Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00092)
| Name |
Isocitrate dehydrogenase NADP 2 (IDH2)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
IDH; ICD-M; IDP; NADP(+)-specific ICDH; Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
IDH2
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr15:90083045-90102477[-]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MAGYLRVVRSLCRASGSRPAWAPAALTAPTSQEQPRRHYADKRIKVAKPVVEMDGDEMTR
IIWQFIKEKLILPHVDIQLKYFDLGLPNRDQTDDQVTIDSALATQKYSVAVKCATITPDE ARVEEFKLKKMWKSPNGTIRNILGGTVFREPIICKNIPRLVPGWTKPITIGRHAHGDQYK ATDFVADRAGTFKMVFTPKDGSGVKEWEVYNFPAGGVGMGMYNTDESISGFAHSCFQYAI QKKWPLYMSTKNTILKAYDGRFKDIFQEIFDKHYKTDFDKNKIWYEHRLIDDMVAQVLKS SGGFVWACKNYDGDVQSDILAQGFGSLGLMTSVLVCPDGKTIEAEAAHGTVTRHYREHQK GRPTSTNPIASIFAWTRGLEHRGKLDGNQDLIRFAQMLEKVCVETVESGAMTKDLAGCIH GLSNVKLNEHFLNTTDFLDTIKSNLDRALGRQ Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Function |
Plays a role in intermediary metabolism and energy production. It may tightly associate or interact with the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
2 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.02] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Dichloroacetate | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Brain cancer [ICD-11: 2A00] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.21E-01 Fold-change: 9.39E-03 Z-score: 1.55E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | DBTRG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1169 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis; RT-qPCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Colorimetric SRB assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The potential of miR-144 overexpression to reduce GB cell malignancy, both by decreasing Cell migration and invasion abilities and by sensitizing resistant tumor cells to chemotherapy, paving the way to a novel and more effective GB therapy. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cytarabine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | HL-60 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0002 |
| KG-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0374 | |
| In Vivo Model | SPF-grade (BALB/C) nude mice model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR; Glycolysis metabolic enzyme assay; Flow cytometry; Western blot assay; Transcriptome sequencingc assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell proliferation assay; Drug sensitivity testing | |||
| Mechanism Description | OE-IDH2 in AML cells, enhances resistance to the Ara-C, promotes cell proliferation and glycolysis, and inhibits apoptosis. KD-IDH2 exhibits opposite effects. Both IDH2 mutations and OE-IDH2 produce similar effects on these cellular processes. The increase in glycolysis levels following IDH2 mutation may contribute to the reduced efficacy of Enasidenib in inhibiting the proliferation of IDH-mutant AML cells. Transcriptome sequencing results indicate an enrichment of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in IDH2-mutant AML cells. BEZ235 significantly inhibits the expression of phosphorylated PI3K (p-PI3K), phosphorylated Akt (p-Akt), mTOR, glycolytic metabolism, and Ara-C resistance both in vitro and in vivo. Overexpression and mutation of IDH2 coordinate with the Warburg effect through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway to promote Ara-C resistance in AML. | |||
Clinical Trial Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Hematologic Cancer [ICD-11: MG24.Y] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Hematologic Cancer [ICD-11: MG24.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172K (c.515G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
40
|
-
A
-
D
-
K
-
R
-
I
-
K
-
V
-
A
-
K
-
P
50
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
60
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
Q
-
F
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
70
|
-
L
-
I
-
L
-
P
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
Q
-
L
80
|
-
K
-
Y
-
F
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
R
90
|
-
D
-
Q
-
T
-
D
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
I
-
D
100
|
-
S
-
A
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
Y
-
S
-
V
110
|
-
A
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
120
|
-
E
-
A
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
130
|
-
K
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
140
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
150
|
-
E
-
P
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
160
|
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
S
K
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
A
-
D
-
R
-
A
190
|
-
G
-
T
-
F
-
K
-
M
-
V
