Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00124)
| Name |
Myc proto-oncogene protein (MYC)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 39; bHLHe39; Proto-oncogene c-Myc; Transcription factor p64; BHLHE39
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MYC
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr8:127735434-127742951[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MPLNVSFTNRNYDLDYDSVQPYFYCDEEENFYQQQQQSELQPPAPSEDIWKKFELLPTPP
LSPSRRSGLCSPSYVAVTPFSLRGDNDGGGGSFSTADQLEMVTELLGGDMVNQSFICDPD DETFIKNIIIQDCMWSGFSAAAKLVSEKLASYQAARKDSGSPNPARGHSVCSTSSLYLQD LSAAASECIDPSVVFPYPLNDSSSPKSCASQDSSAFSPSSDSLLSSTESSPQGSPEPLVL HEETPPTTSSDSEEEQEDEEEIDVVSVEKRQAPGKRSESGSPSAGGHSKPPHSPLVLKRC HVSTHQHNYAAPPSTRKDYPAAKRVKLDSVRVLRQISNNRKCTSPRSSDTEENVKRRTHN VLERQRRNELKRSFFALRDQIPELENNEKAPKVVILKKATAYILSVQAEEQKLISEEDLL RKRREQLKHKLEQLRNSCA Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Transcription factor that binds DNA in a non-specific manner, yet also specifically recognizes the core sequence 5'-CAC[GA]TG-3'. Activates the transcription of growth-related genes. Binds to the VEGFA promoter, promoting VEGFA production and subsequent sprouting angiogenesis. Regulator of somatic reprogramming, controls self-renewal of embryonic stem cells. Functions with TAF6L to activate target gene expression through RNA polymerase II pause release. Positively regulates transcription of HNRNPA1, HNRNPA2 and PTBP1 which in turn regulate splicing of pyruvate kinase PKM by binding repressively to sequences flanking PKM exon 9, inhibiting exon 9 inclusion and resulting in exon 10 inclusion and production of the PKM M2 isoform.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
7 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Sarcoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Muscle tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.55E-174 Fold-change: 4.90E-01 Z-score: 3.44E+01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SW-872 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1730 |
| SW-1353 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0543 | |
| TE-671 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1756 | |
| SW-684 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1726 | |
| SW-982 cells | Testicular | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1734 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | By investigating of important regulators of stem cell biology, real-time RT-PCR data showed an increased expression of c-Myc, beta-catenin, and SOX-2 in the ALDH1high population and a significant higher level of ABCG2. Statistical analysis of data demonstrated that ALDH1high cells of SW-982 and SW-1353 showed higher resistance to commonly used chemotherapeutic agents like doxorubicin, epirubicin, and cisplatin than ALDH1low cells. This study demonstrates that in different sarcoma cell lines, high ALDH1 activity can be used to identify a subpopulation of cells characterized by a significantly higher proliferation rate, increased colony forming, increased expression of ABC transporter genes and stemness markers compared to control cells. In addition, enhanced drug resistance was demonstrated. | |||
