Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00224)
| Name |
ALK tyrosine kinase receptor (ALK)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ALK
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr2:29192774-29921586[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MGAIGLLWLLPLLLSTAAVGSGMGTGQRAGSPAAGPPLQPREPLSYSRLQRKSLAVDFVV
PSLFRVYARDLLLPPSSSELKAGRPEARGSLALDCAPLLRLLGPAPGVSWTAGSPAPAEA RTLSRVLKGGSVRKLRRAKQLVLELGEEAILEGCVGPPGEAAVGLLQFNLSELFSWWIRQ GEGRLRIRLMPEKKASEVGREGRLSAAIRASQPRLLFQIFGTGHSSLESPTNMPSPSPDY FTWNLTWIMKDSFPFLSHRSRYGLECSFDFPCELEYSPPLHDLRNQSWSWRRIPSEEASQ MDLLDGPGAERSKEMPRGSFLLLNTSADSKHTILSPWMRSSSEHCTLAVSVHRHLQPSGR YIAQLLPHNEAAREILLMPTPGKHGWTVLQGRIGRPDNPFRVALEYISSGNRSLSAVDFF ALKNCSEGTSPGSKMALQSSFTCWNGTVLQLGQACDFHQDCAQGEDESQMCRKLPVGFYC NFEDGFCGWTQGTLSPHTPQWQVRTLKDARFQDHQDHALLLSTTDVPASESATVTSATFP APIKSSPCELRMSWLIRGVLRGNVSLVLVENKTGKEQGRMVWHVAAYEGLSLWQWMVLPL LDVSDRFWLQMVAWWGQGSRAIVAFDNISISLDCYLTISGEDKILQNTAPKSRNLFERNP NKELKPGENSPRQTPIFDPTVHWLFTTCGASGPHGPTQAQCNNAYQNSNLSVEVGSEGPL KGIQIWKVPATDTYSISGYGAAGGKGGKNTMMRSHGVSVLGIFNLEKDDMLYILVGQQGE DACPSTNQLIQKVCIGENNVIEEEIRVNRSVHEWAGGGGGGGGATYVFKMKDGVPVPLII AAGGGGRAYGAKTDTFHPERLENNSSVLGLNGNSGAAGGGGGWNDNTSLLWAGKSLQEGA TGGHSCPQAMKKWGWETRGGFGGGGGGCSSGGGGGGYIGGNAASNNDPEMDGEDGVSFIS PLGILYTPALKVMEGHGEVNIKHYLNCSHCEVDECHMDPESHKVICFCDHGTVLAEDGVS CIVSPTPEPHLPLSLILSVVTSALVAALVLAFSGIMIVYRRKHQELQAMQMELQSPEYKL SKLRTSTIMTDYNPNYCFAGKTSSISDLKEVPRKNITLIRGLGHGAFGEVYEGQVSGMPN DPSPLQVAVKTLPEVCSEQDELDFLMEALIISKFNHQNIVRCIGVSLQSLPRFILLELMA GGDLKSFLRETRPRPSQPSSLAMLDLLHVARDIACGCQYLEENHFIHRDIAARNCLLTCP GPGRVAKIGDFGMARDIYRASYYRKGGCAMLPVKWMPPEAFMEGIFTSKTDTWSFGVLLW EIFSLGYMPYPSKSNQEVLEFVTSGGRMDPPKNCPGPVYRIMTQCWQHQPEDRPNFAIIL ERIEYCTQDPDVINTALPIEYGPLVEEEEKVPVRPKDPEGVPPLLVSQQAKREEERSPAA PPPLPTTSSGKAAKKPTAAEISVRVPRGPAVEGGHVNMAFSQSNPPSELHKVHGSRNKPT SLWNPTYGSWFTEKPTKKNNPIAKKEPHDRGNLGLEGSCTVPPNVATGRLPGASLLLEPS SLTANMKEVPLFRLRHFPCGNVNYGYQQQGLPLEAATAPGAGHYEDTILKSKNSMNQPGP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Neuronal receptor tyrosine kinase that is essentially and transiently expressed in specific regions of the central and peripheral nervous systems and plays an important role in the genesis and differentiation of the nervous system. Transduces signals from ligands at the cell surface, through specific activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. Phosphorylates almost exclusively at the first tyrosine of the Y-x-x-x-Y-Y motif. Following activation by ligand, ALK induces tyrosine phosphorylation of CBL, FRS2, IRS1 and SHC1, as well as of the MAP kinases MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1. Acts as a receptor for ligands pleiotrophin (PTN), a secreted growth factor, and midkine (MDK), a PTN-related factor, thus participating in PTN and MDK signal transduction. PTN-binding induces MAPK pathway activation, which is important for the anti-apoptotic signaling of PTN and regulation of cell proliferation. MDK-binding induces phosphorylation of the ALK target insulin receptor substrate (IRS1), activates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and PI3-kinase, resulting also in cell proliferation induction. Drives NF-kappa-B activation, probably through IRS1 and the activation of the AKT serine/threonine kinase. Recruitment of IRS1 to activated ALK and the activation of NF-kappa-B are essential for the autocrine growth and survival signaling of MDK. Thinness gene involved in the resistance to weight gain: in hypothalamic neurons, controls energy expenditure acting as a negative regulator of white adipose tissue lipolysis and sympathetic tone to fine-tune energy homeostasis (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NBLW cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ90 | |||||||||