-
F
-
T
-
P
-
K
200
|
-
D
-
G
-
S
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
E
-
W
-
E
-
V
210
|
-
Y
-
N
-
F
-
P
-
A
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
G
-
M
220
|
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
T
-
D
-
E
-
S
-
I
-
S
230
|
-
G
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
C
-
F
-
Q
-
Y
-
A
240
|
-
I
-
Q
-
K
-
K
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
M
-
S
250
|
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
A
-
Y
-
D
260
|
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
-
I
270
|
-
F
-
D
-
K
-
H
-
Y
-
K
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
D
280
|
-
K
-
N
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
L
290
|
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
V
-
L
-
K
300
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
V
-
W
-
A
-
C
-
K
310
|
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
-
I
320
|
-
L
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
F
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
-
L
330
|
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
-
G
340
|
-
K
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
-
G
350
|
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
E
-
H
-
Q
360
|
-
K
-
G
-
R
-
P
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
-
I
370
|
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
-
L
380
|
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
G
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
G
-
N
-
Q
390
|
-
D
-
L
-
I
-
R
-
F
-
A
-
Q
-
M
-
L
-
E
400
|
-
K
-
V
-
C
-
V
-
E
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
S
-
G
410
|
-
A
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
C
-
I
420
|
-
H
-
G
-
L
-
S
-
N
-
V
-
K
-
L
-
N
-
E
430
|
-
H
-
F
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
L
-
D
440
|
-
T
-
I
-
K
-
S
-
N
-
L
-
D
-
R
-
A
-
L
450
|
-
G
-
R
-
Q
-
S
-
L
-
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
460
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172K (c.515G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
40
|
-
A
-
D
-
K
-
R
-
I
-
K
-
V
-
A
-
K
-
P
50
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
60
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
Q
-
F
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
70
|
-
L
-
I
-
L
-
P
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
Q
-
L
80
|
-
K
-
Y
-
F
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
R
90
|
-
D
-
Q
-
T
-
D
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
I
-
D
100
|
-
S
-
A
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
Y
-
S
-
V
110
|
-
A
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
120
|
-
E
-
A
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
130
|
-
K
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
140
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
150
|
-
E
-
P
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
160
|
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
S
K
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
A
-
D
-
R
-
A
190
|
-
G
-
T
-
F
-
K
-
M
-
V
-
F
-
T
-
P
-
K
200
|
-
D
-
G
-
S
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
E
-
W
-
E
-
V
210
|
-
Y
-
N
-
F
-
P
-
A
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
G
-
M
220
|
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
T
-
D
-
E
-
S
-
I
-
S
230
|
-
G
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
C
-
F
-
Q
-
Y
-
A
240
|
-
I
-
Q
-
K
-
K
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
M
-
S
250
|
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
A
-
Y
-
D
260
|
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
-
I
270
|
-
F
-
D
-
K
-
H
-
Y
-
K
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
D
280
|
-
K
-
N
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
L
290
|
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
V
-
L
-
K
300
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
V
-
W
-
A
-
C
-
K
310
|
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
-
I
320
|
-
L
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
F
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
-
L
330
|
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
-
G
340
|
-
K
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
-
G
350
|
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
E
-
H
-
Q
360
|
-
K
-
G
-
R
-
P
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
-
I
370
|
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
-
L
380
|
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
G
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
G
-
N
-
Q
390
|
-
D
-
L
-
I
-
R
-
F
-
A
-
Q
-
M
-
L
-
E
400
|
-
K
-
V
-
C
-
V
-
E
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
