Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00044)
| Name |
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1A (CDKN1A)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
CDK-interacting protein 1; Melanoma differentiation-associated protein 6; MDA-6; p21; CAP20; CDKN1; CIP1; MDA6; PIC1; SDI1; WAF1
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
CDKN1A
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chr6:36676460-36687337[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MSEPAGDVRQNPCGSKACRRLFGPVDSEQLSRDCDALMAGCIQEARERWNFDFVTETPLE
GDFAWERVRGLGLPKLYLPTGPRRGRDELGGGRRPGTSPALLQGTAEEDHVDLSLSCTLV PRSGEQAEGSPGGPGDSQGRKRRQTSMTDFYHSKRRLIFSKRKP Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
May be involved in p53/TP53 mediated inhibition of cellular proliferation in response to DNA damage. Binds to and inhibits cyclin-dependent kinase activity, preventing phosphorylation of critical cyclin-dependent kinase substrates and blocking cell cycle progression. Functions in the nuclear localization and assembly of cyclin D-CDK4 complex and promotes its kinase activity towards RB1. At higher stoichiometric ratios, inhibits the kinase activity of the cyclin D-CDK4 complex. Inhibits DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase delta by competing with POLD3 for PCNA binding. Plays an important role in controlling cell cycle progression and DNA damage-induced G2 arrest.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Approved Drug(s)
6 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-01 Fold-change: -7.82E-02 Z-score: -1.08E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| p21 | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| p21 | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-224 could promote the in vitro and in vivo DDP resistance of LA cells via regulating G1/S cell cycle transition and apoptosis. p21WAF1/CIP1, a potent cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, was identified as the direct and functional target gene of miR-224. Overexpression of p21WAF1/CIP1 could phenocopy the effect of miR-224 downregulation and silencing of p21WAF1/CIP1 could partially reverse