Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00221)
| Name |
RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase (AKT1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Protein kinase B; PKB; Protein kinase B alpha; PKB alpha; Proto-oncogene c-Akt; RAC-PK-alpha; PKB; RAC
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
AKT1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr14:104769349-104795751[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSDVAIVKEGWLHKRGEYIKTWRPRYFLLKNDGTFIGYKERPQDVDQREAPLNNFSVAQC
QLMKTERPRPNTFIIRCLQWTTVIERTFHVETPEEREEWTTAIQTVADGLKKQEEEEMDF RSGSPSDNSGAEEMEVSLAKPKHRVTMNEFEYLKLLGKGTFGKVILVKEKATGRYYAMKI LKKEVIVAKDEVAHTLTENRVLQNSRHPFLTALKYSFQTHDRLCFVMEYANGGELFFHLS RERVFSEDRARFYGAEIVSALDYLHSEKNVVYRDLKLENLMLDKDGHIKITDFGLCKEGI KDGATMKTFCGTPEYLAPEVLEDNDYGRAVDWWGLGVVMYEMMCGRLPFYNQDHEKLFEL ILMEEIRFPRTLGPEAKSLLSGLLKKDPKQRLGGGSEDAKEIMQHRFFAGIVWQHVYEKK LSPPFKPQVTSETDTRYFDEEFTAQMITITPPDQDDSMECVDSERRPHFPQFSYSASGTA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
AKT1 is one of 3 closely related serine/threonine-protein kinases (AKT1, AKT2 and AKT3) called the AKT kinase, and which regulate many processes including metabolism, proliferation, cell survival, growth and angiogenesis. This is mediated through serine and/or threonine phosphorylation of a range of downstream substrates. Over 100 substrate candidates have been reported so far, but for most of them, no isoform specificity has been reported. AKT is responsible of the regulation of glucose uptake by mediating insulin-induced translocation of the SLC2A4/GLUT4 glucose transporter to the cell surface. Phosphorylation of PTPN1 at 'Ser-50' negatively modulates its phosphatase activity preventing dephosphorylation of the insulin receptor and the attenuation of insulin signaling. Phosphorylation of TBC1D4 triggers the binding of this effector to inhibitory 14-3-3 proteins, which is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport. AKT regulates also the storage of glucose in the form of glycogen by phosphorylating GSK3A at 'Ser-21' and GSK3B at 'Ser-9', resulting in inhibition of its kinase activity. Phosphorylation of GSK3 isoforms by AKT is also thought to be one mechanism by which cell proliferation is driven. AKT regulates also cell survival via the phosphorylation of MAP3K5 (apoptosis signal-related kinase). Phosphorylation of 'Ser-83' decreases MAP3K5 kinase activity stimulated by oxidative stress and thereby prevents apoptosis. AKT mediates insulin-stimulated protein synthesis by phosphorylating TSC2 at 'Ser-939' and 'Thr-1462', thereby activating mTORC1 signaling and leading to both phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and in activation of RPS6KB1. AKT is involved in the phosphorylation of members of the FOXO factors (Forkhead family of transcription factors), leading to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and cytoplasmic localization. In particular, FOXO1 is phosphorylated at 'Thr-24', 'Ser-256' and 'Ser-319'. FOXO3 and FOXO4 are