S
-
G
410
|
-
A
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
C
-
I
420
|
-
H
-
G
-
L
-
S
-
N
-
V
-
K
-
L
-
N
-
E
430
|
-
H
-
F
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
L
-
D
440
|
-
T
-
I
-
K
-
S
-
N
-
L
-
D
-
R
-
A
-
L
450
|
-
G
-
R
-
Q
-
S
-
L
-
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
460
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | U87MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GP63 | |||||||||
| TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Acute myeloid leukemia xenograft mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140Q (c.419G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.54 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
40
|
A
A
D
D
K
K
R
R
I
I
K
K
V
V
A
A
K
K
P
P
50
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
D
D
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
F
F
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
70
|
L
L
I
I
L
L
P
P
H
H
V
V
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
80
|
K
K
Y
Y
F
F
D
D
L
L
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
R
R
90
|
D
D
Q
Q
T
T
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
I
I
D
D
100
|
S
S
A
A
L
L
A
A
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Y
Y
S
S
V
V
110
|
A
A
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
120
|
E
E
A
A
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
130
|
K
K
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
140
|
R
Q
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
150
|
E
E
P
P
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
160
|
L
L
V
V
P
P
G
G
W
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
K
R
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
A
A
D
D
R
R
A
A
190
|
G
G
T
T
F
F
K
K
M
M
V
V
F
F
T
T
P
P
K
K
200
|
D
D
G
G
S
S
G
G
V
V
K
K
E
E
W
W
E
E
V
V
210
|
Y
Y
N
N
F
F
P
P
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
M
M
220
|
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
T
T
D
D
E
E
S
S
I
I
S
S
230
|
G
G
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
C
C
F
F
Q
Q
Y
Y
A
A
240
|
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
K
K
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
250
|
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
A
A
Y
Y
D
D
260
|
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
I
I
270
|
F
F
D
D
K
K
H
H
Y
Y
K
K
T
T
D
D
F
F
D
D
280
|
K
K
N
N
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
L
L
290
|
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
K
K
300
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
G
G
F
F
V
V
W
W
A
A
C
C
K
K
310
|
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
I
I
320
|
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
F
F
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
330
|
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
G
G
340
|
K
K
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
G
G
350
|
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
360
|
K
K
G
G
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
I
I
370
|
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
L
L
380
|
E
E
H
H
R
R
G
G
K
K
L
L
D
D
G
G
N
N
Q
Q
390
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
R
R
F
F
A
A
Q
Q
M
M
L
L
E
E
400
|
K
K
V
V
C
C
V
V
E
E
T
T
V
V
E
E
S
S
G
G
410
|
A
A
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
G
G
C
C
I
I
420
|
H
H
G
G
L
L
S
S
N
N
V
V
K
K
L
L
N
N
E
E
430
|
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
T
T
T
T
D
D
F
F
L
L
D
D
440
|
T
T
I
I
K
K
S
S
N
N
L
L
D
D
R
R
A
A
L
L
450
|
G
G
R
R
Q
Q
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
460
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | U87MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GP63 | |||||||||
| TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | Acute myeloid leukemia xenograft mouse model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
IC50 assay | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Hematologic Cancer [ICD-11: MG24.Y] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Hematologic Cancer [ICD-11: MG24.Y] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140K (c.418_419delCGinsAA) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140G (c.418C>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140W (c.418C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140L (c.419G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172G (c.514A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172W (c.514A>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172M (c.515G>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [4] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172S (c.516G>C) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Continuous daily enasidenib treatment was generally well tolerated and induced hematologic responses in patients for whom prior AML therapy had failed. Inducing differentiation of myeloblasts, not cytotoxicity, seems to drive the clinical efficacy of enasidenib. | ||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172K (c.515G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