the effect of miR-224 downregulation on DDP resistance of DDP-resistant LA cells. In addition, miR-224 could affect the G1/S transition of cell cycle and apoptosis in LA cells through the p21WAF1/CIP1-pRb pathway and the intrinsic mitochondrial death pathway. Furthermore, miR-224 was found to be downregulated in DDP-responding LA tissues, and its expression was inversely correlated with p21WAF1/CIP1. Multivariate analyses indicated that the status of miR-224 might be an independent prognostic factor for predicting the survival of LA patients. | |||
| Disease Class: Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.38E-16 Fold-change: -8.94E-02 Z-score: -8.67E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| A549/DDP cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 | |
| In Vivo Model | BALB/c nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Upregulation of HOTAIR contributes to the cisplatin resistance of LAD cells, at least in part, through the regulation of p21 expression. | |||
| Disease Class: Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | [6] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Cervical cancer [ICD-11: 2C77.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | Hela cells | Cervix uteri | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0030 |
| HeLa/DDP cells | Uterus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_C869 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK8 assay; EdU assay; Flow cytometric analysis | |||
| Mechanism Description | UCA1 suppressed apoptosis by downregulating caspase 3 and upregulating CDk2, whereas enhanced cell proliferation by increased level of survivin and decreased level of p21. | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.5] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.79E-01 Fold-change: -7.82E-02 Z-score: -1.08E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Inhibition | hsa05200 | ||
| NER signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | ||