phosphorylated on equivalent sites. AKT has an important role in the regulation of NF-kappa-B-dependent gene transcription and positively regulates the activity of CREB1 (cyclic AMP (cAMP)-response element binding protein). The phosphorylation of CREB1 induces the binding of accessory proteins that are necessary for the transcription of pro-survival genes such as BCL2 and MCL1. AKT phosphorylates 'Ser-454' on ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), thereby potentially regulating ACLY activity and fatty acid synthesis. Activates the 3B isoform of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE3B) via phosphorylation of 'Ser-273', resulting in reduced cyclic AMP levels and inhibition of lipolysis. Phosphorylates PIKFYVE on 'Ser-318', which results in increased PI(3)P-5 activity. The Rho GTPase-activating protein DLC1 is another substrate and its phosphorylation is implicated in the regulation cell proliferation and cell growth. AKT plays a role as key modulator of the AKT-mTOR signaling pathway controlling the tempo of the process of newborn neurons integration during adult neurogenesis, including correct neuron positioning, dendritic development and synapse formation. Signals downstream of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI(3)K) to mediate the effects of various growth factors such as platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I). AKT mediates the antiapoptotic effects of IGF-I. Essential for the SPATA13-mediated regulation of cell migration and adhesion assembly and disassembly. May be involved in the regulation of the placental development. Phosphorylates STK4/MST1 at 'Thr-120' and 'Thr-387' leading to inhibition of its: kinase activity, nuclear translocation, autophosphorylation and ability to phosphorylate FOXO3. Phosphorylates STK3/MST2 at 'Thr-117' and 'Thr-384' leading to inhibition of its: cleavage, kinase activity, autophosphorylation at Thr-180, binding to RASSF1 and nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates SRPK2 and enhances its kinase activity towards SRSF2 and ACIN1 and promotes its nuclear translocation. Phosphorylates RAF1 at 'Ser-259' and negatively regulates its activity. Phosphorylation of BAD stimulates its pro-apoptotic activity. Phosphorylates KAT6A at 'Thr-369' and this phosphorylation inhibits the interaction of KAT6A with PML and negatively regulates its acetylation activity towards p53/TP53. Phosphorylates palladin (PALLD), modulating cytoskeletal organization and cell motility. Phosphorylates prohibitin (PHB), playing an important role in cell metabolism and proliferation. Phosphorylates CDKN1A, for which phosphorylation at 'Thr-145' induces its release from CDK2 and cytoplasmic relocalization. These recent findings indicate that the AKT1 isoform has a more specific role in cell motility and proliferation. Phosphorylates CLK2 thereby controlling cell survival to ionizing radiation. Phosphorylates PCK1 at 'Ser-90', reducing the binding affinity of PCK1 to oxaloacetate and changing PCK1 into an atypical protein kinase activity using GTP as donor. Also acts as an activator of TMEM175 potassium channel activity in response to growth factors: forms the lysoK(GF) complex together with TMEM175 and acts by promoting TMEM175 channel activation, independently of its protein kinase activity.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| Siha cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0032 | |