| NBLW-R cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ91 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sangersequencing assay; Targeted deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Array CGH assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the sensitivity of NBLW and NBLW-R cells to a panel of ALk inhibitors (TAE-684, Crizotinib, Alectinib and Lorlatinib) revealed differences between the paired cell lines, and overall NBLW-R cells with the F1174L mutation were more resistant to ALk inhibitor induced apoptosis compared with NBLW cells. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [2], [3] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Positron emission tomography assay; Computed tomography assay; Analysis of progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Here, we report a patient with NSCLC harboring a novel HIP1-ALk fusion variant (H30; A20). This patient and another patient with EML4-ALk variant 3a/b initially responded sequentially to crizotinib and then alectinib, a next-generation ALk inhibitor, but developed acquired resistance to alectinib with the presence of a mutation in amino acid residue 1171 (I1171N and I1171S respectively) located in the hydrophobic regulatory spine (R-spine) of the ALk kinase in both the cases. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay; Whole genome sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Some acquired ALk mutations may cause co-resistance to other ALk inhibitors. Re-biopsy for ALk mutation analysis might be suggested prior to choosing a second-line ALk inhibitor treatment. A special mutation, G1202R, was resistant to crizotinib as well as to alectinib and ceritinib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171N |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR assay; Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Although an in vitro mutagenesis screen identified I1171T in the ALk gene, mutations at codon 1171, which is located in the vicinity of the kinase DFG (Asp-Phe-Gly) motif of the activation loop, have yet to be identified in patients with ALk-rearranged NSCLC who have acquired resistance to ALk inhibitors. In addition, in vitro analyses howed that I1171T and I1171N confer resistance to crizotinib. In addition to the novel finding of mutations at I1171 in ALk-rearranged patients, it is intriguing that mutations at I1171 confer resistance to both crizotinib and alectinib, which is a representative second-generation ALk inhibitor. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1180L |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | We identified a novel V1180L gatekeeper mutation from the cell line model and a second novel I1171T mutation from the patient who developed resistance to alectinib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | A novel, secondary mutation in ALK exon 23 (L1196Q) was identified in patient 1 after alectinib resistance developed. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor [ICD-11: 2E92.1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Alectinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196Q |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | A novel, secondary mutation in ALK exon 23 (L1196Q) was identified in patient 1 after alectinib resistance developed. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Brigatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R (c.3604G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Thymidine Incorporation assay | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1269A (c.3806G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
1070
|
-
M
-
A
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
D
-
Y
1080
|
-
G
-
I
-
P
-
T
-
T
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
1090
|
-
Q
-
G
-
S
-
N
M
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
A
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
L
V
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| PC12 cells | Adrenal gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0481 | ||||||||||
| CLB-PE cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9534 | ||||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196M (c.3586C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.66 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L (c.3520T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F1174L (c.3520T>C) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.V1180L (c.3538G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | PC9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_B260 | |||||||||
| NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1128A (c.3383G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G1128A (c.3383G>C) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171N (c.3512T>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.I1171N (c.3512T>A) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R1192P (c.3575G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R1192P (c.3575G>C) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1245C (c.3734T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F1245C (c.3734T>G) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R1275Q (c.3824G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R1275Q (c.3824G>A) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y1278S (c.3833A>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y1278S (c.3833A>C) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Brigatinib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Brigatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174V (c.3520T>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| PC12 cells | Adrenal gland | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | CVCL_0481 | ||||||||||
| CLB-PE cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9534 | ||||||||||
| CLB-GE cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9530 | ||||||||||
| CLB-BAR cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_9519 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female Balbc/nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunohistochemistry assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Resazurin disc test assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) is a tyrosine kinase receptor which has been implicated in numerous solid and hematologic cancers. Brigatinib is an effective inhibitor of ALK kinase activity in ALK addicted neuroblastoma | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ceritinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.66 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ceritinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ceritinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174V |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ceritinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [12] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Ceritinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1123S |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computed tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Identification of a Novel ALk G1123S Mutation in a Patient with ALk-rearranged Non-small-cell Lung Cancer Exhibiting Resistance to Ceritinib. The present report showed that therapy with alectinib may overcome ceritinib resistance through the G1123S mutation, a novel and effective sequential use of ALk inhibitors. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11], [13], [14] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1269A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
1070
|
-
M
-
A
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
D
-
Y
1080
|
-
G
-
I
-
P
-
T
-
T
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
1090
|
-
Q
-
G
-
S
-
N
M
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
A
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
L
V
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay; Pyrosequencing analysis; Droplet digital PCR assay; Next generation deep sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay; Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay; Analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) assay; Computerized tomography assay; Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. By applying a base-pair specific error-weighted mutation calling algorithm (BASCA) that we developed for this assay, genomic DNA analysis from thirteen relapsed patients revealed three known crizotinib resistance mutations, C1156Y, L1196M and G1269A. Our assay demonstrates robust and sensitive detection of ALk kinase mutations in NSCLC tumor samples and aids in the elucidation of resistance mechanisms pertinent to the clinical setting. Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [15], [16] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1269A |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.70 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