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Alamar blue assay; EdU cell proliferation assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | miR-33-3b-3p exerted a critical role in modulating the cisplatin sensitivity of lung cancer cells, which might probably through suppressing the p21 expression. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prolactin-secreting adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.Y] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prolactin-secreting adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Bromocriptine | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| Cell migration | Activation | hsa04670 | ||
| In Vitro Model | C4-2 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4782 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Knockdown of mir-93 increased the sensitivity of MMQ cells to bromocriptine treatment, and these effects were abolished when p21 was knocked-down using siRNA. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Prolactin-secreting adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.Y] | [5] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Prolactin-secreting adenoma [ICD-11: 2F37.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cabergoline | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | C4-2 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_4782 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Knockdown of mir-93 increased the sensitivity of MMQ cells to bromocriptine treatment, and these effects were abolished when p21 was knocked-down using siRNA. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C60.1] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Eribulin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Notch signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04330 | |
| JAK-STAT signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04630 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 ER cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Annexin V/PI assay; MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | We confirmed that BYL-719 could inhibit BCSC-like cell proliferation in 3D cultures and that the stemness characteristics of BCSC-like cells were inhibited. The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway could be inhibited by BYL-719, and the Notch, JAK-STAT and MAPK/ERK signaling pathways which have crosstalk in the tumor microenvironment (TME) are also inhibited. By comparing eribulin-resistant breast cancer cell lines, we confirmed that BYL-719 could effectively overcome drug resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | [7] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Acute myeloid leukemia [ICD-11: 2A60.0] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Idarubicin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | DNA Damage Response Mechanism | Regulation | N.A. | |
| In Vitro Model | MV-4-11 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0064 |
| MOLM-13 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_2119 | |
| Kasumi-1 cells | Peripheral blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0589 | |
| TF-1 cells | Blood | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0559 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
RT-qPCR; Western blot assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay; Trypan blue assay; Clonogenicity assay; IC50 assay; Flow cytometry assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | DNA Damage Response Mechanism (DDR) comprises numerous molecules and pathways intended to arrest the cell cycle until DNA damage is repaired or else drive the cell to apoptosis.DDR regulators demonstrate increased expression in patients with high cytogenetic risk possibly reflecting increased genotoxic stress.Using PCR arrays we observed an upregulation of of several DDR genes (CDKN1A, GADD45A, GADD45G, EXO1, and PPP1R15A) in KASUMI-1 and MV4-11 cell lines that survived following treatment with Idarubicin and Cytarabine. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | [8] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Tamoxifen | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Inhibition | hsa04210 | |
| Cell proliferation | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | MCF-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0031 |
| BT474 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0179 | |
| MCF7/TAMR cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_EG55 | |
