Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00404)
| Name |
Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
HD1; Protein deacetylase HDAC1; Protein decrotonylase HDAC1; RPD3L1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
HDAC1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr1:32292083-32333635[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAQTQGTRRKVCYYYDGDVGNYYYGQGHPMKPHRIRMTHNLLLNYGLYRKMEIYRPHKAN
AEEMTKYHSDDYIKFLRSIRPDNMSEYSKQMQRFNVGEDCPVFDGLFEFCQLSTGGSVAS AVKLNKQQTDIAVNWAGGLHHAKKSEASGFCYVNDIVLAILELLKYHQRVLYIDIDIHHG DGVEEAFYTTDRVMTVSFHKYGEYFPGTGDLRDIGAGKGKYYAVNYPLRDGIDDESYEAI FKPVMSKVMEMFQPSAVVLQCGSDSLSGDRLGCFNLTIKGHAKCVEFVKSFNLPMLMLGG GGYTIRNVARCWTYETAVALDTEIPNELPYNDYFEYFGPDFKLHISPSNMTNQNTNEYLE KIKQRLFENLRMLPHAPGVQMQAIPEDAIPEESGDEDEDDPDKRISICSSDKRIACEEEF SDSEEEGEGGRKNSSNFKKAKRVKTEDEKEKDPEEKKEVTEEEKTKEEKPEAKGVKEEVK LA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Histone deacetylase that catalyzes the deacetylation of lysine residues on the N-terminal part of the core histones (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4). Histone deacetylation gives a tag for epigenetic repression and plays an important role in transcriptional regulation, cell cycle progression and developmental events. Histone deacetylases act via the formation of large multiprotein complexes. Also functions as deacetylase for non-histone targets, such as NR1D2, RELA, SP1, SP3 and TSHZ3. Deacetylates SP proteins, SP1 and SP3, and regulates their function. Component of the BRG1-RB1-HDAC1 complex, which negatively regulates the CREST-mediated transcription in resting neurons. Upon calcium stimulation, HDAC1 is released from the complex and CREBBP is recruited, which facilitates transcriptional activation. Deacetylates TSHZ3 and regulates its transcriptional repressor activity. Deacetylates 'Lys-310' in RELA and thereby inhibits the transcriptional activity of NF-kappa-B. Deacetylates NR1D2 and abrogates the effect of KAT5-mediated relieving of NR1D2 