Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00317)
| Name |
Deoxycytidine kinase (DCK)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
dCK; Deoxyadenosine kinase; Deoxyguanosine kinase
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
DCK
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr4:70992538-71030914[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MATPPKRSCPSFSASSEGTRIKKISIEGNIAAGKSTFVNILKQLCEDWEVVPEPVARWCN
VQSTQDEFEELTMSQKNGGNVLQMMYEKPERWSFTFQTYACLSRIRAQLASLNGKLKDAE KPVLFFERSVYSDRYIFASNLYESECMNETEWTIYQDWHDWMNNQFGQSLELDGIIYLQA TPETCLHRIYLRGRNEEQGIPLEYLEKLHYKHESWLLHRTLKTNFDYLQEVPILTLDVNE DFKDKYESLVEKVKEFLSTL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Phosphorylates the deoxyribonucleosides deoxycytidine, deoxyguanosine and deoxyadenosine. Has broad substrate specificity, and does not display selectivity based on the chirality of the substrate. It is also an essential enzyme for the phosphorylation of numerous nucleoside analogs widely employed as antiviral and chemotherapeutic agents.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.56E-05 Fold-change: 3.46E-02 Z-score: 4.41E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | |
| SW1573 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1720 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT -PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamide B (SRB) test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Deoxycytidine kinase (dCk) is essential for phosphorylation of natural deoxynucleosides andanalogs, such as gemcitabine and cytarabine, two widely used anticancer compounds. miR-330 expression negatively correlated withdCk mRNA expression, suggesting a role of miR-330 in post-transcriptional regulationof dCk. Expression of miR-330 in various colon and lung cancer cell lines,as measured by QRT-PCR, varied five-fold between samples and correlated with in-vitro gemcitabineresistance. | |||
| Disease Class: Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Colon cancer [ICD-11: 2B90] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.10E-05 Fold-change: 3.16E-02 Z-score: 4.49E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 |
| Colo320 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1989 | |
| WiDR cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2760 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT -PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamide B (SRB) test assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Deoxycytidine kinase (dCk) is essential for phosphorylation of natural deoxynucleosides andanalogs, such as gemcitabine and cytarabine, two widely used anticancer compounds. miR-330 expression negatively correlated withdCk mRNA expression, suggesting a role of miR-330 in post-transcriptional regulationof dCk. Expression of miR-330 in various colon and lung cancer cell lines,as measured by QRT-PCR, varied five-fold between samples and correlated with in-vitro gemcitabineresistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C10.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gemcitabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Once taken up into the cell, gemcitabine is phosphorylated by deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) to produce dFdCMP. In turn, dFdCMP is converted by other pyrimidine kinases to its active diphosphate and triphosphate derivatives, dFdCDP and dFdCTP. Due to the central role of dCK in gemcitabine metabolism, its deficiency is a major contributor to gemcitabine resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cladribine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Staphylococcus aureus strain | 1280 | ||