40
|
-
A
-
D
-
K
-
R
-
I
-
K
-
V
-
A
-
K
-
P
50
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
60
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
Q
-
F
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
70
|
-
L
-
I
-
L
-
P
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
Q
-
L
80
|
-
K
-
Y
-
F
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
R
90
|
-
D
-
Q
-
T
-
D
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
I
-
D
100
|
-
S
-
A
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
Y
-
S
-
V
110
|
-
A
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
120
|
-
E
-
A
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
130
|
-
K
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
140
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
150
|
-
E
-
P
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
160
|
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
S
K
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
A
-
D
-
R
-
A
190
|
-
G
-
T
-
F
-
K
-
M
-
V
-
F
-
T
-
P
-
K
200
|
-
D
-
G
-
S
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
E
-
W
-
E
-
V
210
|
-
Y
-
N
-
F
-
P
-
A
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
G
-
M
220
|
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
T
-
D
-
E
-
S
-
I
-
S
230
|
-
G
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
C
-
F
-
Q
-
Y
-
A
240
|
-
I
-
Q
-
K
-
K
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
M
-
S
250
|
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
A
-
Y
-
D
260
|
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
-
I
270
|
-
F
-
D
-
K
-
H
-
Y
-
K
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
D
280
|
-
K
-
N
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
L
290
|
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
V
-
L
-
K
300
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
V
-
W
-
A
-
C
-
K
310
|
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
-
I
320
|
-
L
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
F
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
-
L
330
|
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
-
G
340
|
-
K
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
-
G
350
|
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
E
-
H
-
Q
360
|
-
K
-
G
-
R
-
P
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
-
I
370
|
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
-
L
380
|
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
G
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
G
-
N
-
Q
390
|
-
D
-
L
-
I
-
R
-
F
-
A
-
Q
-
M
-
L
-
E
400
|
-
K
-
V
-
C
-
V
-
E
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
S
-
G
410
|
-
A
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
C
-
I
420
|
-
H
-
G
-
L
-
S
-
N
-
V
-
K
-
L
-
N
-
E
430
|
-
H
-
F
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
L
-
D
440
|
-
T
-
I
-
K
-
S
-
N
-
L
-
D
-
R
-
A
-
L
450
|
-
G
-
R
-
Q
-
S
-
L
-
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
460
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | U87MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GP63 | |||||||||
| TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | ||||||||||
| TF-1a cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3608 | ||||||||||
| IDH2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D3DY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic gain-of-function mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDH) 1 and 2 are found in multiple hematologic and solid tumors, leading to accumulation of the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). 2HG competitively inhibits alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases and methylcytosine dioxygenases of the TET family, causing epigenetic dysregulation and a block in cellular differentiation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Colorectal cancer [ICD-11: 2B91.1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172K (c.515G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
40
|
-
A
-
D
-
K
-
R
-
I
-
K
-
V
-
A
-
K
-
P
50
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
60
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
Q
-
F
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
70
|
-
L
-
I
-
L
-
P
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
Q
-
L
80
|
-
K
-
Y
