Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00394)
| Name |
G-protein coupled estrogen receptor 1 (GPER1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Chemoattractant receptor-like 2; Flow-induced endothelial G-protein coupled receptor 1; FEG-1; G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1; G-protein coupled receptor 30; GPCR-Br; IL8-related receptor DRY12; Lymphocyte-derived G-protein coupled receptor; LYGPR; Membrane estrogen receptor; mER; CEPR; CMKRL2; DRY12; GPER; GPR30
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
GPER1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr7:1082208-1093815[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDVTSQARGVGLEMYPGTAQPAAPNTTSPELNLSHPLLGTALANGTGELSEHQQYVIGLF
LSCLYTIFLFPIGFVGNILILVVNISFREKMTIPDLYFINLAVADLILVADSLIEVFNLH ERYYDIAVLCTFMSLFLQVNMYSSVFFLTWMSFDRYIALARAMRCSLFRTKHHARLSCGL IWMASVSATLVPFTAVHLQHTDEACFCFADVREVQWLEVTLGFIVPFAIIGLCYSLIVRV LVRAHRHRGLRPRRQKALRMILAVVLVFFVCWLPENVFISVHLLQRTQPGAAPCKQSFRH AHPLTGHIVNLAAFSNSCLNPLIYSFLGETFRDKLRLYIEQKTNLPALNRFCHAALKAVI PDSTEQSDVRFSSAV Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
G-protein coupled estrogen receptor that binds to 17-beta-estradiol (E2) with high affinity, leading to rapid and transient activation of numerous intracellular signaling pathways. Stimulates cAMP production, calcium mobilization and tyrosine kinase Src inducing the release of heparin-bound epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) and subsequent transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), activating downstream signaling pathways such as PI3K/Akt and ERK/MAPK. Mediates pleiotropic functions among others in the cardiovascular, endocrine, reproductive, immune and central nervous systems. Has a role in cardioprotection by reducing cardiac hypertrophy and perivascular fibrosis in a RAMP3-dependent manner. Regulates arterial blood pressure by stimulating vasodilation and reducing vascular smooth muscle and microvascular endothelial cell proliferation. Plays a role in blood glucose homeostasis contributing to the insulin secretion response by pancreatic beta cells. Triggers mitochondrial apoptosis during pachytene spermatocyte differentiation. Stimulates uterine epithelial cell proliferation. Enhances uterine contractility in response to oxytocin. Contributes to thymic atrophy by inducing apoptosis. Attenuates TNF-mediated endothelial expression of leukocyte adhesion molecules. Promotes neuritogenesis in developing hippocampal neurons. Plays a role in acute neuroprotection against NMDA-induced excitotoxic neuronal