| Caski cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1100 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | GAS5 knockdown (SiHa/cDDP-GAS5-siRNA) and SiHa cells with miR21 overexpression (SiHa/cDDP-miR21) had an up-regulated level of pAkt. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT/mTOR signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04150 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SW480 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0546 |
| DLD1 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0248 | |
| SW620 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0547 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| LOVO cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0399 | |
| HT-29 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0320 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Colony formation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpressed RP11-708H21.4 suppresses CRC cell proliferation through inducing G1 arrest. Moreover, up-regulation of RP11-708H21.4 inhibits cell migration and invasion, causes cell apoptosis, and enhances 5-FU sensitivity of CRC cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Gefitinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Mutation | . |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | ERK/MAPKsignaling pathway | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | NSCLC cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| In Vivo Model | A retrospective survey in conducting clinical studies | Homo sapiens | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Next-generation sequencing assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Liquid biopsy; ATP-binding pocket affinity comparison assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Known mechanisms are secondary resistance mutations occurring in the ATP-binding domain (such as T790M and C797S), mutation or amplification of bypass signallings (such as AXL, Hh, ERBb2, CRIPTO, etc), activating mutations in the downstream pathways (PI3k, AkT, MEk, RAF), low levels of mRNA or polymorphisms of the pro-apoptotic protein BIM, induction of a transcription programme for EMT and phenotypical changes, or induction of elevated tumour PD-L1 levels. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