-
F
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
R
90
|
-
D
-
Q
-
T
-
D
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
I
-
D
100
|
-
S
-
A
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
Y
-
S
-
V
110
|
-
A
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
120
|
-
E
-
A
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
130
|
-
K
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
140
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
150
|
-
E
-
P
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
160
|
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
S
K
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
A
-
D
-
R
-
A
190
|
-
G
-
T
-
F
-
K
-
M
-
V
-
F
-
T
-
P
-
K
200
|
-
D
-
G
-
S
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
E
-
W
-
E
-
V
210
|
-
Y
-
N
-
F
-
P
-
A
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
G
-
M
220
|
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
T
-
D
-
E
-
S
-
I
-
S
230
|
-
G
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
C
-
F
-
Q
-
Y
-
A
240
|
-
I
-
Q
-
K
-
K
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
M
-
S
250
|
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
A
-
Y
-
D
260
|
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
-
I
270
|
-
F
-
D
-
K
-
H
-
Y
-
K
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
D
280
|
-
K
-
N
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
L
290
|
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
V
-
L
-
K
300
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
V
-
W
-
A
-
C
-
K
310
|
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
-
I
320
|
-
L
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
F
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
-
L
330
|
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
-
G
340
|
-
K
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
-
G
350
|
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
E
-
H
-
Q
360
|
-
K
-
G
-
R
-
P
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
-
I
370
|
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
-
L
380
|
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
G
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
G
-
N
-
Q
390
|
-
D
-
L
-
I
-
R
-
F
-
A
-
Q
-
M
-
L
-
E
400
|
-
K
-
V
-
C
-
V
-
E
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
S
-
G
410
|
-
A
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
C
-
I
420
|
-
H
-
G
-
L
-
S
-
N
-
V
-
K
-
L
-
N
-
E
430
|
-
H
-
F
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
L
-
D
440
|
-
T
-
I
-
K
-
S
-
N
-
L
-
D
-
R
-
A
-
L
450
|
-
G
-
R
-
Q
-
S
-
L
-
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
460
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | U87MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GP63 | |||||||||
| TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | ||||||||||
| TF-1a cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3608 | ||||||||||
| IDH2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D3DY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic gain-of-function mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDH) 1 and 2 are found in multiple hematologic and solid tumors, leading to accumulation of the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). 2HG competitively inhibits alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases and methylcytosine dioxygenases of the TET family, causing epigenetic dysregulation and a block in cellular differentiation. | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | [5] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | Enasidenib | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140Q (c.419G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.54 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
40
|
A
A
D
D
K
K
R
R
I
I
K
K
V
V
A
A
K
K
P
P
50
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
D
D
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
F
F
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
70
|
L
L
I
I
L
L
P
P
H
H
V
V
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
80
|
K
K
Y
Y
F
F
D
D
L
L
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
R
R
90
|
D
D
Q
Q
T
T
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
I
I
D
D
100
|
S
S
A
A
L
L
A
A
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Y
Y
S
S
V
V
110
|
A
A
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
120
|
E
E
A
A
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
130
|
K
K
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
140
|
R
Q
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
150
|
E
E
P
P
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
160
|
L
L
V
V
P
P
G
G
W
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
