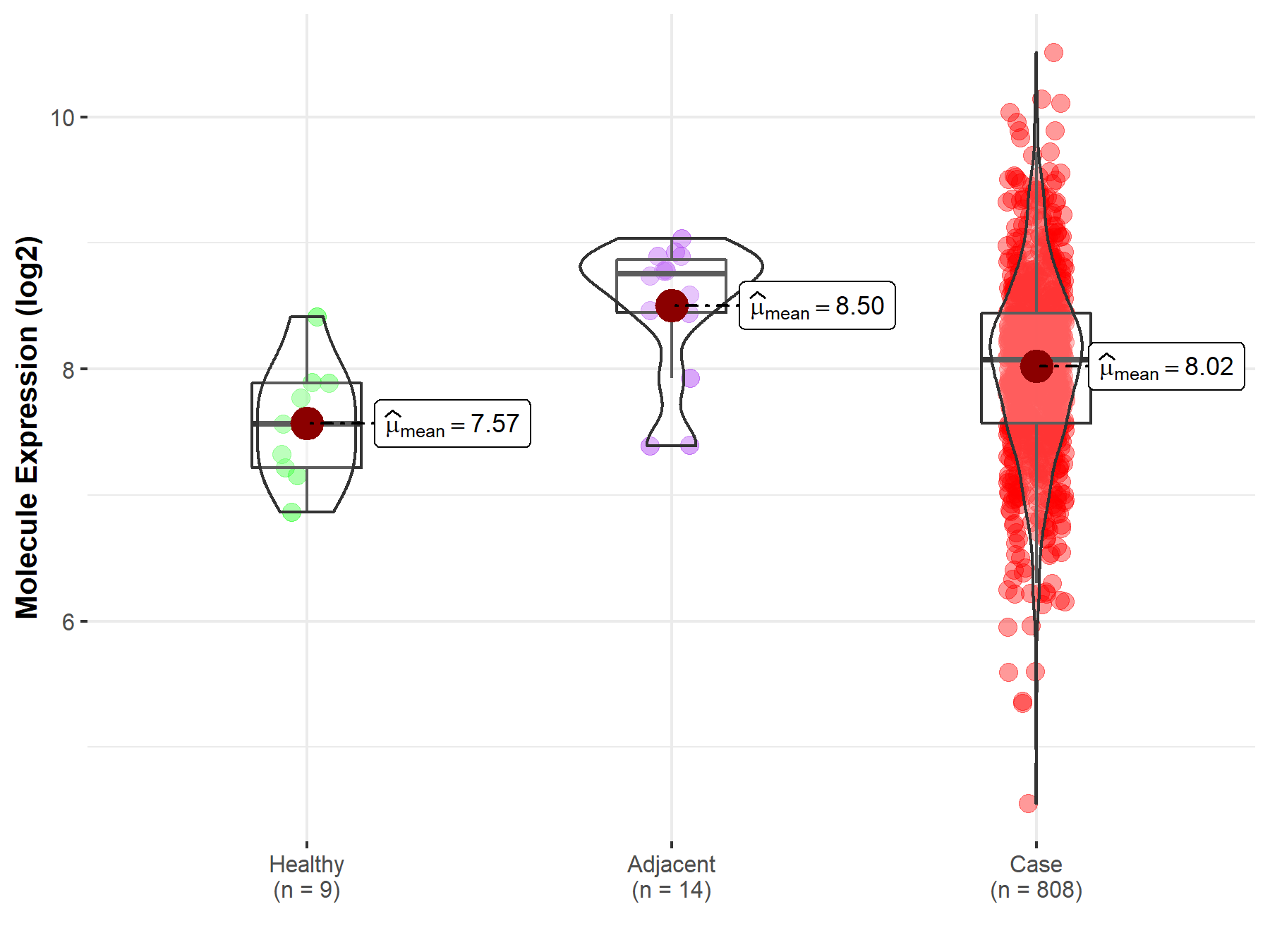
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

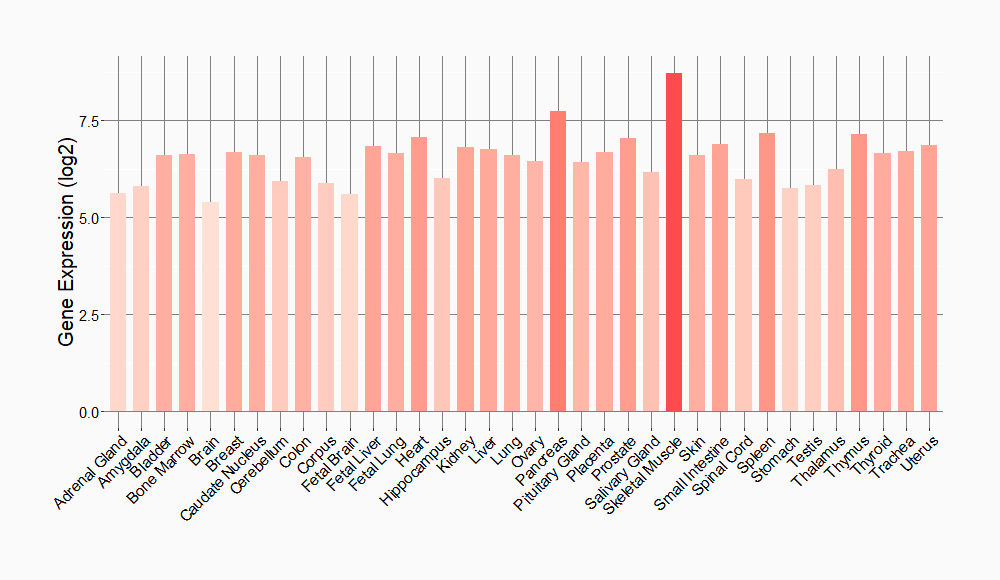
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