5 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Brain glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Brain glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Brain | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Parotid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2B67.0] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Parotid gland cancer [ICD-11: 2B67.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Leiomyosarcoma [ICD-11: 2B58.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | [7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | ER positive breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Granulosa cell tumor [ICD-11: 2F76.0] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Granulosa cell tumor [ICD-11: 2F76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: ER negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.7] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | ER negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.7] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [9] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Male nude mouse (nu/nu:Alpk) xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole-exome sequencing | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [10] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Duplication | p.P68_C77 (c.202_231) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The duplication p.P68_C77 (c.202_231) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [8] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Capivasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Q79K (c.235C>A) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Breast | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Q79K (c.235C>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Capivasertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | [11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | HER2 negative breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.11] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Ipatasertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | AKT signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04151 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID beige mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTitre-Glo assay; Wallac multilabel reader assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Ipatasertib (GDC-0068) is a novel selective ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor of AKT that preferentially targets active phosphorylated AKT (pAKT) and is potent in cell lines with evidence of AKT activation. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [12] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Miransertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Miransertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Miransertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | |||||||||
| LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| HCC70 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1270 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| Caco2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 | ||||||||||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| NCI-60 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| KU-19 cells | Blood | Bos taurus (Bovine) | CVCL_VN09 | ||||||||||