K
R
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
A
A
D
D
R
R
A
A
190
|
G
G
T
T
F
F
K
K
M
M
V
V
F
F
T
T
P
P
K
K
200
|
D
D
G
G
S
S
G
G
V
V
K
K
E
E
W
W
E
E
V
V
210
|
Y
Y
N
N
F
F
P
P
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
M
M
220
|
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
T
T
D
D
E
E
S
S
I
I
S
S
230
|
G
G
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
C
C
F
F
Q
Q
Y
Y
A
A
240
|
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
K
K
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
250
|
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
A
A
Y
Y
D
D
260
|
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
I
I
270
|
F
F
D
D
K
K
H
H
Y
Y
K
K
T
T
D
D
F
F
D
D
280
|
K
K
N
N
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
L
L
290
|
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
K
K
300
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
G
G
F
F
V
V
W
W
A
A
C
C
K
K
310
|
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
I
I
320
|
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
F
F
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
330
|
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
G
G
340
|
K
K
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
G
G
350
|
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
360
|
K
K
G
G
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
I
I
370
|
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
L
L
380
|
E
E
H
H
R
R
G
G
K
K
L
L
D
D
G
G
N
N
Q
Q
390
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
R
R
F
F
A
A
Q
Q
M
M
L
L
E
E
400
|
K
K
V
V
C
C
V
V
E
E
T
T
V
V
E
E
S
S
G
G
410
|
A
A
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
G
G
C
C
I
I
420
|
H
H
G
G
L
L
S
S
N
N
V
V
K
K
L
L
N
N
E
E
430
|
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
T
T
T
T
D
D
F
F
L
L
D
D
440
|
T
T
I
I
K
K
S
S
N
N
L
L
D
D
R
R
A
A
L
L
450
|
G
G
R
R
Q
Q
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
460
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | U87MG cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_GP63 | |||||||||
| TF-1 cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | ||||||||||
| TF-1a cells | Bone marrow | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3608 | ||||||||||
| IDH2 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_D3DY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | NSG mouse PDX model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | Somatic gain-of-function mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenases (IDH) 1 and 2 are found in multiple hematologic and solid tumors, leading to accumulation of the oncometabolite (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate (2HG). 2HG competitively inhibits alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including histone demethylases and methylcytosine dioxygenases of the TET family, causing epigenetic dysregulation and a block in cellular differentiation. | ||||||||||||
Preclinical Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [6] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | AGI-6780 | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140Q (c.419G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.54 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
40
|
A
A
D
D
K
K
R
R
I
I
K
K
V
V
A
A
K
K
P
P
50
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
D
D
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
F
F
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
70
|
L
L
I
I
L
L
P
P
H
H
V
V
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
80
|
K
K
Y
Y
F
F
D
D
L
L
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
R
R
90
|
D
D
Q
Q
T
T
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
I
I
D
D
100
|
S
S
A
A
L
L
A
A
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Y
Y
S
S
V
V
110
|
A
A
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
120
|
E
E
A
A
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
130
|
K
K
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
140
|
R
Q
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
150
|
E
E
P
P
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
160
|
L
L
V
V
P
P
G
G
W
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
K
R
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
A
A
D
D
R
R
A
A
190
|
G
G
T
T
F
F
K
K
M
M
V
V
F
F
T
T
P
P
K
K
200
|
D
D
G
G
S
S
G
G
V
V
K
K
E
E
W
W
E
E
V
V
210
|
Y
Y
N
N
F
F
P
P
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
M
M
220
|
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
T
T
D
D
E
E
S
S
I
I
S
S
230
|
G
G
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
C
C
F
F
Q
Q
Y
Y
A
A
240
|
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
K
K
