Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00130)
| Name |
Nuclear receptor subfamily 2 group C2 (NR2C2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Orphan nuclear receptor TAK1; Orphan nuclear receptor TR4; Testicular receptor 4; TAK1; TR4
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
NR2C2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr3:14947583-15053600[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MTSPSPRIQIISTDSAVASPQRIQIVTDQQTGQKIQIVTAVDASGSPKQQFILTSPDGAG
TGKVILASPETSSAKQLIFTTSDNLVPGRIQIVTDSASVERLLGKTDVQRPQVVEYCVVC GDKASGRHYGAVSCEGCKGFFKRSVRKNLTYSCRSNQDCIINKHHRNRCQFCRLKKCLEM GMKMESVQSERKPFDVQREKPSNCAASTEKIYIRKDLRSPLIATPTFVADKDGARQTGLL DPGMLVNIQQPLIREDGTVLLATDSKAETSQGALGTLANVVTSLANLSESLNNGDTSEIQ PEDQSASEITRAFDTLAKALNTTDSSSSPSLADGIDTSGGGSIHVISRDQSTPIIEVEGP LLSDTHVTFKLTMPSPMPEYLNVHYICESASRLLFLSMHWARSIPAFQALGQDCNTSLVR ACWNELFTLGLAQCAQVMSLSTILAAIVNHLQNSIQEDKLSGDRIKQVMEHIWKLQEFCN SMAKLDIDGYEYAYLKAIVLFSPDHPGLTSTSQIEKFQEKAQMELQDYVQKTYSEDTYRL ARILVRLPALRLMSSNITEELFFTGLIGNVSIDSIIPYILKMETAEYNGQITGASL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Orphan nuclear receptor that can act as a repressor or activator of transcription. An important repressor of nuclear receptor signaling pathways such as retinoic acid receptor, retinoid X, vitamin D3 receptor, thyroid hormone receptor and estrogen receptor pathways. May regulate gene expression during the late phase of spermatogenesis. Together with NR2C1, forms the core of the DRED (direct repeat erythroid-definitive) complex that represses embryonic and fetal globin transcription including that of GATA1. Binds to hormone response elements (HREs) consisting of two 5'-AGGTCA-3' half site direct repeat consensus sequences. Plays a fundamental role in early embryonic development and embryonic stem cells. Required for normal spermatogenesis and cerebellum development. Appears to be important for neurodevelopmentally regulated behavior (By similarity). Activates transcriptional activity of LHCG. Antagonist of PPARA-mediated transactivation.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Liver cancer [ICD-11: 2C12] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.03E-05 Fold-change: 7.29E-02 Z-score: 4.71E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Huh-7 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0336 |
| BEL-7402 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5492 | |
| SMMC7721 cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0534 | |
| Skhep1 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0525 | |
| MHCC97-H cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4972 | |