| EVSA-T cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1207 | ||||||||||
| CAL-120 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1104 | ||||||||||
| BT-549 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| BT-20 cells | Mammary gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0178 | ||||||||||
| B16F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NMRI (nu/nu) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Miransertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [14] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Uprosertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 | |||||||||
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female nu/nu CD-1 mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of Uprosertib by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [15] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Uprosertib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | 19 drug na?ve cell lines and four sub-lines | N.A. | N.A. | N.A. | |||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
ATP-based luminescent assay; Flow cytometry assay | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Anal canal cancer [ICD-11: 2C00.0] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Anal canal cancer [ICD-11: 2C00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | BAY1125976 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| HCC70 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1270 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| Caco2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 | ||||||||||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | ||||||||||
| NCI-60 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EVSA-T cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1207 | ||||||||||
| KU-19 cells | Blood | Bos taurus (Bovine) | CVCL_VN09 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| CAL-120 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1104 | ||||||||||
| BT-549 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| BT-20 cells | Mammary gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0178 | ||||||||||
| B16F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NMRI (nu/nu) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of BAY1125976 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [16] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | BAY1125976 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | |||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| HCC70 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1270 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| Caco2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 | ||||||||||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | ||||||||||
| NCI-60 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| EVSA-T cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1207 | ||||||||||