| Disease Class: Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Malignant pleural mesothelioma [ICD-11: 2C26.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | MSTO-211H cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1430 |
| NCI-H2052 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1518 | |
| NCI-H2452 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1553 | |
| NCI-H28 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1555 | |
| HCT-4012 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_IT30 | |
| HP10 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HP3 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C311 | |
| HP5 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HP7 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| HP9 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| MET-5A cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3749 | |
| Meso cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5759 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | c-Myc and PVT1 co-amplification is frequent in MPM. C-MYC and PVT1 cooperation helps to stimulate proliferation, decrease sensitivity to platinum therapy, and reduce apoptosis. Both genes also help to regulate apoptosis-related genes, with C-MYC revealing a tendency to maintain a balance between pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic genes, whereas PVT1 revealed a tendency to upregulate pro-apoptotic genes and downregulate anti-apoptotic genes, thereby helping to suppress apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dasatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lin-CD34+CD38- cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Lin-CD34-CD38- CML cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR494-3p down-regulation in CML LSCs, leading to c-MYC up-regulation, was able to decrease TkI-induced apoptosis. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Docetaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition | Activation | hsa01521 | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| miR451/cMyc/ERK/GSk3Beta signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | SPC-A1 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6955 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-451 was found to be significantly downregulated in docetaxel-resistant LAD cells, and re-expression of miR-451 could reverse EMT to mesenchymal-epithelial transition (MET) and inhibit invasion and metastasis of docetaxel-resistant LAD cells both in vitro and in vivo. and the overexpressionof c-Myc which induced extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERk)-dependent glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSk-3beta) inactivation and subsequent snail activation is essential for acquisition of EMT phenotype induced by loss of miR-451. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SW-872 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1730 |
| SW-1353 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0543 | |
| TE-671 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1756 | |
| SW-684 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1726 | |
| SW-982 cells | Testicular | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1734 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | By investigating of important regulators of stem cell biology, real-time RT-PCR data showed an increased expression of c-Myc, beta-catenin, and SOX-2 in the ALDH1high population and a significant higher level of ABCG2. Statistical analysis of data demonstrated that ALDH1high cells of SW-982 and SW-1353 showed higher resistance to commonly used chemotherapeutic agents like doxorubicin, epirubicin, and cisplatin than ALDH1low cells. This study demonstrates that in different sarcoma cell lines, high ALDH1 activity can be used to identify a subpopulation of cells characterized by a significantly higher proliferation rate, increased colony forming, increased expression of ABC transporter genes and stemness markers compared to control cells. In addition, enhanced drug resistance was demonstrated. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Sarcoma [ICD-11: 2C35.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Epirubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | SW-872 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1730 |
| SW-1353 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0543 | |
| TE-671 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1756 | |
| SW-684 cells | Skin | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1726 | |
| SW-982 cells | Testicular | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1734 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | By investigating of important regulators of stem cell biology, real-time RT-PCR data showed an increased expression of c-Myc, beta-catenin, and SOX-2 in the ALDH1high population and a significant higher level of ABCG2. Statistical analysis of data demonstrated that ALDH1high cells of SW-982 and SW-1353 showed higher resistance to commonly used chemotherapeutic agents like doxorubicin, epirubicin, and cisplatin than ALDH1low cells. This study demonstrates that in different sarcoma cell lines, high ALDH1 activity can be used to identify a subpopulation of cells characterized by a significantly higher proliferation rate, increased colony forming, increased expression of ABC transporter genes and stemness markers compared to control cells. In addition, enhanced drug resistance was demonstrated. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lin-CD34+CD38- cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Lin-CD34-CD38- CML cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR494-3p down-regulation in CML LSCs, leading to c-MYC up-regulation, was able to decrease TkI-induced apoptosis. | |||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Imatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| PI3K/AKT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04151 | ||
| In Vitro Model | KG-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0374 |
| THP-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 | |
| K562 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0004 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Long noncoding RNA HULC promotes cell proliferation by regulating PI3k/AkT signaling pathway in chronic myeloid leukemia. HULC aggrevates CML by regulating PI3k/AkT. Inhibition of HULC enhances imatinib induced CML apoptosis. 3. HULC increased c-Myc and Bcl-2 by sequestering miR200a-3p. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chronic myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A20.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Ponatinib | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Lin-CD34+CD38- cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Lin-CD34-CD38- CML cells | Bone | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR494-3p down-regulation in CML LSCs, leading to c-MYC up-regulation, was able to decrease TkI-induced apoptosis. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Myelofibrosis | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.42E-06; Fold-change: -1.20E+00; Z-score: -4.48E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
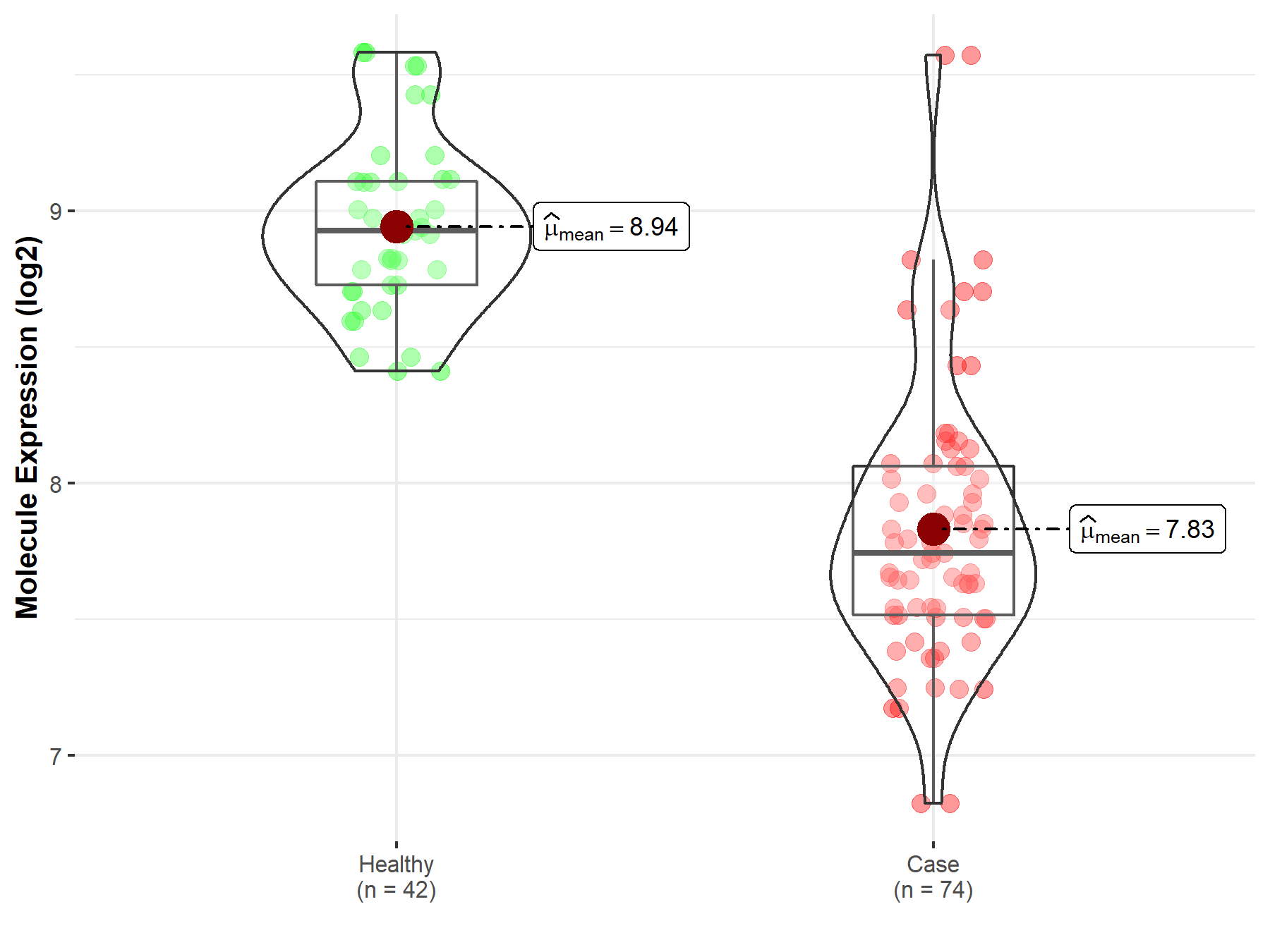
| The Studied Tissue | Whole blood | |
| The Specified Disease | Polycythemia vera | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.27E-27; Fold-change: -1.18E+00; Z-score: -3.75E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.28E-02; Fold-change: -4.37E-02; Z-score: -4.27E-02 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.98E-08; Fold-change: -5.51E-01; Z-score: -5.29E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
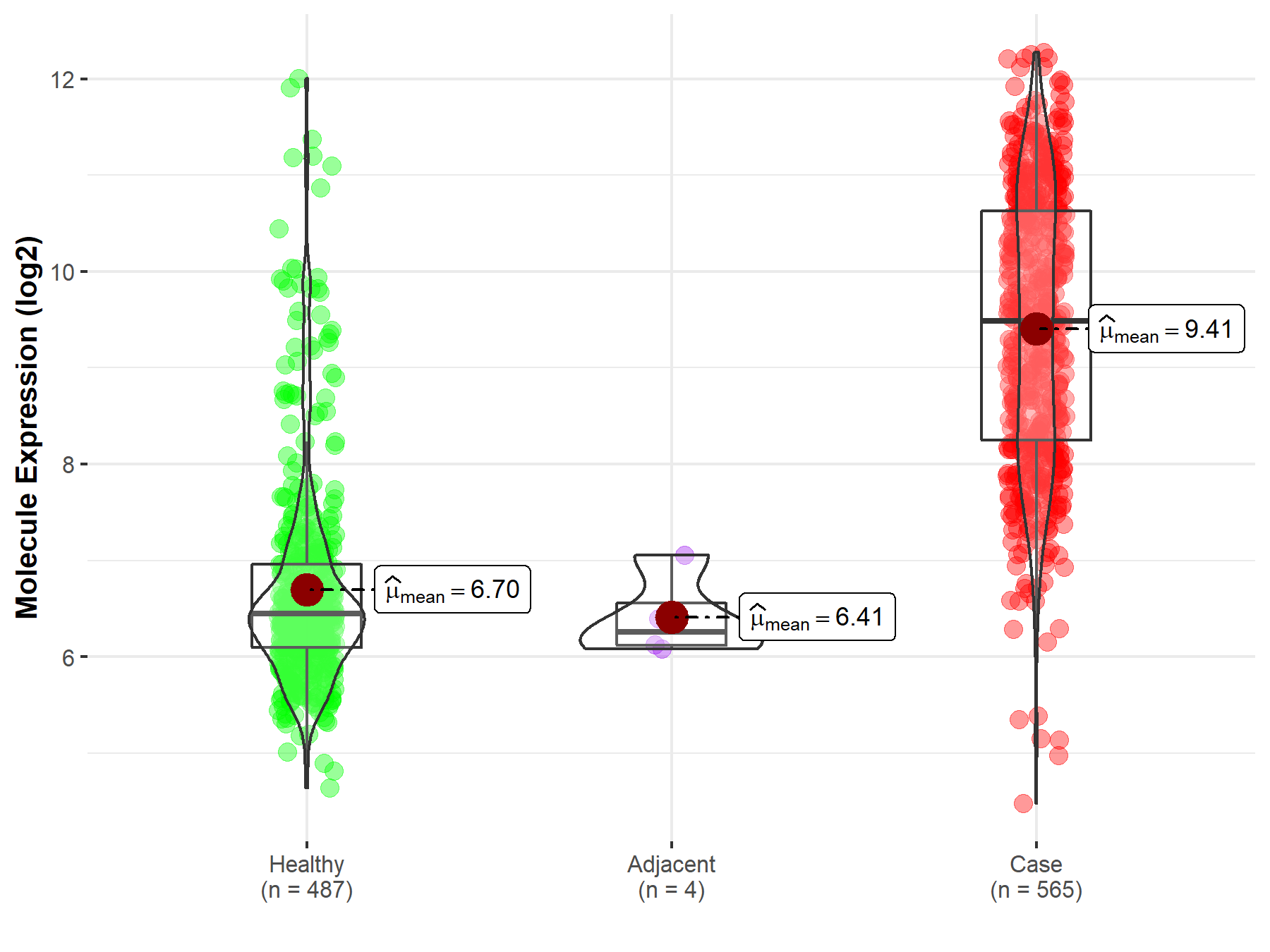
| The Studied Tissue | Muscle | |
| The Specified Disease | Sarcoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.55E-174; Fold-change: 3.04E+00; Z-score: 2.75E+00 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 4.82E-04; Fold-change: 3.23E+00; Z-score: 7.21E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
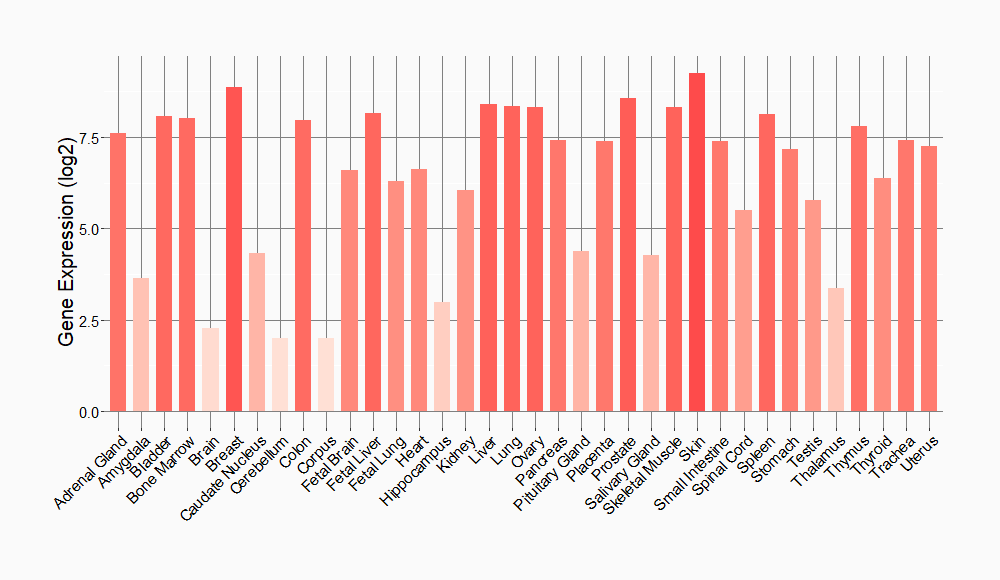
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