1070
|
-
M
-
A
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
D
-
Y
1080
|
-
G
-
I
-
P
-
T
-
T
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
Y
-
F
1090
|
-
Q
-
G
-
S
-
N
M
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
A
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
L
V
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H2228 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1543 | |||||||||
| NCI-H3122 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5160 | ||||||||||
| SNU-2535 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_R756 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay; Digital droplet PCR assay; Sanger sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Progression-free survival (PFS) assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Three patients harbored secondary ALk mutations, including one patient with both mutations: L1196M (n = 2) and G1269A (n = 2). Genetic changes associated with crizotinib resistance are heterogeneous in ALk-rearranged NSCLC patients who respond to crizotinib and subsequently develop resistance. ALk-dependent mechanisms include gatekeeper (L1196M) or other mutations such as C1156Y and G1269A in the ALk kinase domain and ALk copy number gain. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.66 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. By applying a base-pair specific error-weighted mutation calling algorithm (BASCA) that we developed for this assay, genomic DNA analysis from thirteen relapsed patients revealed three known crizotinib resistance mutations, C1156Y, L1196M and G1269A. Our assay demonstrates robust and sensitive detection of ALk kinase mutations in NSCLC tumor samples and aids in the elucidation of resistance mechanisms pertinent to the clinical setting. Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. In contrast, cells expressing either the C1156Y or L1196M mutant form manifested a markedly reduced sensitivity to the drug. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18], [15] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.L1196M |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.66 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
M
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H2228 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1543 | |||||||||
| NCI-H3122 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5160 | ||||||||||
| SNU-2535 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_R756 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay; Sanger dideoxynucleotide sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Three patients harbored secondary ALk mutations, including one patient with both mutations: L1196M (n = 2) and G1269A (n = 2). Genetic changes associated with crizotinib resistance are heterogeneous in ALk-rearranged NSCLC patients who respond to crizotinib and subsequently develop resistance. In 1 of the 15 cases examined, ALk FISH revealed high-level gene amplification. No ALk resistance mutations were found in this specimen, so it appears that high-level amplification of the wild-type ALk fusion gene is sufficient to cause resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NBLW cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ90 | |||||||||
| NBLW-R cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ91 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sangersequencing assay; Targeted deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Array CGH assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the sensitivity of NBLW and NBLW-R cells to a panel of ALk inhibitors (TAE-684, Crizotinib, Alectinib and Lorlatinib) revealed differences between the paired cell lines, and overall NBLW-R cells with the F1174L mutation were more resistant to ALk inhibitor induced apoptosis compared with NBLW cells. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C1156Y |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
Y