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
250
|
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
A
A
Y
Y
D
D
260
|
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
I
I
270
|
F
F
D
D
K
K
H
H
Y
Y
K
K
T
T
D
D
F
F
D
D
280
|
K
K
N
N
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
L
L
290
|
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
K
K
300
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
G
G
F
F
V
V
W
W
A
A
C
C
K
K
310
|
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
I
I
320
|
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
F
F
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
330
|
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
G
G
340
|
K
K
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
G
G
350
|
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
360
|
K
K
G
G
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
I
I
370
|
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
L
L
380
|
E
E
H
H
R
R
G
G
K
K
L
L
D
D
G
G
N
N
Q
Q
390
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
R
R
F
F
A
A
Q
Q
M
M
L
L
E
E
400
|
K
K
V
V
C
C
V
V
E
E
T
T
V
V
E
E
S
S
G
G
410
|
A
A
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
G
G
C
C
I
I
420
|
H
H
G
G
L
L
S
S
N
N
V
V
K
K
L
L
N
N
E
E
430
|
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
T
T
T
T
D
D
F
F
L
L
D
D
440
|
T
T
I
I
K
K
S
S
N
N
L
L
D
D
R
R
A
A
L
L
450
|
G
G
R
R
Q
Q
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
460
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | Blood | N.A. | |||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R140Q (c.419G>A) in gene IDH2 cause the sensitivity of AGI-6780 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | IDH2 inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R172K (c.515G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
40
|
-
A
-
D
-
K
-
R
-
I
-
K
-
V
-
A
-
K
-
P
50
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
60
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
Q
-
F
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
70
|
-
L
-
I
-
L
-
P
-
H
-
V
-
D
-
I
-
Q
-
L
80
|
-
K
-
Y
-
F
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
R
90
|
-
D
-
Q
-
T
-
D
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
I
-
D
100
|
-
S
-
A
-
L
-
A
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
Y
-
S
-
V
110
|
-
A
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
120
|
-
E
-
A
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
130
|
-
K
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
140
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
150
|
-
E
-
P
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
160
|
-
L
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
S
K
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
A
-
D
-
R
-
A
190
|
-
G
-
T
-
F
-
K
-
M
-
V
-
F
-
T
-
P
-
K
200
|
-
D
-
G
-
S
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
E
-
W
-
E
-
V
210
|
-
Y
-
N
-
F
-
P
-
A
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
G
-
M
220
|
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
T
-
D
-
E
-
S
-
I
-
S
230
|
-
G
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
C
-
F
-
Q
-
Y
-
A
240
|
-
I
-
Q
-
K
-
K
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
M
-
S
250
|
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
A
-
Y
-
D
260
|
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
-
I
270
|
-
F
-
D
-
K
-
H
-
Y
-
K
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
D
280
|
-
K
-
N
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
L
290
|
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
V
-
L
-
K
300
|
-
S
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
V
-
W
-
A
-
C
-
K
310
|
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
-
I
320
|
-
L
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
F
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
-
L
330
|
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
-
G
340
|
-
K
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
-
G
350
|
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
E
-
H
-
Q
360
|
-
K
-
G
-
R
-
P
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
-
I
370
|
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
-
L
380
|
-
E
-
H
-
R
-
G
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
G
-
N
-
Q
390
|
-
D
-
L
-
I
-
R
-
F
-
A
-
Q
-
M
-
L
-
E
400
|
-
K
-
V
-
C
-
V
-
E
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
S
-
G
410
|
-
A
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
G
-
C
-
I
420
|
-
H
-
G
-
L
-
S
-
N
-
V
-
K
-
L
-
N
-
E
430
|
-
H
-
F
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
L
-
D
440
|
-
T
-
I
-
K
-
S
-
N
-
L
-
D
-
R
-
A
-
L
450
|
-
G
-
R
-
Q
-
S
-
L
-
E
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