| HCC-LM3 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6832 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8; Flow cytometry assay; EdU assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Ectopic expression of SNHG6-003 in HCC cells promoted cell proliferation and induced drug resistance, whereas SNHG6-003 knockdown promoted apoptosis. Moreover, SNHG6-003 functioned as a competitive endogenous RNA (ceRNA), effectively becoming sponge for miR-26a/b and thereby modulating the expression of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAk1). Importantly, expression analysis revealed that both SNHG6-003 and TAk1 were upregulated in human cancers, exhibiting a co-expression pattern. In HCC patients, high expression of SNHG6-003 closely correlated with tumor progression and shorter survival. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04064 | ||
| In Vitro Model | QGY-7703 cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6715 |
| MHCC97-H cells | Liver | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4972 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-26b suppresses NF-kB signaling and thereby sensitized HCC cells to the doxorubicin-induced apoptosis by inhibiting the expression of TAk1 and TAB3. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B.0] | [3] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B6B.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Calycosin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| TRAF6-related signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | CNE2 cells | Nasopharynx | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6889 |
| C666-1 cells | Throat | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_7949 | |
| CNE1 cells | Throat | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6888 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; BrdU assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Calycosin inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by downregulating EWSAT1 expression to regulate the TRAF6-related pathways. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Liver | |
| The Specified Disease | Liver cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.03E-05; Fold-change: 2.99E-01; Z-score: 7.65E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 3.21E-05; Fold-change: 1.48E-01; Z-score: 3.12E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Other Disease Section | p-value: 3.00E-01; Fold-change: 1.84E-01; Z-score: 4.31E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
Molecule expression in tissue other than the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
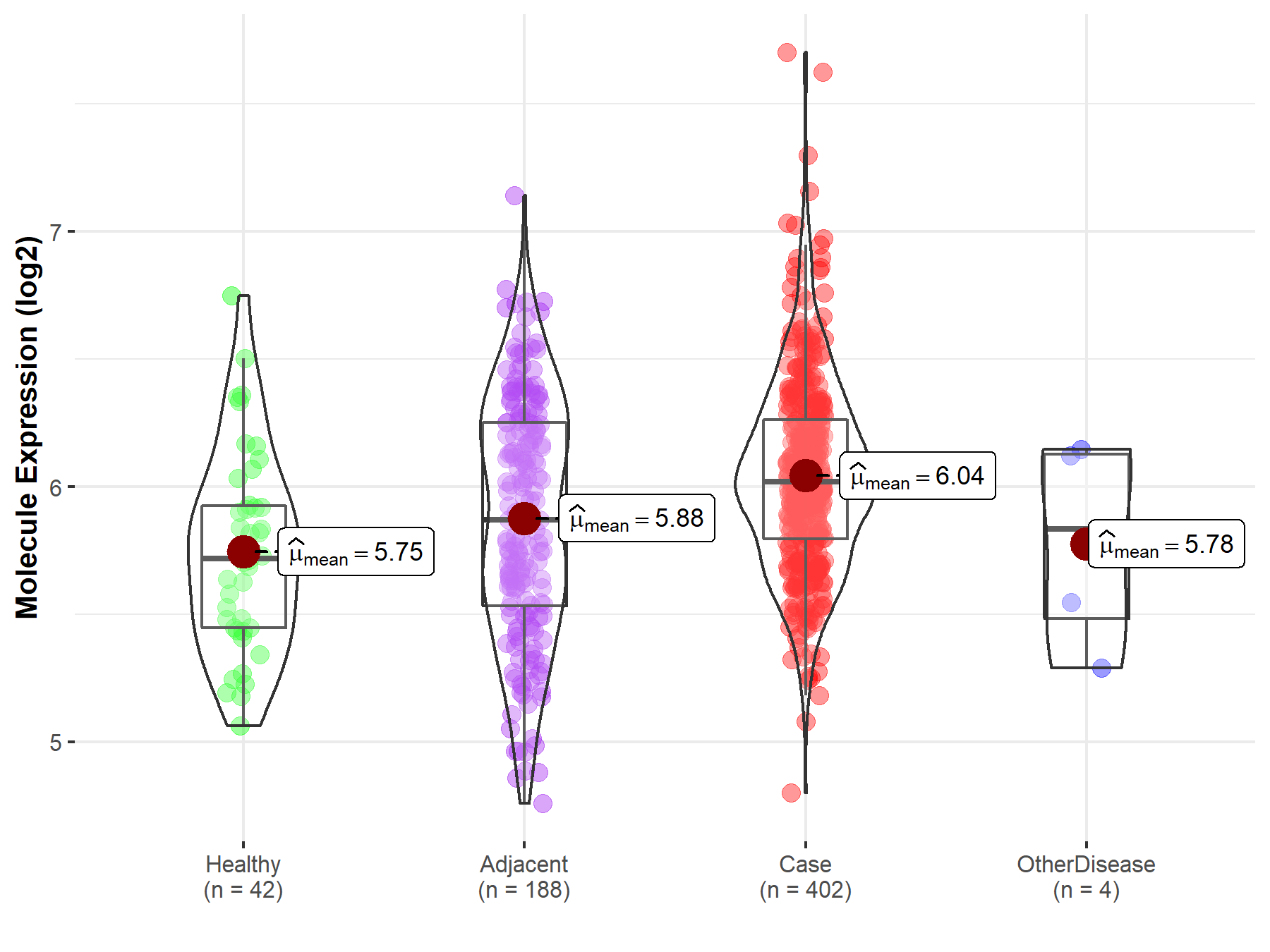
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

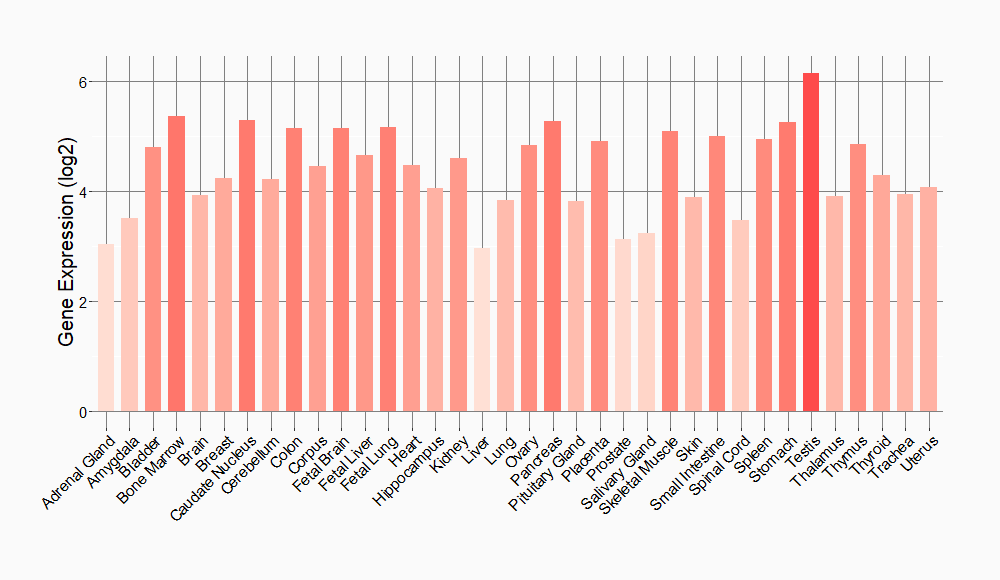
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