| KU-19 cells | Blood | Bos taurus (Bovine) | CVCL_VN09 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| CAL-120 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1104 | ||||||||||
| BT-549 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| BT-20 cells | Mammary gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0178 | ||||||||||
| B16F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NMRI (nu/nu) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of BAY1125976 by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
Preclinical Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Allosteric AKT inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | |||||||||
| HEK293 cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0045 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NOD/SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of allosteric AKT inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [17] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Allosteric AKT inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | |||||||||
| HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NOD/SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Deactivation of Akt by a small molecule inhibitor ,SC66, targeting pleckstrin homology domain and facilitating Akt ubiquitination. A cancer-relevant Akt1 (e17k) mutant is unstable, making it intrinsically sensitive to functional inhibition by SC66 in cellular contexts in which the PI3K inhibition has little inhibitory effect. | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | [13] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Endometrial adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C76.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | ARQ 751 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | DU-145 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0105 | |||||||||
| LNCaP cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0395 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 | ||||||||||
| Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 | ||||||||||
| T47D cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0553 | ||||||||||
| NCI-H460 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0459 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-453 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0418 | ||||||||||
| MDA-MB-468 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0419 | ||||||||||
| HCC70 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1270 | ||||||||||
| A2058 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1059 | ||||||||||
| Caco2 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0025 | ||||||||||
| MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | ||||||||||
| ZR75-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0588 | ||||||||||
| NCI-60 cells | N.A. | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | ||||||||||
| KU-19 cells | Blood | Bos taurus (Bovine) | CVCL_VN09 | ||||||||||