460
|
-
H
-
H
-
H
-
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [3] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Drug | IDH2 inhibitors | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R140Q (c.419G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.10 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.54 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
40
|
A
A
D
D
K
K
R
R
I
I
K
K
V
V
A
A
K
K
P
P
50
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
D
D
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
60
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
Q
Q
F
F
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
70
|
L
L
I
I
L
L
P
P
H
H
V
V
D
D
I
I
Q
Q
L
L
80
|
K
K
Y
Y
F
F
D
D
L
L
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
R
R
90
|
D
D
Q
Q
T
T
D
D
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
I
I
D
D
100
|
S
S
A
A
L
L
A
A
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
Y
Y
S
S
V
V
110
|
A
A
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
120
|
E
E
A
A
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
130
|
K
K
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
140
|
R
Q
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
150
|
E
E
P
P
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
160
|
L
L
V
V
P
P
G
G
W
W
T
T
K
K
P
P
I
I
T
T
170
|
I
I
G
G
K
R
H
H
A
A
H
H
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
180
|
K
K
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
A
A
D
D
R
R
A
A
190
|
G
G
T
T
F
F
K
K
M
M
V
V
F
F
T
T
P
P
K
K
200
|
D
D
G
G
S
S
G
G
V
V
K
K
E
E
W
W
E
E
V
V
210
|
Y
Y
N
N
F
F
P
P
A
A
G
G
G
G
V
V
G
G
M
M
220
|
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
T
T
D
D
E
E
S
S
I
I
S
S
230
|
G
G
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
C
C
F
F
Q
Q
Y
Y
A
A
240
|
I
I
Q
Q
K
K
K
K
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
M
M
S
S
250
|
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
A
A
Y
Y
D
D
260
|
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
I
I
270
|
F
F
D
D
K
K
H
H
Y
Y
K
K
T
T
D
D
F
F
D
D
280
|
K
K
N
N
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
L
L
290
|
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
V
V
L
L
K
K
300
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
G
G
F
F
V
V
W
W
A
A
C
C
K
K
310
|
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
I
I
320
|
L
L
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
F
F
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
L
L
330
|
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
G
G
340
|
K
K
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
G
G
350
|
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
E
E
H
H
Q
Q
360
|
K
K
G
G
R
R
P
P
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
I
I
370
|
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
L
L
380
|
E
E
H
H
R
R
G
G
K
K
L
L
D
D
G
G
N
N
Q
Q
390
|
D
D
L
L
I
I
R
R
F
F
A
A
Q
Q
M
M
L
L
E
E
400
|
K
K
V
V
C
C
V
V
E
E
T
T
V
V
E
E
S
S
G
G
410
|
A
A
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
G
G
C
C
I
I
420
|
H
H
G
G
L
L
S
S
N
N
V
V
K
K
L
L
N
N
E
E
430
|
H
H
F
F
L
L
N
N
T
T
T
T
D
D
F
F
L
L
D
D
440
|
T
T
I
I
K
K
S
S
N
N
L
L
D
D
R
R
A
A
L
L
450
|
G
G
R
R
Q
Q
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
460
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
-
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Nervous tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Brain cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.21E-01; Fold-change: -6.37E-02; Z-score: -1.02E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
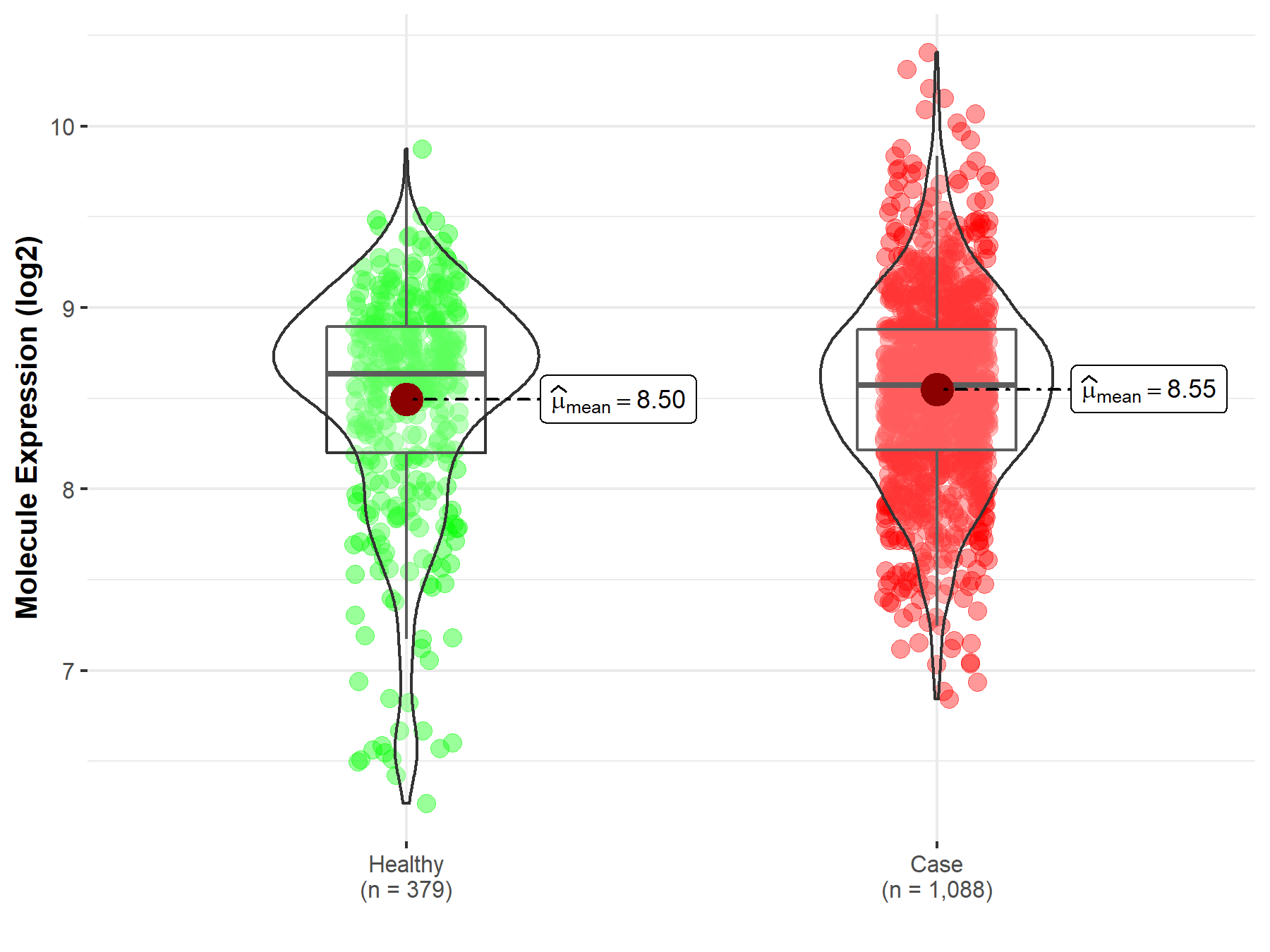
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 5.29E-01; Fold-change: 3.97E-01; Z-score: 6.63E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
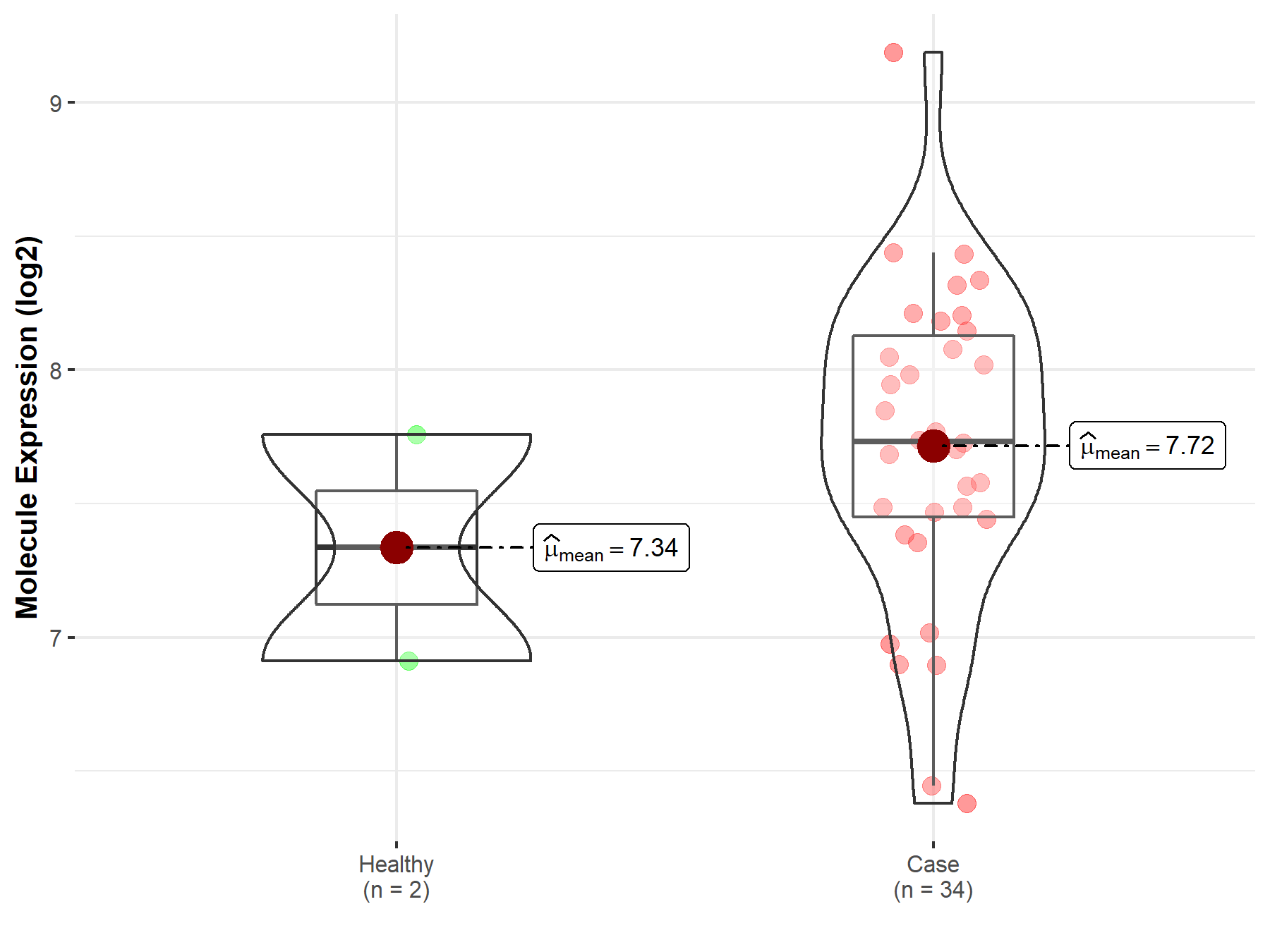
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | White matter | |
| The Specified Disease | Glioma | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 7.86E-01; Fold-change: -4.82E-02; Z-score: -1.50E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
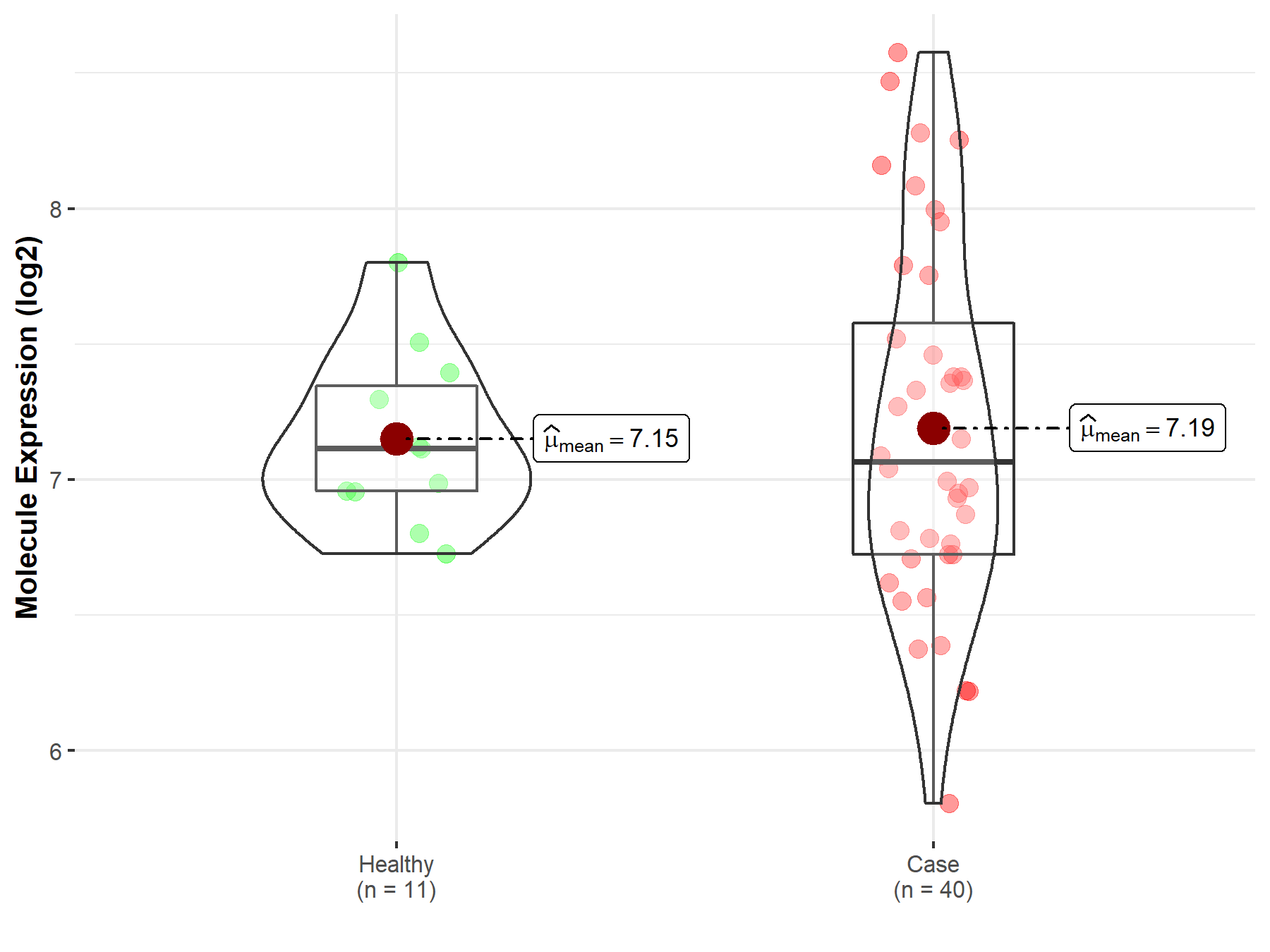
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| The Studied Tissue | Brainstem tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Neuroectodermal tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 4.48E-01; Fold-change: 2.57E-01; Z-score: 5.98E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
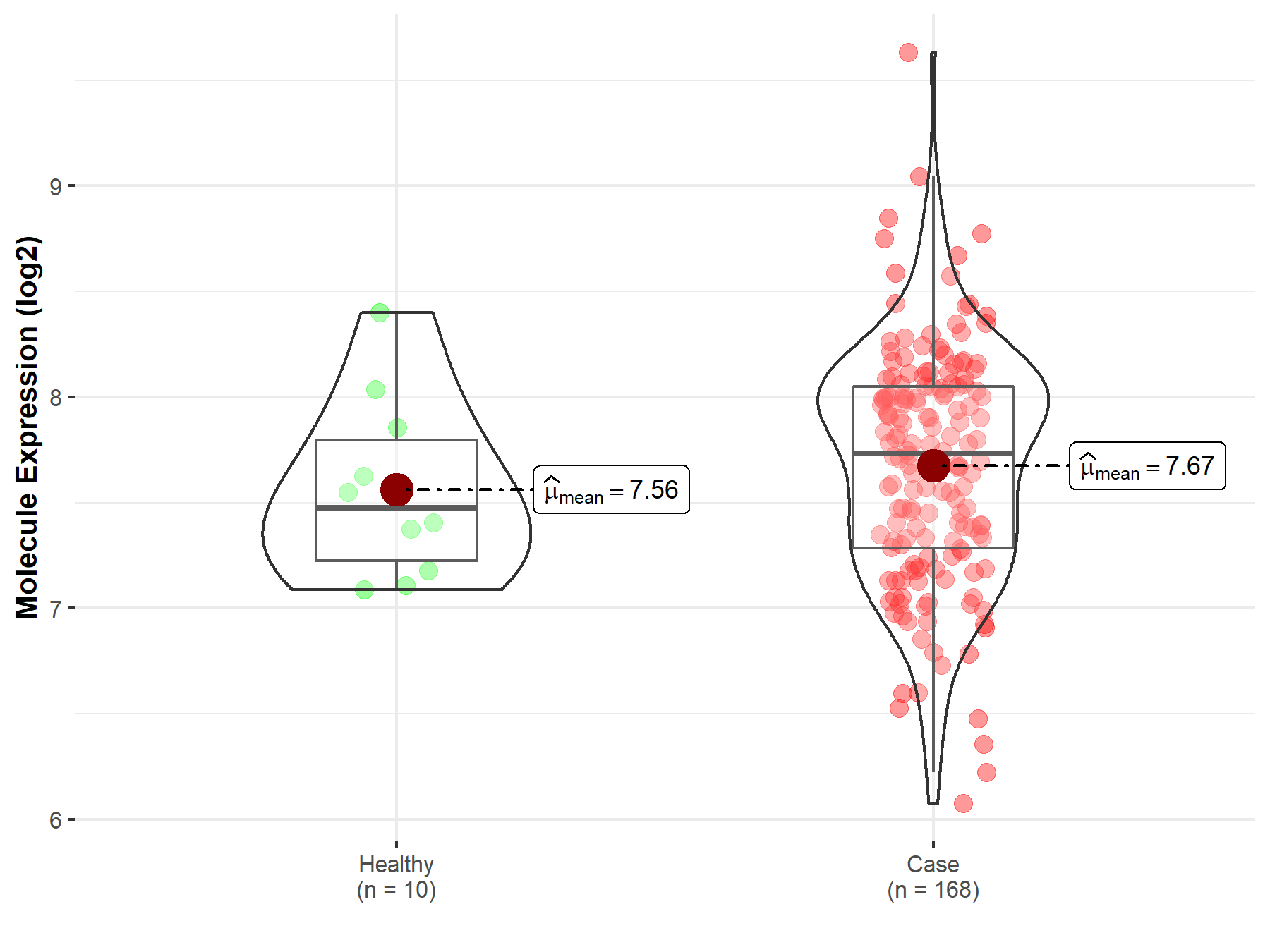
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Bone marrow | |
| The Specified Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 6.06E-02; Fold-change: 1.15E-01; Z-score: 2.41E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