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Digital droplet PCR assay; Sanger sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | ALk-dependent mechanisms include gatekeeper (L1196M) or other mutations such as C1156Y and G1269A in the ALk kinase domain and ALk copy number gain. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [13], [19], [20] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C1156Y |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
Y
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Liquid biopsy assay; Next-generation sequencing assay; Circulating-free DNA assay; Digital PCR assay; Pyrosequencing analysis; Droplet digital PCR assay; Next generation deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Analysis of progression-free survival (PFS) assay; Overall and disease-free assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In contrast, cells expressing either the C1156Y or L1196M mutant form manifested a markedly reduced sensitivity to the drug (23836314; 20979470). By applying a base-pair specific error-weighted mutation calling algorithm (BASCA) that we developed for this assay, genomic DNA analysis from thirteen relapsed patients revealed three known crizotinib resistance mutations, C1156Y, L1196M and G1269A. Our assay demonstrates robust and sensitive detection of ALk kinase mutations in NSCLC tumor samples and aids in the elucidation of resistance mechanisms pertinent to the clinical setting. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [11], [14], [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S1206Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay; Computerized tomography assay; Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. Non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) harboring anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALk) gene rearrangements invariably develop resistance to the ALk tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TkI) crizotinib. In particular, ceritinib effectively inhibits ALk harboring L1196M, G1269A, I1171T and S1206Y mutations, and a co-crystal of ceritinib bound to ALk provides structural bases for this increased potency. Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [14], [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174C |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | JAKT/STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | ALCL cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughout experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
X-ray tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The L1196M gatekeeper mutation is the most common ALk mutation conferring crizotinib resistance while other resistance mutations include I1171T, F1174C, G1202R, S1206Y, and G1269A. The drugs bind to an inactive enzyme and they do not extend past the gatekeeper into the back pocket of the drug binding site. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T1151_L1152insT |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger dideoxynucleotide sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In 1 of the 15 cases examined, ALk FISH revealed high-level gene amplification. No ALk resistance mutations were found in this specimen, so it appears that high-level amplification of the wild-type ALk fusion gene is sufficient to cause resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S1206Y |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger dideoxynucleotide sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In 1 of the 15 cases examined, ALk FISH revealed high-level gene amplification. No ALk resistance mutations were found in this specimen, so it appears that high-level amplification of the wild-type ALk fusion gene is sufficient to cause resistance. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18], [21] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sanger dideoxynucleotide sequencing assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay; Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | In 1 of the 15 cases examined, ALk FISH revealed high-level gene amplification. No ALk resistance mutations were found in this specimen, so it appears that high-level amplification of the wild-type ALk fusion gene is sufficient to cause resistance. Next-Generation Sequencing Reveals a Novel NSCLC ALk F1174V Mutation and Confirms ALk G1202R Mutation Confers High-Level Resistance to Alectinib (CH5424802/RO5424802) in ALk-Rearranged NSCLC Patients Who Progressed on Crizotinib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.I1171T |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-PCR assay; Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Computerized tomography assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | A rebiopsy of the pleural effusion showed a previously unidentified secondary mutation of the ALk gene at codon 1171 (I1171T). | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | 1151Tins |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Low throughput experiment assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Acquired resistance can occur through failure of drug delivery to the target, as in isolated central nervous system (CNS) progression, or by selection of biological variants during TkI exposure. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [22] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ALK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |||||||||||
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NCI-H3122 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5160 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Direct sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | There is a C to G mutation (asterix) in codon 3522 in exon 23 resulting in the F1174L mutation. When present in cis with an ALk translocation, this mutation (also detected in neuroblastomas) causes an increase in ALk phosphorylation, cell growth and downstream signaling. Furthermore, the F1174L mutation inhibits crizotinib mediated downregulation of ALk signaling and blocks apoptosis in RANBP2-ALk Ba/F3 cells. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: ALk-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.6] | [23], [24] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | ALk-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.6] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Crizotinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
FISH assay; Next-generation sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Progression-free survival assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Alterations in the drug target comprising ALk mutations and ALk copy number gain have been described in approximately 30-45% of crizotinib-resistant cases. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [25] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Entrectinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1245V (c.3733T>G) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | Lorlatinib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NBLW cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ90 | |||||||||
| NBLW-R cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ91 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sangersequencing assay; Targeted deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Array CGH assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the sensitivity of NBLW and NBLW-R cells to a panel of ALk inhibitors (TAE-684, Crizotinib, Alectinib and Lorlatinib) revealed differences between the paired cell lines, and overall NBLW-R cells with the F1174L mutation were more resistant to ALk inhibitor induced apoptosis compared with NBLW cells. | ||||||||||||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [26] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | AUY922 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.C1156Y (c.3467G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.60 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
-
T
M
S
A
T
H
I
H
M
H
1090
|
T
H
D
H
Y
H
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
C
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
Y
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
F
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
V