death. Increases firing activity and intracellular calcium oscillations in luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) neurons. Inhibits early osteoblast proliferation at growth plate during skeletal development. Inhibits mature adipocyte differentiation and lipid accumulation. Involved in the recruitment of beta-arrestin 2 ARRB2 at the plasma membrane in epithelial cells. Functions also as a receptor for aldosterone mediating rapid regulation of vascular contractibility through the PI3K/ERK signaling pathway. Involved in cancer progression regulation. Stimulates cancer-associated fibroblast (CAF) proliferation by a rapid genomic response through the EGFR/ERK transduction pathway. Associated with EGFR, may act as a transcription factor activating growth regulatory genes (c-fos, cyclin D1). Promotes integrin alpha-5/beta-1 and fibronectin (FN) matrix assembly in breast cancer cells.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: ER negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.7] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | ER negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.7] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Calycosin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell growth | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| WDR7-7/GPR30 signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| SkBR3 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0033 | |
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | |
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | |
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | |
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Luciferase reporter assay; Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Calycosin inhibited the proliferation of breast cancer cells through WDR7-7-GPR30 signaling. WDR7-7 overexpression led to the inhibition of the GPR30-mediated phosphorylation of SRC, EGFR, ERk1/2, and Akt, ultimately resulting in reduced cell growth, which are key regulators of cell proliferation and survival in breast cancer cells, act as downstream effectors of the WDR7-7-GPR30 pathway. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.38E-42; Fold-change: -6.48E-01; Z-score: -1.13E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.37E-05; Fold-change: -3.86E-01; Z-score: -5.61E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
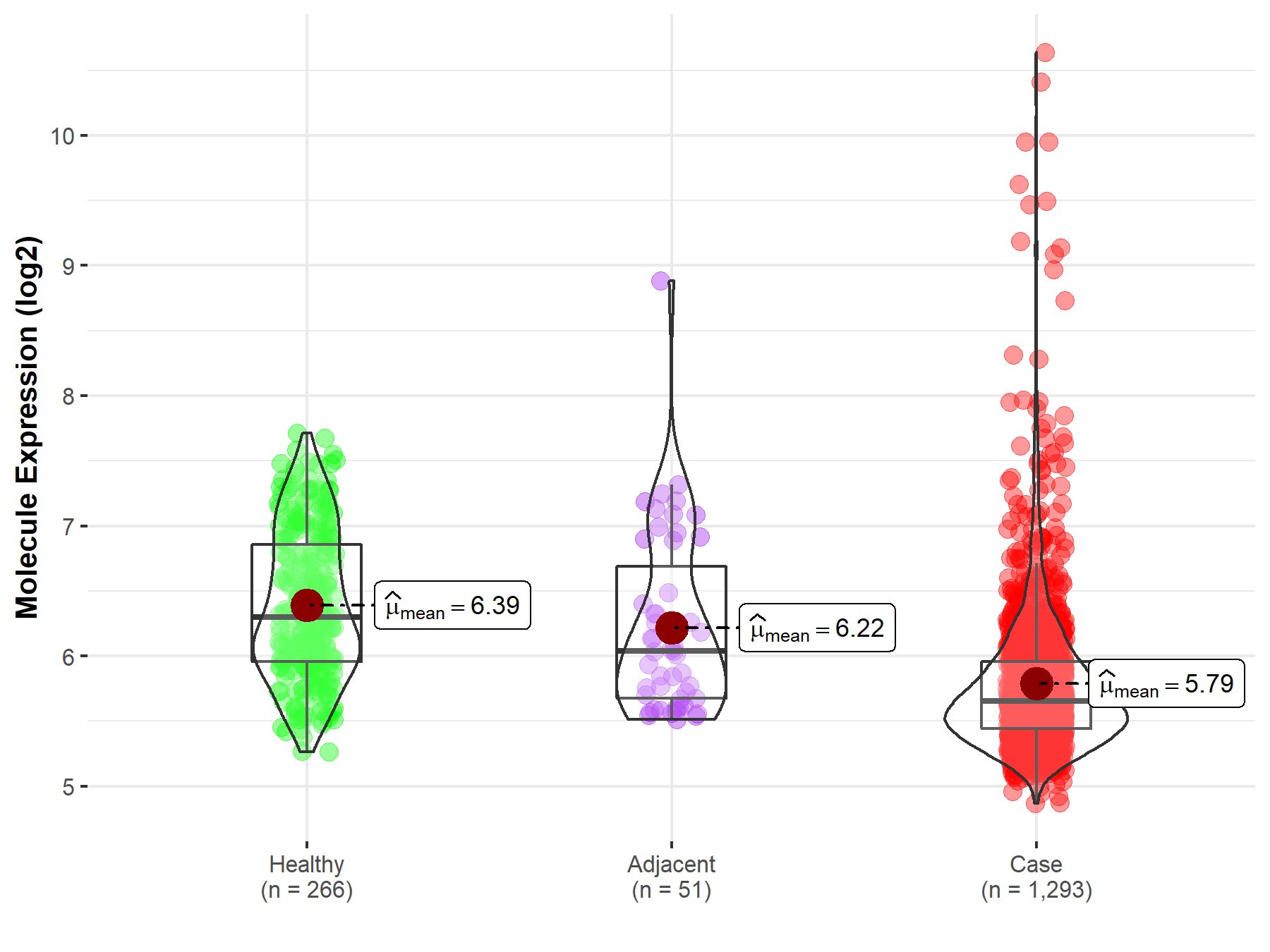
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

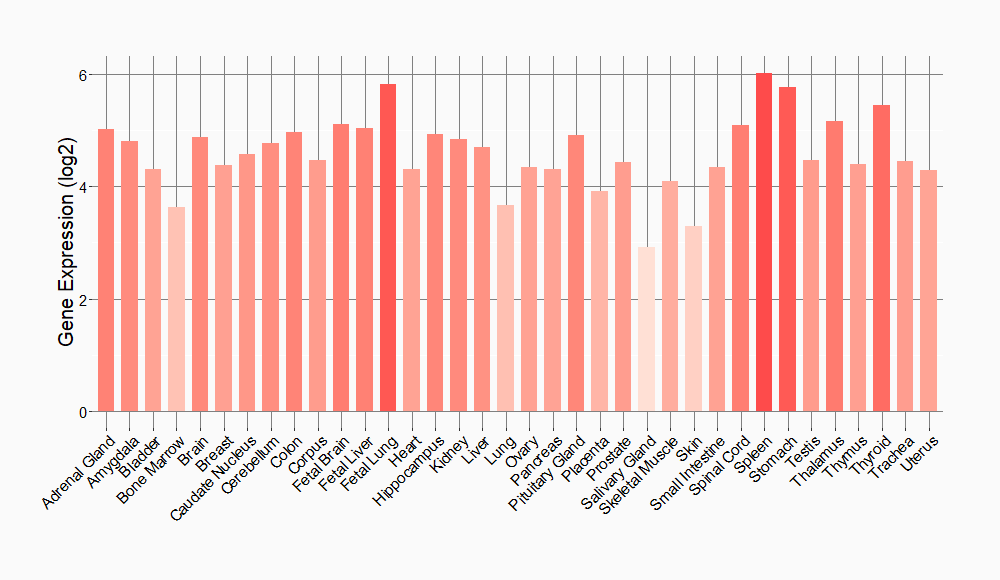
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
