Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00114)
| Name |
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 1 (MAPK1)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
MAP kinase 1; MAPK 1; ERT1; Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2; ERK-2; MAP kinase isoform p42; p42-MAPK; Mitogen-activated protein kinase 2; MAP kinase 2; MAPK 2; ERK2; PRKM1; PRKM2
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
MAPK1
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr22:21759657-21867680[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAAAAAAGAGPEMVRGQVFDVGPRYTNLSYIGEGAYGMVCSAYDNVNKVRVAIKKISPFE
HQTYCQRTLREIKILLRFRHENIIGINDIIRAPTIEQMKDVYIVQDLMETDLYKLLKTQH LSNDHICYFLYQILRGLKYIHSANVLHRDLKPSNLLLNTTCDLKICDFGLARVADPDHDH TGFLTEYVATRWYRAPEIMLNSKGYTKSIDIWSVGCILAEMLSNRPIFPGKHYLDQLNHI LGILGSPSQEDLNCIINLKARNYLLSLPHKNKVPWNRLFPNADSKALDLLDKMLTFNPHK RIEVEQALAHPYLEQYYDPSDEPIAEAPFKFDMELDDLPKEKLKELIFEETARFQPGYRS Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
Serine/threonine kinase which acts as an essential component of the MAP kinase signal transduction pathway. MAPK1/ERK2 and MAPK3/ERK1 are the 2 MAPKs which play an important role in the MAPK/ERK cascade. They participate also in a signaling cascade initiated by activated KIT and KITLG/SCF. Depending on the cellular context, the MAPK/ERK cascade mediates diverse biological functions such as cell growth, adhesion, survival and differentiation through the regulation of transcription, translation, cytoskeletal rearrangements. The MAPK/ERK cascade plays also a role in initiation and regulation of meiosis, mitosis, and postmitotic functions in differentiated cells by phosphorylating a number of transcription factors. About 160 substrates have already been discovered for ERKs. Many of these substrates are localized in the nucleus, and seem to participate in the regulation of transcription upon stimulation. However, other substrates are found in the cytosol as well as in other cellular organelles, and those are responsible for processes such as translation, mitosis and apoptosis. Moreover, the MAPK/ERK cascade is also involved in the regulation of the endosomal dynamics, including lysosome processing and endosome cycling through the perinuclear recycling compartment (PNRC); as well as in the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus during mitosis. The substrates include transcription factors (such as ATF2, BCL6, ELK1, ERF, FOS, HSF4 or SPZ1), cytoskeletal elements (such as CANX, CTTN, GJA1, MAP2, MAPT, PXN, SORBS3 or STMN1), regulators of apoptosis (such as BAD, BTG2, CASP9, DAPK1, IER3, MCL1 or PPARG), regulators of translation (such as EIF4EBP1) and a variety of other signaling-related molecules (like ARHGEF2, DCC, FRS2 or GRB10). Protein kinases (such as RAF1, RPS6KA1/RSK1, RPS6KA3/RSK2, RPS6KA2/RSK3, RPS6KA6/RSK4, SYK, MKNK1/MNK1, MKNK2/MNK2, RPS6KA5/MSK1, RPS6KA4/MSK2, MAPKAPK3 or MAPKAPK5) and phosphatases (such as DUSP1, DUSP4, DUSP6 or DUSP16) are other substrates which enable the propagation the MAPK/ERK signal to additional cytosolic and nuclear targets, thereby extending the specificity of the cascade. Mediates phosphorylation of TPR in response to EGF stimulation. May play a role in the spindle assembly checkpoint. Phosphorylates PML and promotes its interaction with PIN1, leading to PML degradation. Phosphorylates CDK2AP2 (By similarity).
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
8 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.02E-01 Fold-change: 9.56E-02 Z-score: 1.84E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; Flow cytometry assay; Colony formation assays | |||
| Mechanism Description | Linc00161 regulated the drug resistance of ovarian cancer by sponging microRNA-128 and modulating MAPk1. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [5] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | SkOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0532 |
| HEK293T cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0063 | |
| OVCAR3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0465 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-378a-3p sensitizes ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin through downregulating MAPk1/GRB2. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tryptophan | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Melanoma [ICD-11: 2C30] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.72E-01 Fold-change: 3.27E-02 Z-score: 9.09E-01 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04010 | |
| In Vivo Model | VillinCreErt2 and VillinCreErt2 APCfl/fl KRASG12D/+ C57BL/6J mouse model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Amino acid mass spectrometry assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Flow cytometry (SIINFEKL assays); T cell killing assay and clonogenic assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Sloppiness is defined by ribosomal frameshifting upon tryptophan shortage. MAPK pathway hyperactivation links sloppiness to cancer. Drug-resistant cancer cells remain sloppy and are targeted by T cells. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cabazitaxel | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Phosphorylation | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Oxytocin signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04921 | |
| In Vitro Model | DU145CR cells | prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
MS analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | Pathway analysis revealed that clusters in two cases showed up-regulation of the oxytocin (OXT) receptor-signaling pathway. Spatial gene expression analysis of CBZ-resistant prostate cancer tissues confirmed the heterogeneous expression of OXT-signaling molecules. We identified the OXT-signaling pathway as a potential target for CBZ-resistant CRPC using single-cell transcriptomic analysis of CTCs. CLO may potentially overcome CBZ resistance in CRPC by inhibiting the OXT-signaling pathway. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/BCR/PI signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | SUDHL-4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Blue Cell Viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p miRNAs appear to be the most potent regulators of the MAPk, BCR, and PI signaling system. Overexpression of miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p increases sensitivity to rituximab and doxorubicin. | |||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [4] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK/RAS signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A2780 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0134 |