| CAMA-1 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1115 | |
| HEK293 FT cells | Kidney | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6911 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Promega assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Tamoxifen-resistant cells express miRNA-519a at high levels, which directly represses the expression of PTEN, RB1, and CDkN1A, central nodes of a dense network, allowing the cells to proliferate, even in the presence of tamoxifen. miRNA-519a increases viability and S-phase population of the cell cycle, but does not affect EMT or invasion. miRNA-519a-expressing cells evade tamoxifen-induced apoptosis. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 9.38E-16; Fold-change: -5.57E-01; Z-score: -6.54E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 2.03E-20; Fold-change: -1.02E+00; Z-score: -1.03E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Breast tissue | |
| The Specified Disease | Breast cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.34E-01; Fold-change: 1.70E-01; Z-score: 2.41E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 5.31E-04; Fold-change: -4.08E-01; Z-score: -4.98E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
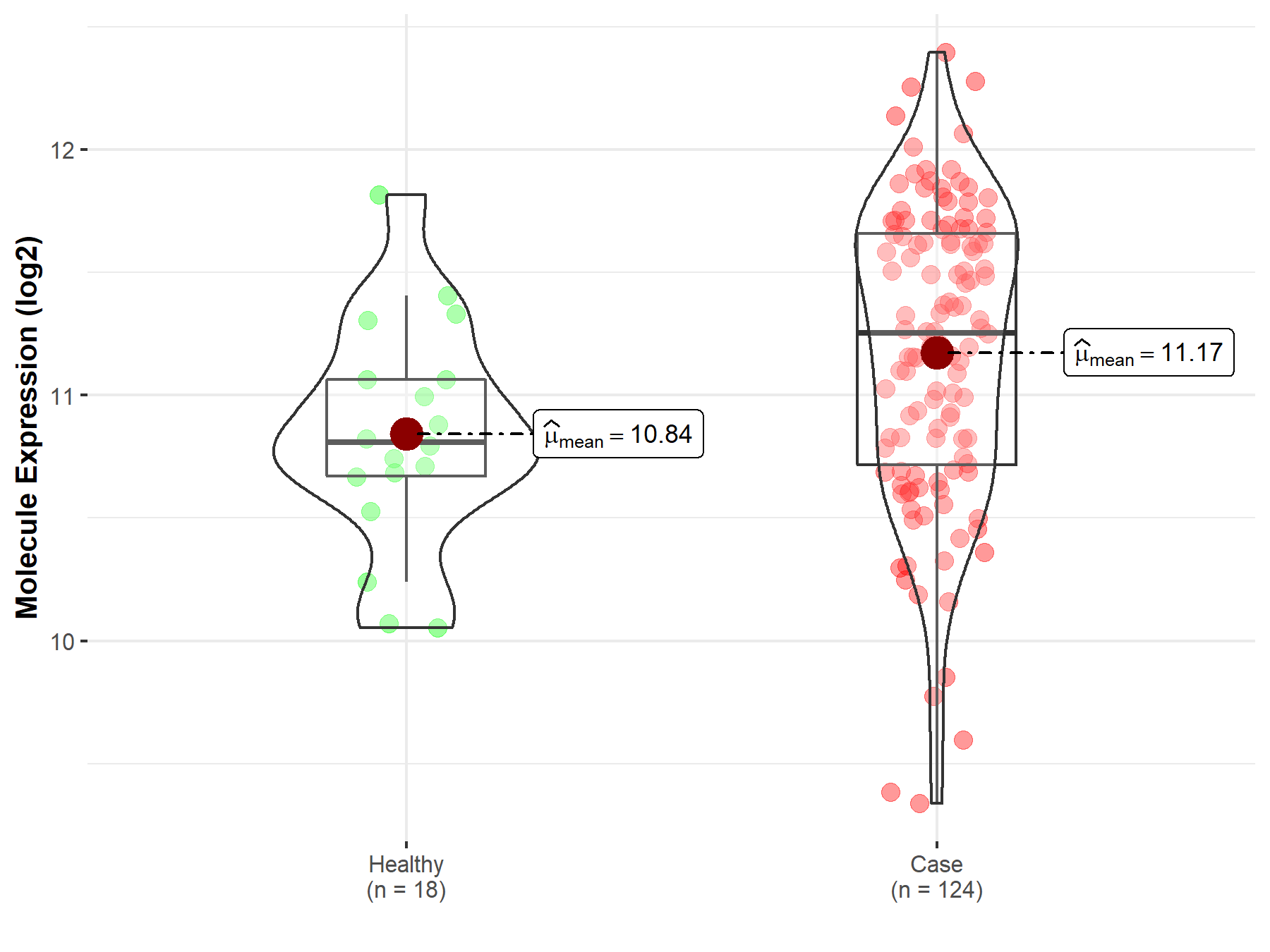
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Cervix uteri | |
| The Specified Disease | Cervical cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.13E-02; Fold-change: 4.46E-01; Z-score: 9.68E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
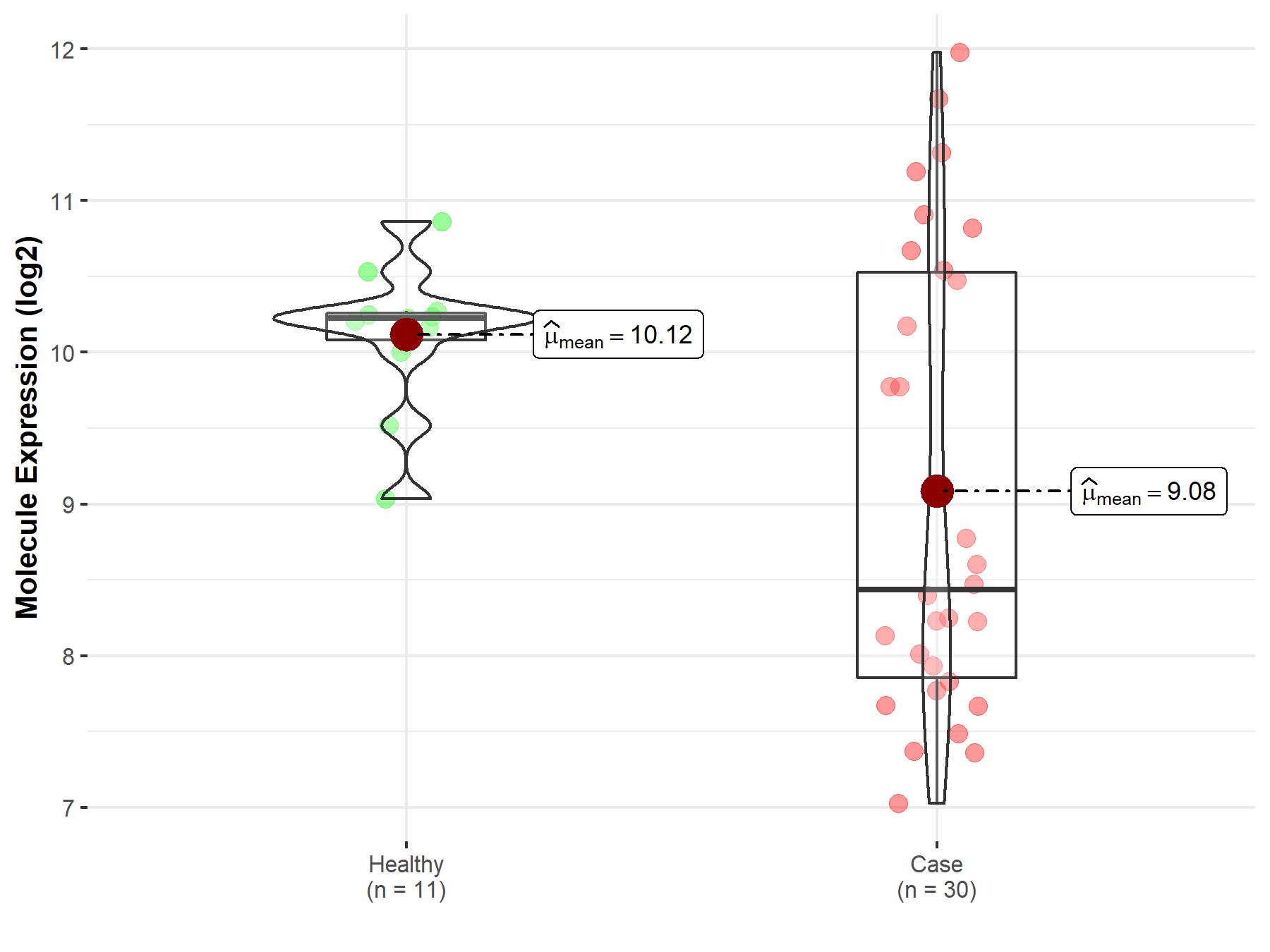
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 2.02E-03; Fold-change: -1.79E+00; Z-score: -3.70E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
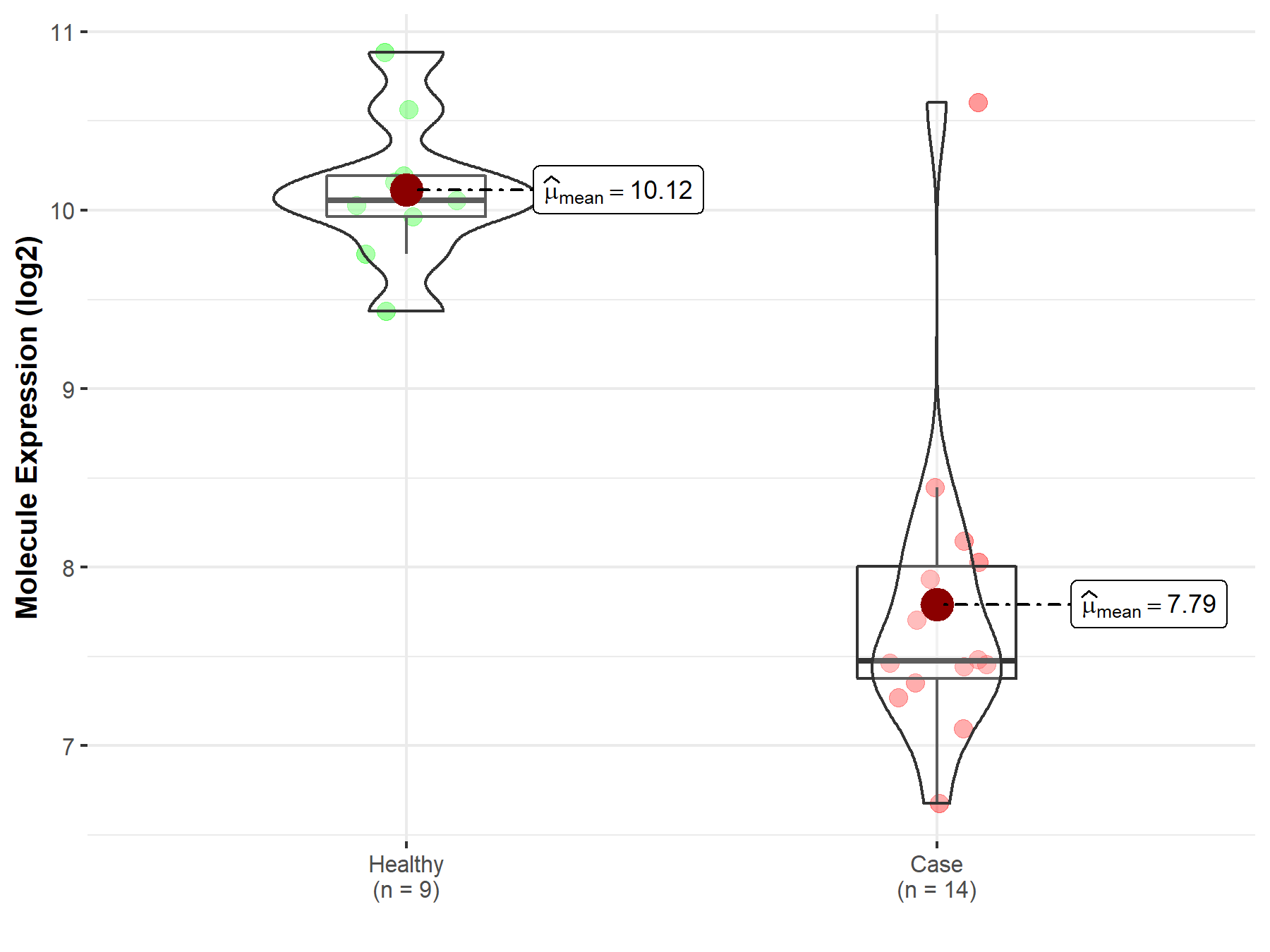
| The Studied Tissue | Pituitary | |
| The Specified Disease | Pituitary gonadotrope tumor | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.09E-07; Fold-change: -2.58E+00; Z-score: -6.10E+00 | |
|
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
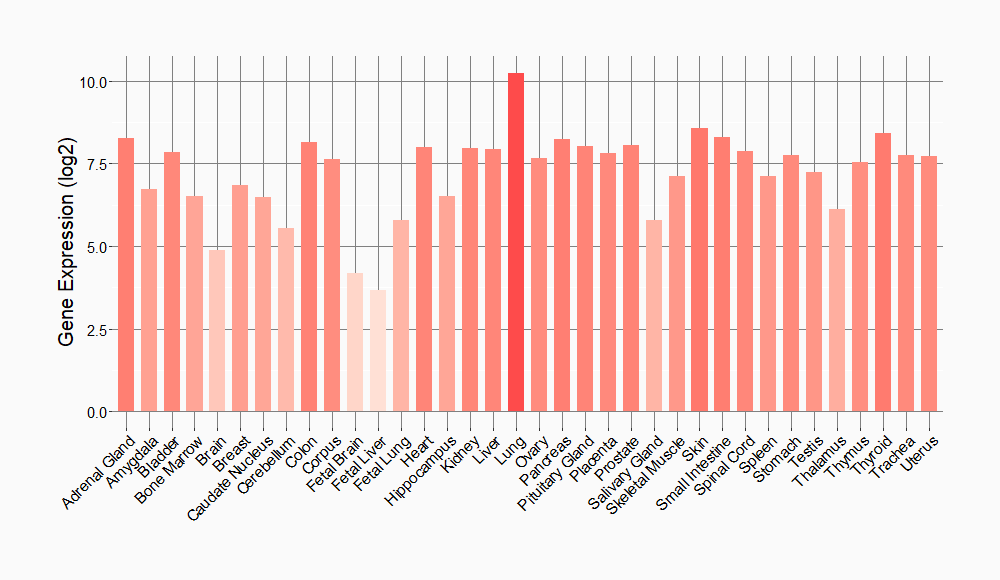
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