| Mechanism Description | Cladribine cannot be deaminated by adenosine deaminase(ADA) and is phosphorylated to cladribine-MP by dCK. Cladribine self potentiates its own activation by activation of dCK. The cytotoxicity mainly depends on the accumulation of cladribine-TP after phosphoryl-ation of cladribine-MP by nucleoside MP kinase and nucleoside diphosphate kinase in the cells. Down regulation of all activating enzymes such as dCK or dGK due to loss of expression or through mutation, has been shown to cause resistance to cladribine. However, the most frequently described form of acquired resistance to cladribine in vitro is dCK de ciency and reduction in dCK activity is probably the major determinant of cladribine resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cytarabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Jurkat cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0065 |
| Nalm-6 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0092 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Real-time quantitative PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Low-concentration cytarabine (Ara-C) continuously induced and cultured Jurkat and Nalm-6 cells to construct cytarabine-resistant cell lines Jurkat/Ara-C and Nalm-6/Ara-C. The results of real-time quantitative PCR showed that the expression of deoxycytidine kinase (DCk) and cytidine deaminase (CDA) were significantly down-regulated in drug-resistant cells (P<0.05). | |||
| Disease Class: Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.6] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cytarabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Deoxycitidine kinase plays a pivotal role since phosphorylation of cytarabine preserves intracellular retention of the drug and prevents from inactivation to its uridine derivative, uracil arabinoside, by cytidine deaminase. The intracellular accumulation of cytarabine triphosphate, the active cytotoxic metabolite, is proportional to the cellular DCk level which has led to the conclusion that DCk enzyme retains a rate-limiting role for the activation of cytarabine. | |||
| Disease Class: Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A90- 2A85] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cytarabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | Deoxycitidine kinase plays a pivotal role since phosphorylation of cytarabine preserves intracellular retention of the drug and prevents from inactivation to its uridine derivative, uracil arabinoside, by cytidine deaminase. The intracellular accumulation of cytarabine triphosphate, the active cytotoxic metabolite, is proportional to the cellular DCk level which has led to the conclusion that DCk enzyme retains a rate-limiting role for the activation of cytarabine. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Tonsil tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Lymphoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.39E-01; Fold-change: 2.33E-01; Z-score: 3.09E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
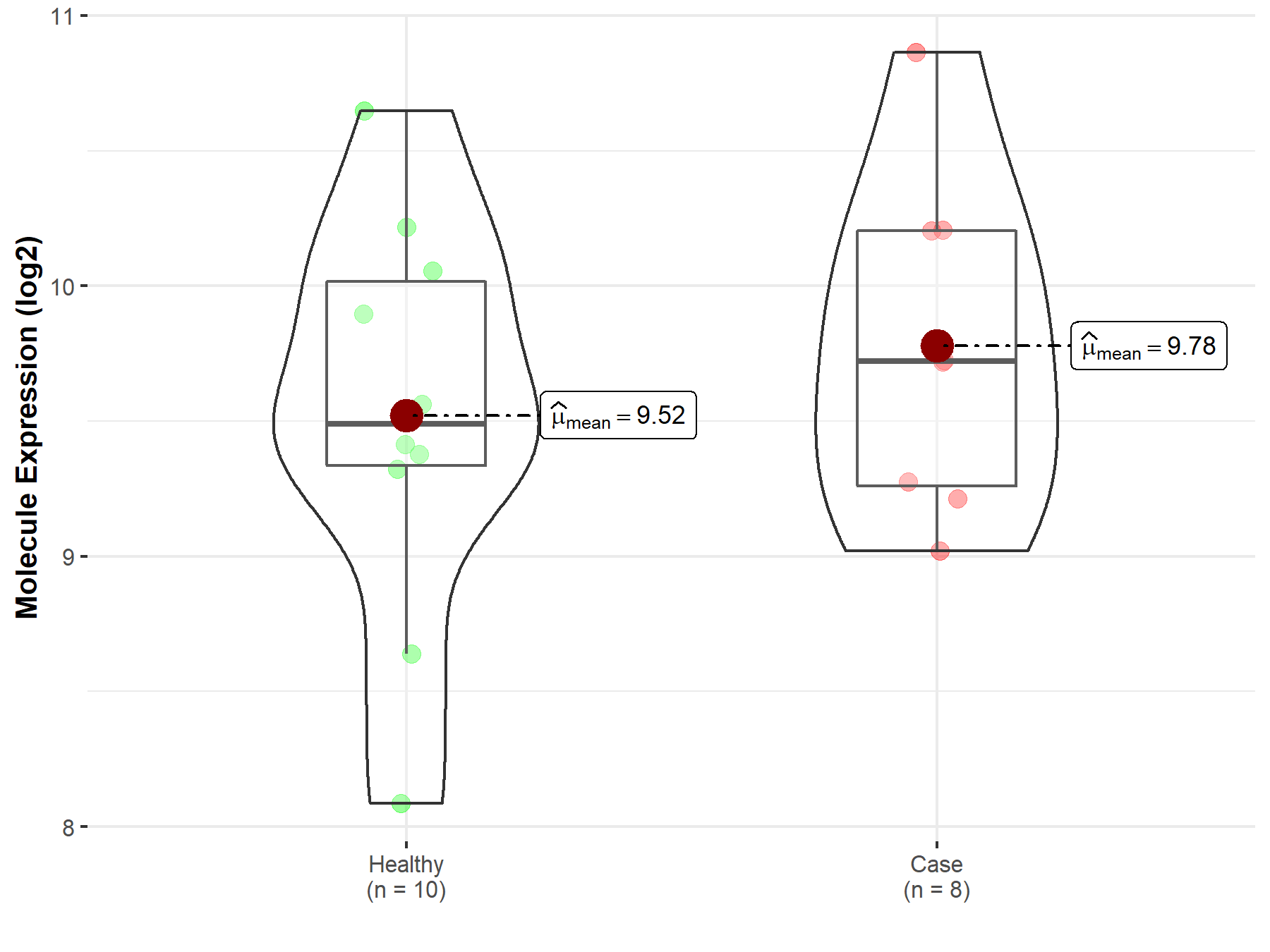
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Colon | |
| The Specified Disease | Colon cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.10E-05; Fold-change: 2.01E-01; Z-score: 4.47E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.34E-01; Fold-change: 1.40E-01; Z-score: 2.14E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pancreas | |
| The Specified Disease | Pancreatic cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.40E-02; Fold-change: 6.67E-01; Z-score: 5.94E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.40E-02; Fold-change: 6.58E-01; Z-score: 6.18E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.56E-05; Fold-change: 8.91E-02; Z-score: 1.55E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.35E-22; Fold-change: 4.71E-01; Z-score: 1.04E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals


|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