transcription repression activity. Component of a RCOR/GFI/KDM1A/HDAC complex that suppresses, via histone deacetylase (HDAC) recruitment, a number of genes implicated in multilineage blood cell development. Involved in CIART-mediated transcriptional repression of the circadian transcriptional activator: CLOCK-ARNTL/BMAL1 heterodimer. Required for the transcriptional repression of circadian target genes, such as PER1, mediated by the large PER complex or CRY1 through histone deacetylation. In addition to protein deacetylase activity, also has protein-lysine deacylase activity: acts as a protein decrotonylase by mediating decrotonylation ((2E)-butenoyl) of histones.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Palbociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.67E-33 Fold-change: 6.64E-02 Z-score: 1.32E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Although the involvement of HDAC in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is currently unknown, inhibition of HDAC may increase the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells by activating p21, resulting in cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M phases, as demonstrated in CDK4/6 inhibitor-sensitive cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| OVCA433 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0475 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Soft agar colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-34a exhibited suppressive effects on OC cells via directly binding and downregulating HDAC1 expression, which subsequently decreased the resistance to cisplatin and suppressed proliferation in OC cells. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MkN-45 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0434 |
| MkN28 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1416 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-520h is up-regulated by doxorubicin to target HDAC1 and sensitizes gastric cancer cells to doxorubicin, doxorubicin down-regulates HDAC1 expression to aggravate DNA-doxorubicin interaction by inducing the expression of HDAC1-targeting miR-520h. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | LY2835219 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Although the involvement of HDAC in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is currently unknown, inhibition of HDAC may increase the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells by activating p21, resulting in cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M phases, as demonstrated in CDK4/6 inhibitor-sensitive cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ribociclib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Although the involvement of HDAC in resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors is currently unknown, inhibition of HDAC may increase the efficacy of CDK4/6 inhibitors in CDK4/6 inhibitor-resistant cells by activating p21, resulting in cell cycle arrest at the G1 and G2/M phases, as demonstrated in CDK4/6 inhibitor-sensitive cells. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.29E-01; Fold-change: 6.89E-01; Z-score: 1.26E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.56E-02; Fold-change: 1.53E-01; Z-score: 4.20E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.67E-33; Fold-change: 4.92E-01; Z-score: 9.29E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.33E-09; Fold-change: 5.50E-01; Z-score: 1.13E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
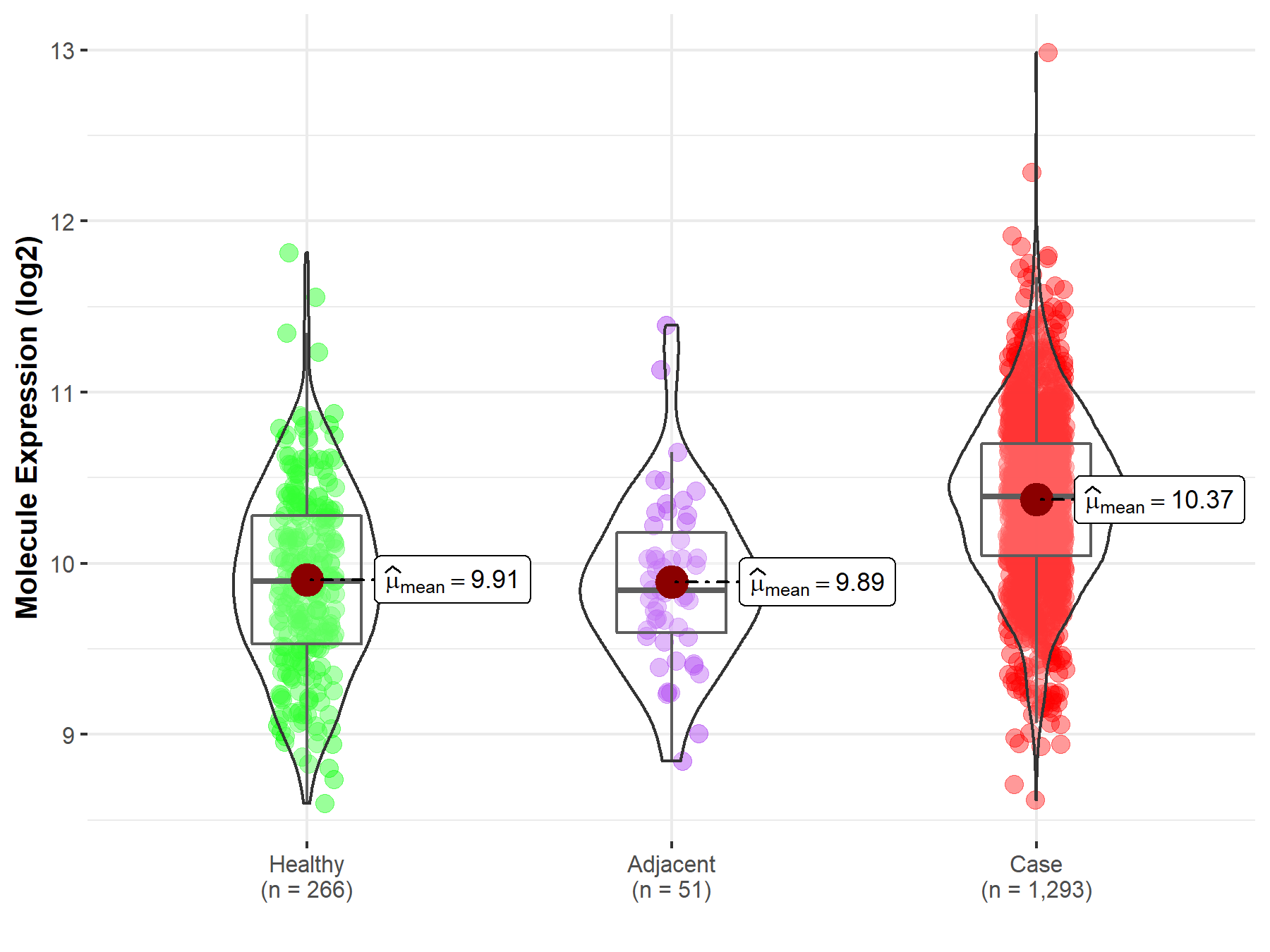
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.88E-01; Fold-change: 1.16E-01; Z-score: 3.34E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 6.96E-01; Fold-change: 4.28E-02; Z-score: 7.08E-02 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
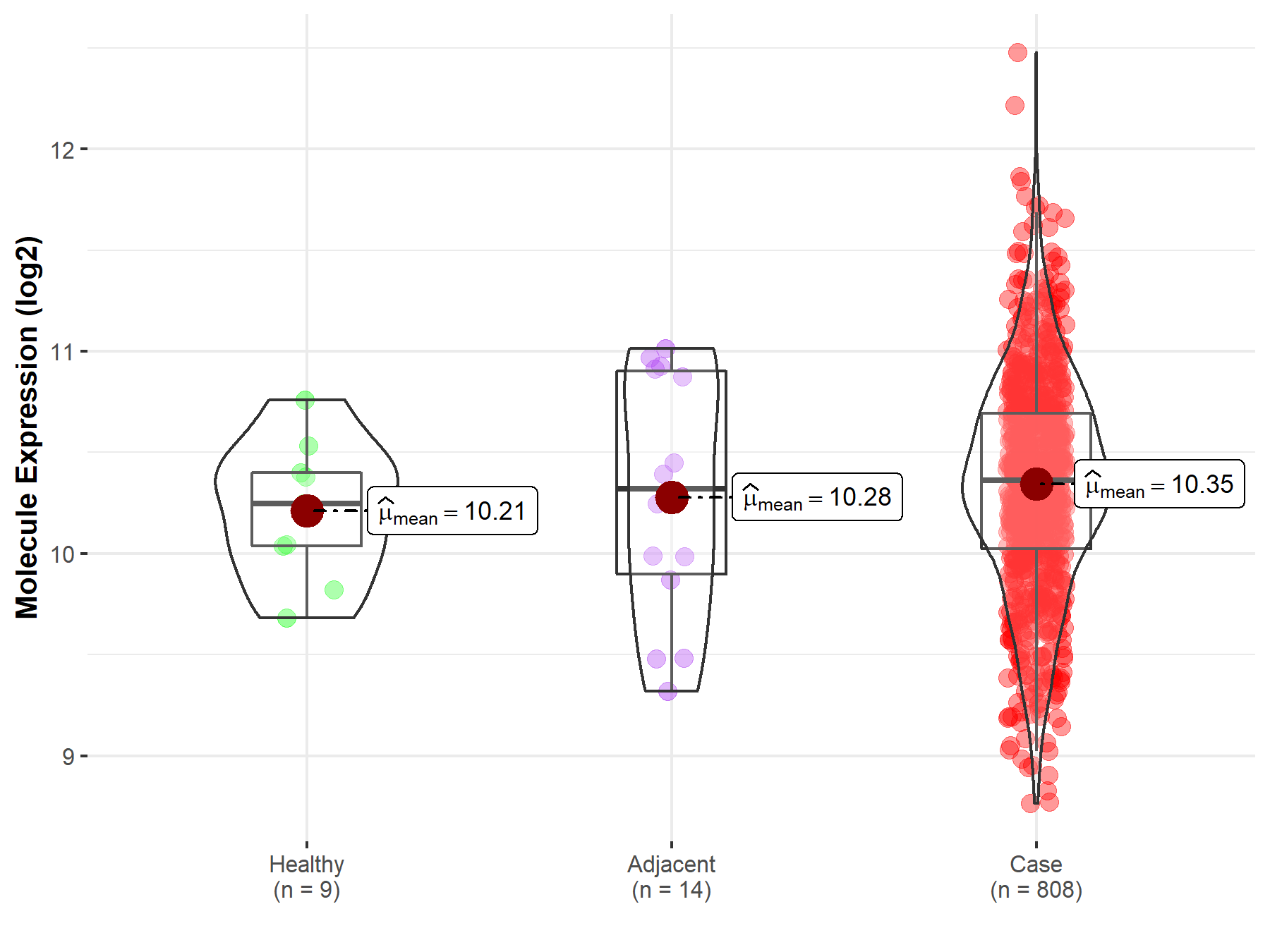
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

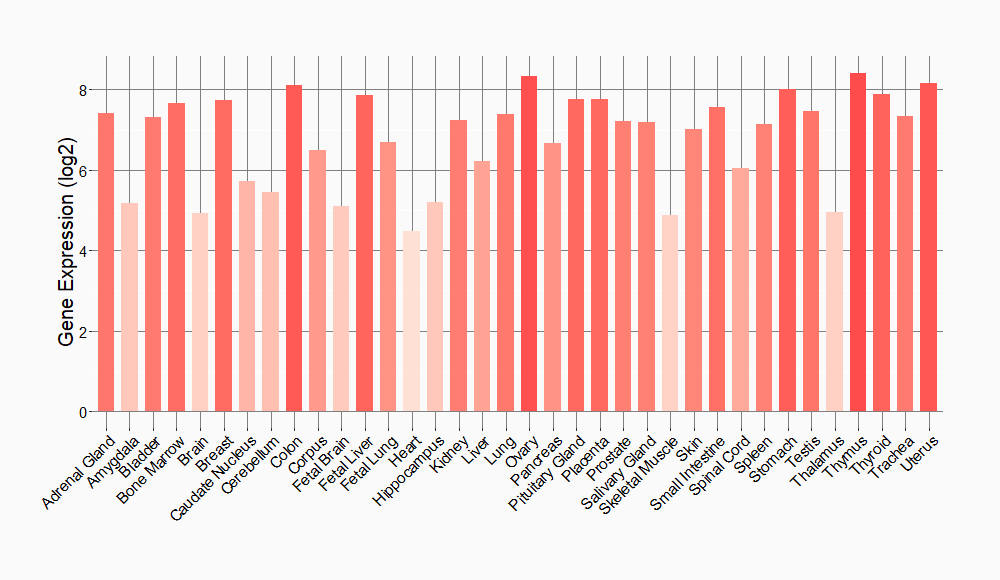
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