| EVSA-T cells | Ascites | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1207 | ||||||||||
| CAL-120 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1104 | ||||||||||
| BT-549 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1092 | ||||||||||
| BT-474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | ||||||||||
| BT-20 cells | Mammary gland | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0178 | ||||||||||
| B16F10 cells | Skin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0159 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Female NMRI (nu/nu) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of ARQ 751 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [18] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MK2206 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W80A (c.238_239delTGinsGC) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | 3T3-L1 cells | Nasopharynx | Mus musculus (Mouse) | CVCL_0123 |
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.W80A (c.238_239delTGinsGC) in gene AKT1 cause the resistance of MK2206 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [19] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | MK2206 | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.W80A (c.238_239delTGinsGC) |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | H1975 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1511 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| HCC827 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2063 | |
| MCF10A cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0598 | |
| HCC4006 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1269 | |
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | |
| GTL-16 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7668 | |
| MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 | |
| HCT116 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0291 | |
| MDA-MB-361 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0620 | |
| H1648 cells | Lymph node | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1482 | |
| EBC1 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2891 | |
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.W80A (c.238_239delTGinsGC) in gene AKT1 cause the resistance of MK2206 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [20] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Non-allosteric AKT inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of non-allosteric AKT inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [20] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Non-allosteric AKT inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | [20] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Solid tumour/cancer [ICD-11: 2A00-2F9Z] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Non-allosteric AKT inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Head and neck cancer [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | [21] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Head and neck cancer [ICD-11: 2D42.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | PI3K pathway inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.E17K (c.49G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.94 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