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Ba/F3 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0161 | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Biochemical and Structural StudiesCo-crystallization analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Glo assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tanespimycin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | IF-insertion | p.T1151_L1152 (c.3453_3454) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H3122 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5160 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The if-insertion p.T1151_L1152 (c.3453_3454) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Tanespimycin by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [18] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Tanespimycin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.G1202R (c.3604G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H3122 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5160 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.G1202R (c.3604G>A) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of Tanespimycin by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | |||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [27] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | AZD3463/Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.D1091N (c.3271G>A) |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | |
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 |
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | |
| LA-N-6 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1363 | |
| In Vivo Model | Athymic NCR nude mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; FACS assay; Propidium iodide staining assay; MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The novel ALK inhibitor alectinib effectively suppressed cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in NB cell lines with either wild-type ALK or mutated ALK (F1174L and D1091N) by blocking ALK-mediated PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. In addition, alectinib enhanced doxorubicin-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis in NB cells. Furthermore, alectinib induced apoptosis in an orthotopic xenograft NB mouse model. Also, in the TH-MYCN transgenic mouse model, alectinib resulted in decreased tumor growth and prolonged survival time. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [28] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | AZD3463 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L (c.3520T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | ||||||||||
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | ||||||||||
| NGP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2141 | ||||||||||
| N b-19 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Orthotopic Mouse Model of NB | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Colony formation assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [28] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | AZD3463 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L (c.3522C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | IMR-32 cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0346 | |||||||||
| Sk-N-AS cells | Adrenal | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1700 | ||||||||||
| SH-SY5Y cells | Abdomen | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0019 | ||||||||||
| NGP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2141 | ||||||||||
| N b-19 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Orthotopic Mouse Model of NB | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay; Colony formation assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [29] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | CEP-28122 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L (c.3520T>C) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 | |||||||||
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.F1174L (c.3520T>C) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of CEP-28122 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [29] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | CEP-28122 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R1275Q (c.3824G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | SUP-M2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2209 | |||||||||