| T24 cells | Bladder | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0554 | |
| HCT8 cells | Colon | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2478 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-634 is an important player in cisplatin-resistance. First of all, miR-634 was the only miR miR-634 overexpression in ovarian cancer cell lines and patient samples negatively regulates important cell-cycle genes (CCND1) and Ras-MAPk pathway components (GRB2, ERk2, RSk1 and RSk2). Inhibition of the Ras-MAPk pathway resulted in increased sensitivity to cisplatin, suggesting that the miR-634-mediated repression of this pathway is responsible for the effect of miR-634 on cisplatin resistance. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [7] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Fluorouracil | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | |
| In Vitro Model | SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | When miR-197 was overexpressed in SGC7901 cells, the protein levels of MAPk1 were downregulated. Furthermore, MAPk1 knockdown significantly increased the growth inhibition rate of the SGC7901/5-FU cells compared with those in the control group. These results indicated that miR-197 may influence the sensitivity of 5-FU treatment in a gastric cancer cell line by targeting MAPk1. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Paediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | [8] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Paediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia [ICD-11: 2B33.4] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Prednisolone | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| NF-kappaB signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | MLL/AF4+ RS4 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0093 |
| 697 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0079 | |
| Sup-B15 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0103 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | MAPk1 is a novel target of MIR335, and that MEk/ERk inhibitor treatment enhanced prednisolone-induced cell death through the activation of BIM (BCL2L11). | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Rituximab | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/BCR/PI signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | SUDHL-4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Blue Cell Viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p miRNAs appear to be the most potent regulators of the MAPk, BCR, and PI signaling system. Overexpression of miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p increases sensitivity to rituximab and doxorubicin. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Solamargine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 | |
| HGC27 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1279 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IncuCyte ZOOM Live-Cell analysis; TUNEL assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Solamargine increased the expression of lncNEAT1_2 via the inhibition of Erk1/2 MAPk signaling and promoted the apoptosis of GC cells. | |||
| Disease Class: Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | [9] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Gastric cancer [ICD-11: 2B72.1] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Solamargine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| MAPK signaling pathway | Inhibition | hsa04010 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MGC-803 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5334 |
| SGC7901 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0520 | |
| BGC823 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3360 | |
| AGS cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0139 | |
| HGC27 cells | Gastric | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1279 | |
| In Vivo Model | Nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IncuCyte ZOOM Live-Cell analysis; TUNEL assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Solamargine increased the expression of lncNEAT1_2 via the inhibition of Erk1/2 MAPk signaling and promoted the apoptosis of GC cells. | |||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | [6] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma [ICD-11: 2A81.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Rituximab/Doxorubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | MAPK/BCR/PI signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | SUDHL-4 cells | Peritoneal effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0539 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CellTiter-Blue Cell Viability assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p miRNAs appear to be the most potent regulators of the MAPk, BCR, and PI signaling system. Overexpression of miR370-3p, miR381-3p, and miR409-3p increases sensitivity to rituximab and doxorubicin. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Gastric tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Gastric cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.17E-01; Fold-change: 2.59E-01; Z-score: 7.08E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.70E-05; Fold-change: 3.19E-01; Z-score: 1.23E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Skin | |
| The Specified Disease | Melanoma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.72E-01; Fold-change: 3.29E-01; Z-score: 3.79E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.02E-01; Fold-change: 4.10E-01; Z-score: 5.67E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.87E-01; Fold-change: 3.89E-01; Z-score: 2.76E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

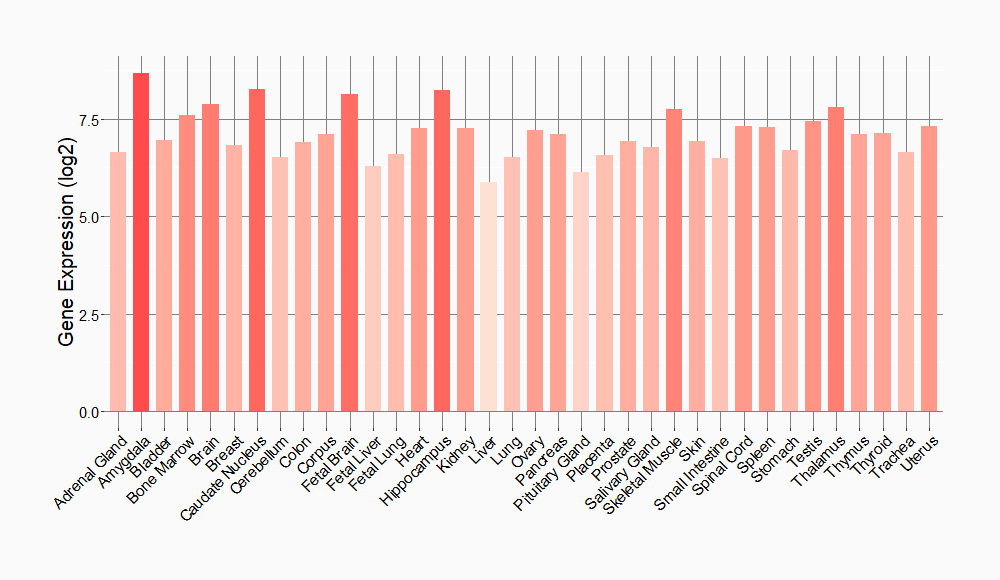
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