0
|
-
S
M
M
S
S
D
D
V
V
A
A
I
I
V
V
K
K
E
E
10
|
G
G
W
W
L
L
H
H
K
K
R
R
G
G
E
K
Y
Y
I
I
20
|
K
K
T
T
W
W
R
R
P
P
R
R
Y
Y
F
F
L
L
L
L
30
|
K
K
N
N
D
D
G
G
T
T
F
F
I
I
G
G
Y
Y
K
K
40
|
E
E
R
R
P
P
Q
Q
D
D
V
V
D
D
Q
Q
R
R
E
E
50
|
A
A
P
P
L
L
N
N
N
N
F
F
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
60
|
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
M
M
K
K
T
T
E
E
R
R
P
P
R
R
70
|
P
P
N
N
T
T
F
F
I
I
I
I
R
R
C
C
L
L
Q
Q
80
|
W
W
T
T
T
T
V
V
I
I
E
E
R
R
T
T
F
F
H
H
90
|
V
V
E
E
T
T
P
P
E
E
E
E
R
R
E
E
E
E
W
W
100
|
T
T
T
T
A
A
I
I
Q
Q
T
T
V
V
A
A
D
D
G
G
110
|
L
L
K
K
K
K
Q
Q
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
E
M
M
D
D
120
|
F
F
R
R
-
S
-
G
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.E17K (c.49G>A) in gene AKT1 cause the sensitivity of PI3K pathway inhibitors by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.17E-11; Fold-change: 1.86E-01; Z-score: 4.96E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.08E-01; Fold-change: -1.96E-01; Z-score: -4.40E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
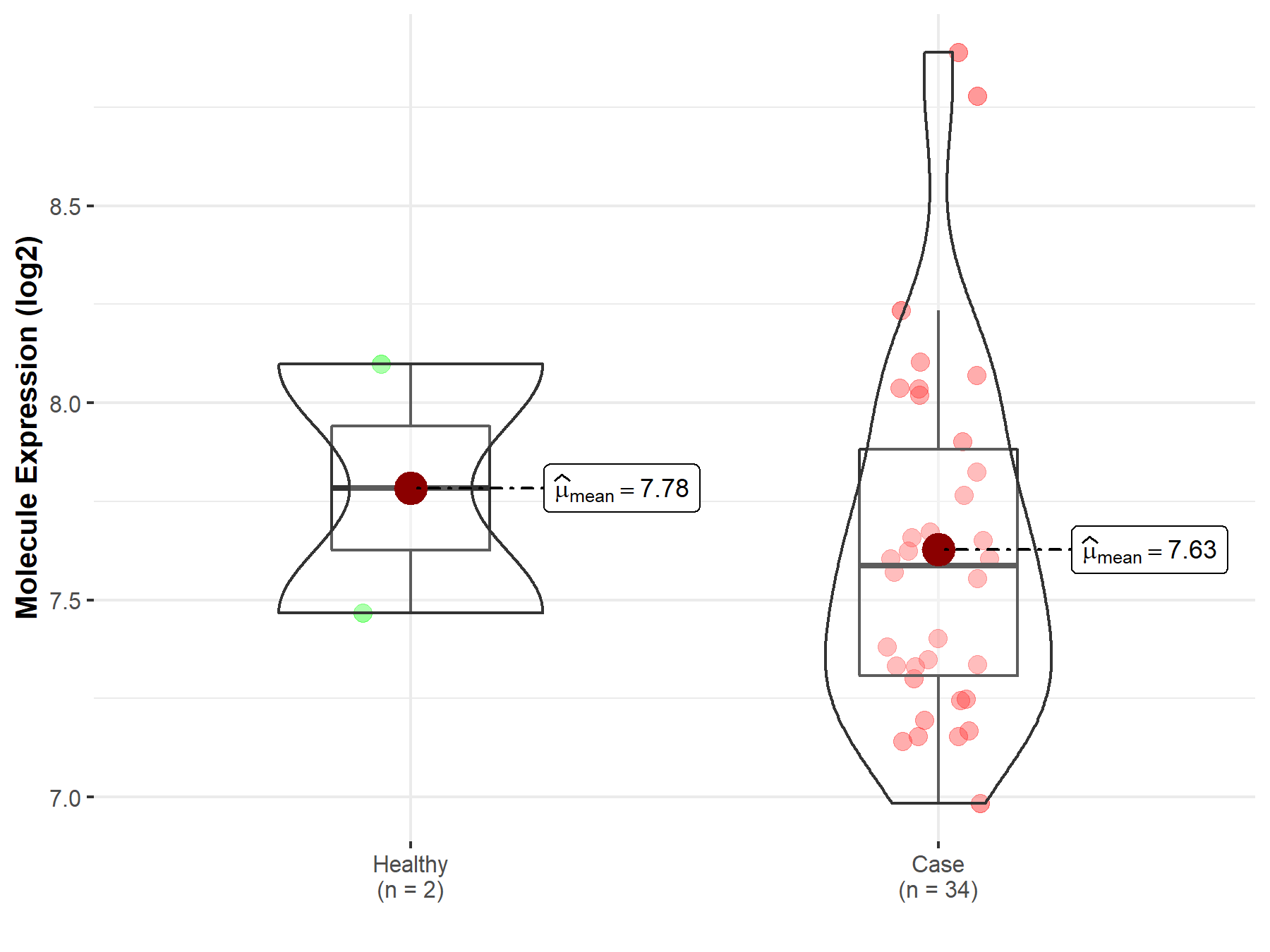
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.78E-02; Fold-change: 3.86E-01; Z-score: 7.39E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.80E-01; Fold-change: -2.05E-01; Z-score: -7.62E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
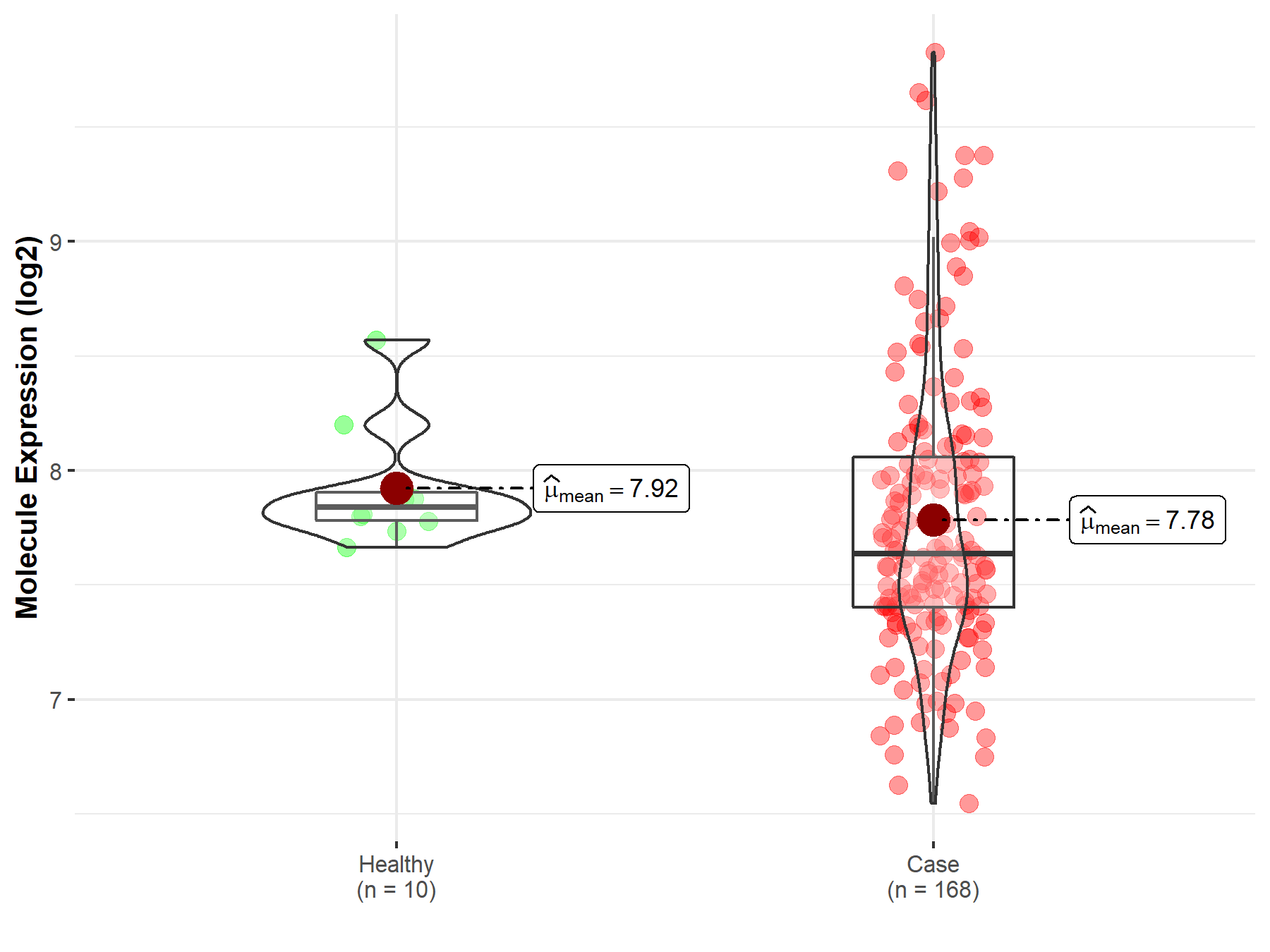
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.63E-16; Fold-change: -3.05E-01; Z-score: -7.97E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.55E-17; Fold-change: -6.10E-01; Z-score: -1.18E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.20E-04; Fold-change: 4.25E-01; Z-score: 6.80E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
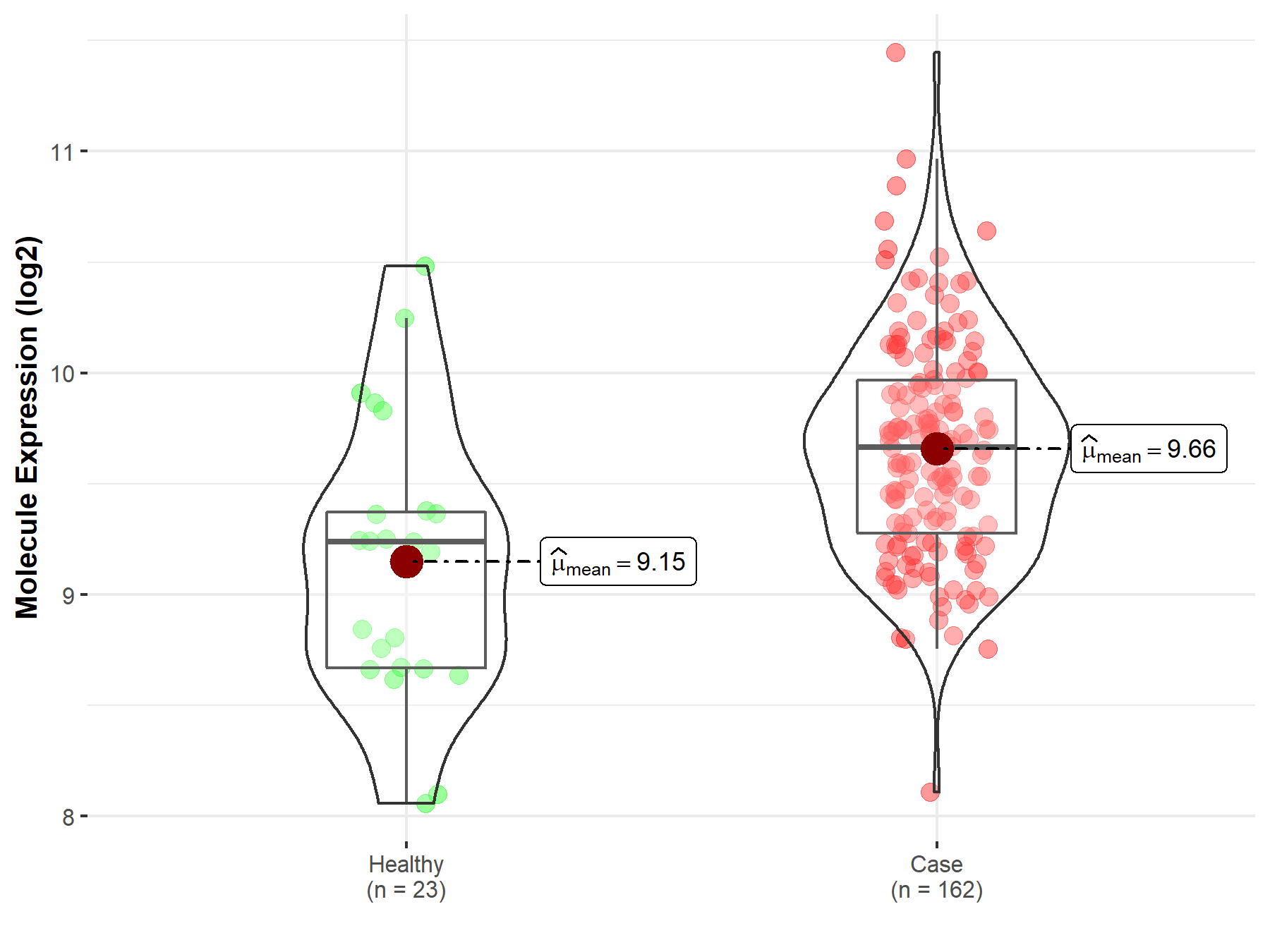
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.76E-37; Fold-change: 5.98E-01; Z-score: 9.55E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.00E-07; Fold-change: 4.07E-01; Z-score: 8.71E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.44E-02; Fold-change: 4.74E-01; Z-score: 8.15E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 8.39E-03; Fold-change: 1.02E+00; Z-score: 1.22E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.30E-03; Fold-change: 2.34E-01; Z-score: 7.02E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Head and neck tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Head and neck cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.59E-01; Fold-change: 4.76E-02; Z-score: 1.16E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
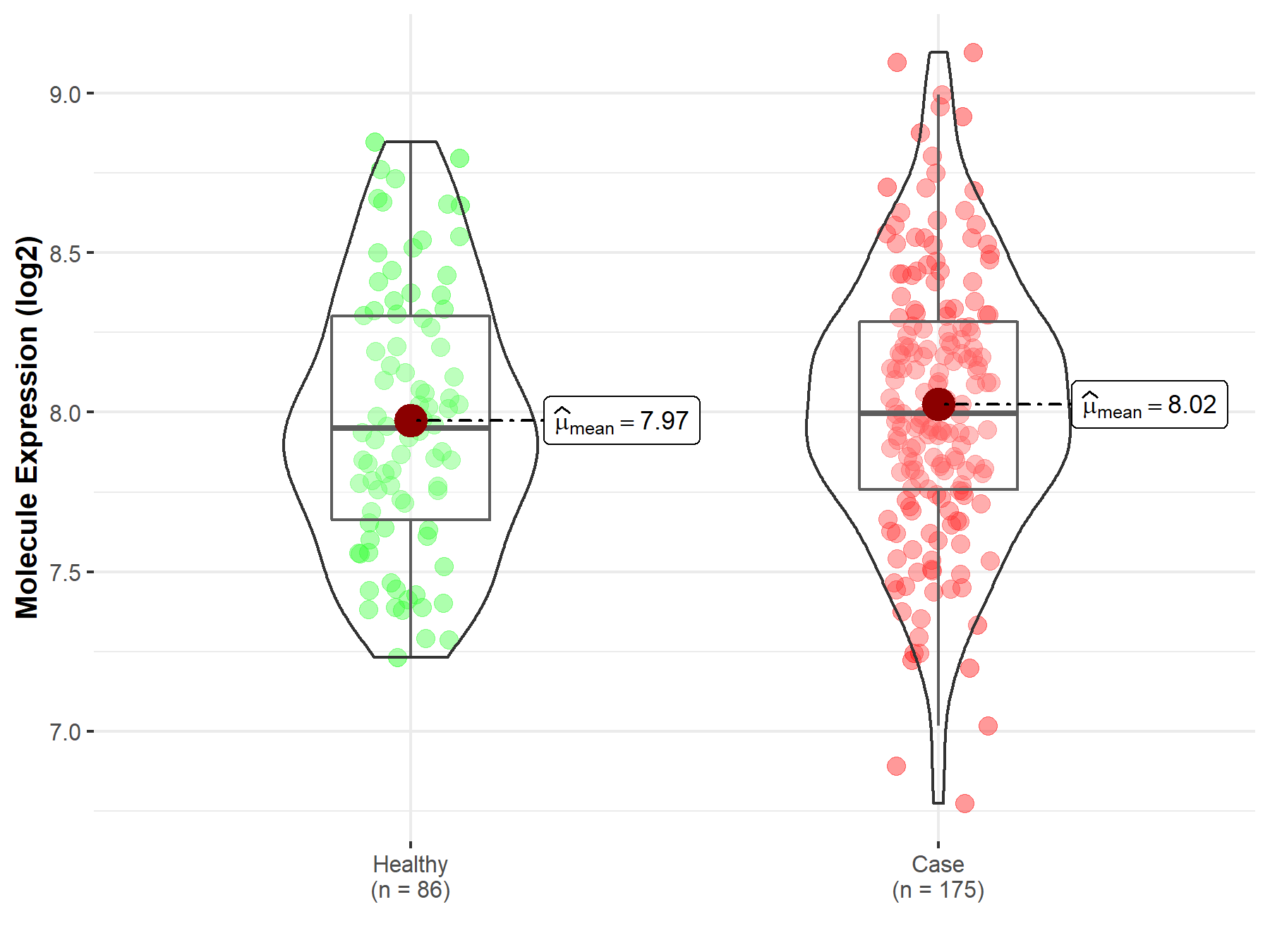
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