| KARPAS-299 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1324 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R1275Q (c.3824G>A) in gene ALK cause the sensitivity of CEP-28122 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Neuroblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.11] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Drug | NVP-TAE684 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.F1174L |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.75 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
G
-
M
-
1070
|
Q
-
M
-
E
-
L
-
Q
-
S
-
P
-
E
-
Y
-
K
-
1080
|
L
-
S
-
K
-
L
-
R
R
T
T
S
S
T
T
I
I
M
M
1090
|
T
T
D
D
Y
Y
N
N
P
P
N
N
Y
Y
C
S
F
F
A
A
1100
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
S
S
S
S
I
I
S
S
D
D
L
L
K
K
1110
|
E
E
V
V
P
P
R
R
K
K
N
N
I
I
T
T
L
L
I
I
1120
|
R
R
G
G
L
L
G
G
H
H
G
G
A
A
F
F
G
G
E
E
1130
|
V
V
Y
Y
E
E
G
G
Q
Q
V
V
S
S
G
G
M
M
P
P
1140
|
N
N
D
D
P
P
S
S
P
P
L
L
Q
Q
V
V
A
A
V
V
1150
|
K
K
T
T
L
L
P
P
E
E
V
V
C
C
S
S
E
E
Q
Q
1160
|
D
D
E
E
L
L
D
D
F
F
L
L
M
M
E
E
A
A
L
L
1170
|
I
I
I
I
S
S
K
K
F
L
N
N
H
H
Q
Q
N
N
I
I
1180
|
V
V
R
R
C
C
I
I
G
G
V
V
S
S
L
L
Q
Q
S
S
1190
|
L
L
P
P
R
R
F
F
I
I
L
L
L
L
E
E
L
L
M
M
1200
|
A
A
G
G
G
G
D
D
L
L
K
K
S
S
F
F
L
L
R
R
1210
|
E
E
T
T
R
R
P
P
R
R
P
P
S
S
Q
Q
P
P
S
S
1220
|
S
S
L
L
A
A
M
M
L
L
D
D
L
L
L
L
H
H
V
V
1230
|
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
A
A
C
C
G
G
C
C
Q
Q
Y
Y
1240
|
L
L
E
E
E
E
N
N
H
H
F
F
I
I
H
H
R
R
D
D
1250
|
I
I
A
A
A
A
R
R
N
N
C
C
L
L
L
L
T
T
C
C
1260
|
P
P
G
G
P
P
G
G
R
R
V
V
A
A
K
K
I
I
G
G
1270
|
D
D
F
F
G
G
M
M
A
A
R
R
D
D
I
I
Y
Y
R
R
1280
|
A
A
S
S
Y
Y
Y
Y
R
R
K
K
G
G
G
G
C
C
A
A
1290
|
M
M
L
L
P
P
V
V
K
K
W
W
M
M
P
P
P
P
E
E
1300
|
A
A
F
F
M
M
E
E
G
G
I
I
F
F
T
T
S
S
K
K
1310
|
T
T
D
D
T
T
W
W
S
S
F
F
G
G
V
V
L
L
L
L
1320
|
W
W
E
E
I
I
F
F
S
S
L
L
G
G
Y
Y
M
M
P
P
1330
|
Y
Y
P
P
S
S
K
K
S
S
N
N
Q
Q
E
E
V
V
L
L
1340
|
E
E
F
F
V
V
T
T
S
S
G
G
G
G
R
R
M
M
D
D
1350
|
P
P
P
P
K
K
N
N
C
C
P
P
G
G
P
P
V
V
Y
Y
1360
|
R
R
I
I
M
M
T
T
Q
Q
C
C
W
W
Q
Q
H
H
Q
Q
1370
|
P
P
E
E
D
D
R
R
P
P
N
N
F
F
A
A
I
I
I
I
1380
|
L
L
E
E
R
R
I
I
E
E
Y
Y
C
C
T
T
Q
Q
D
D
1390
|
P
P
D
D
V
V
I
I
N
N
T
T
A
A
L
L
P
P
I
I
1400
|
E
E
Y
Y
G
G
P
P
L
L
V
V
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
1410
|
K
K
V
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||||||||||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |||||||||||
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | NBLW cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ90 | |||||||||
| NBLW-R cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_VJ91 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Sangersequencing assay; Targeted deep sequencing assay | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Array CGH assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Analysis of the sensitivity of NBLW and NBLW-R cells to a panel of ALk inhibitors (TAE-684, Crizotinib, Alectinib and Lorlatinib) revealed differences between the paired cell lines, and overall NBLW-R cells with the F1174L mutation were more resistant to ALk inhibitor induced apoptosis compared with NBLW cells. | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.81E-05; Fold-change: -2.12E-01; Z-score: -6.60E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
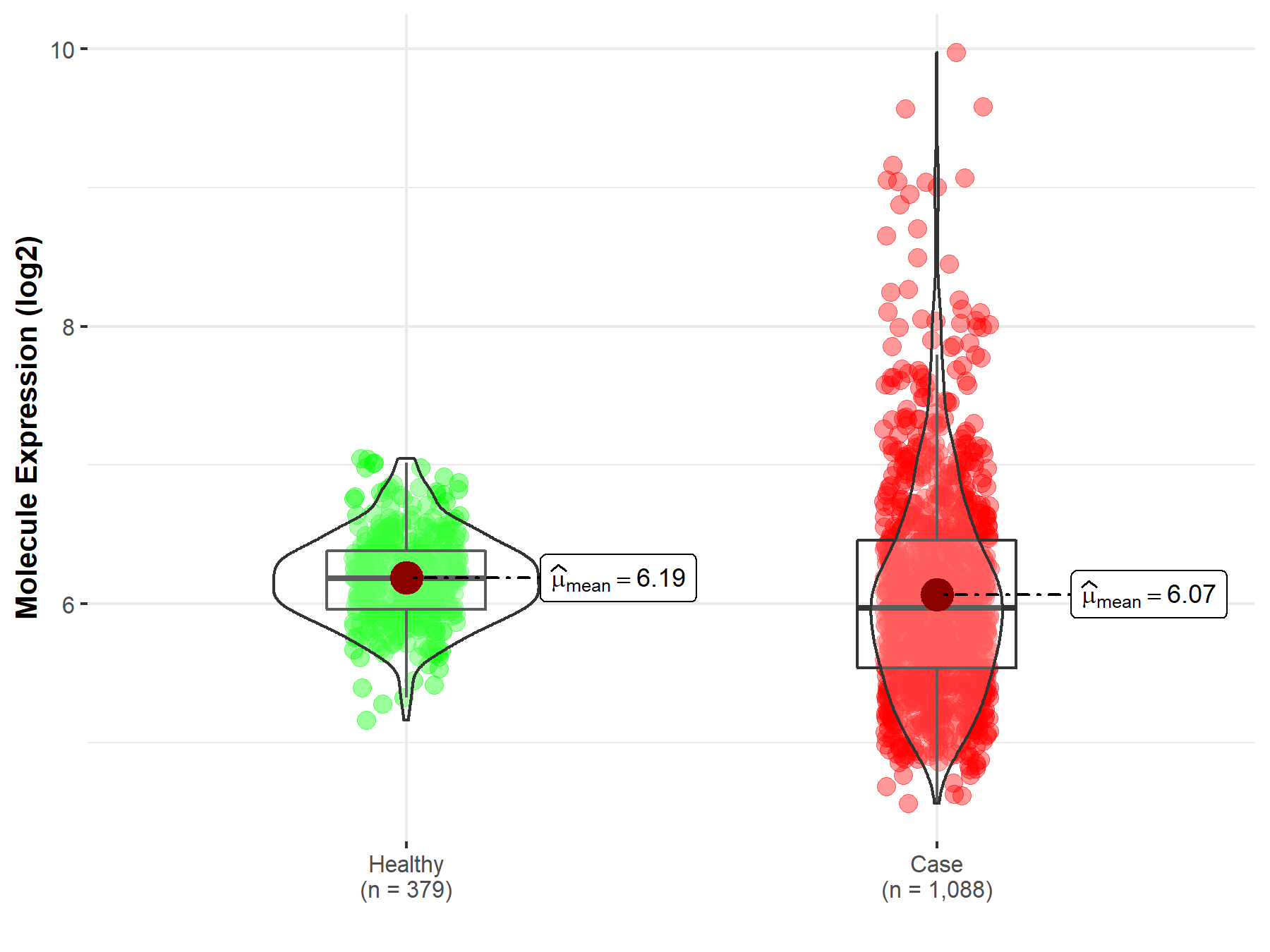
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.07E-01; Fold-change: 3.52E-01; Z-score: 1.03E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.00E-02; Fold-change: 4.68E-01; Z-score: 9.23E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
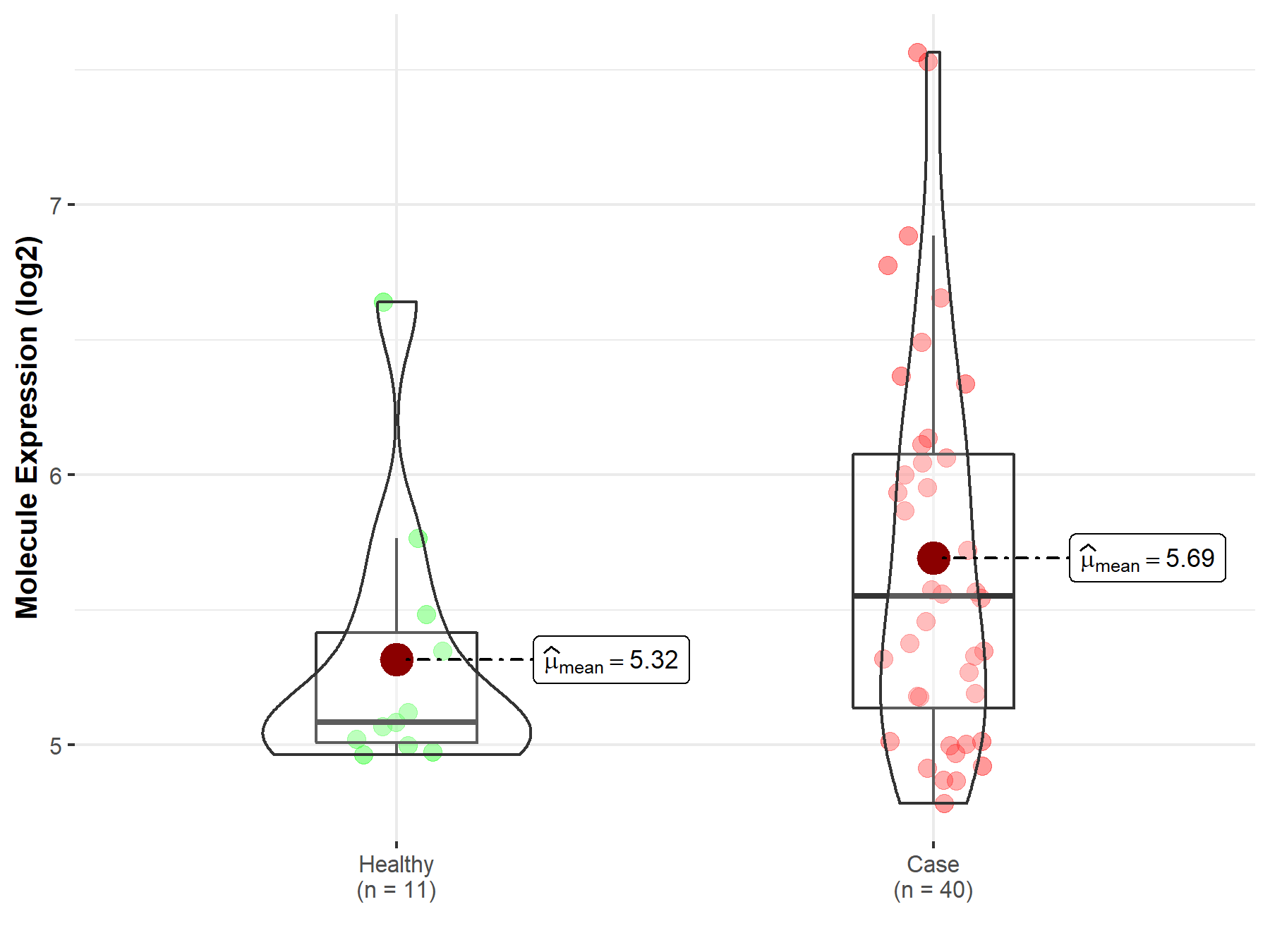
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.02E-03; Fold-change: -6.09E-01; Z-score: -2.71E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.19E-15; Fold-change: 1.80E-01; Z-score: 6.13E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.03E-12; Fold-change: 1.40E-01; Z-score: 5.56E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

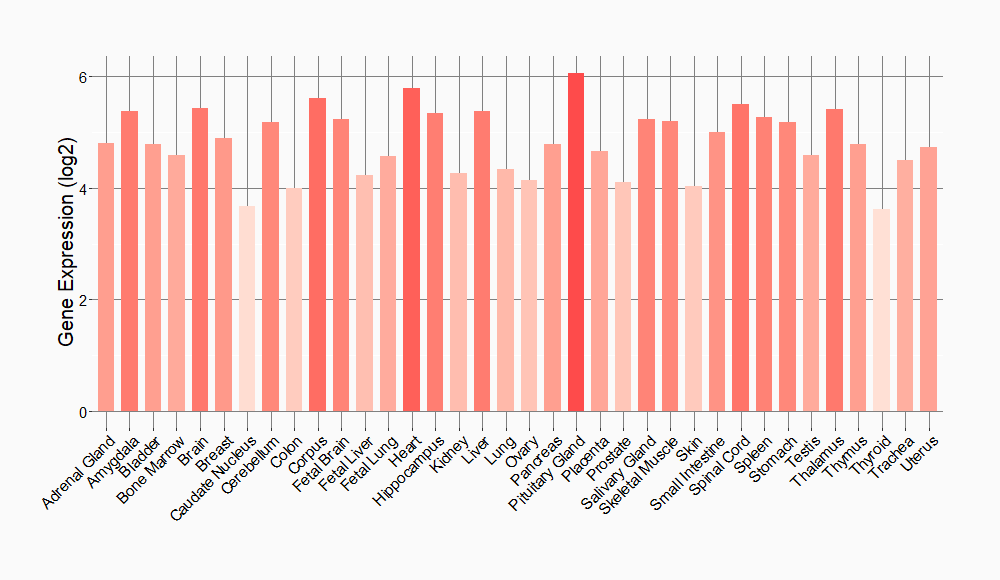
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
