Molecule Information
General Information of the Molecule (ID: Mol00020)
| Name |
Copper-transporting ATPase 1 (ATP7A)
,Homo sapiens
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Copper pump 1; Menkes disease-associated protein; MC1; MNK
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Molecule Type |
Protein
|
||||
| Gene Name |
ATP7A
|
||||
| Gene ID | |||||
| Location |
chrX:77910690-78050395[+]
|
||||
| Sequence |
MDPSMGVNSVTISVEGMTCNSCVWTIEQQIGKVNGVHHIKVSLEEKNATIIYDPKLQTPK
TLQEAIDDMGFDAVIHNPDPLPVLTDTLFLTVTASLTLPWDHIQSTLLKTKGVTDIKIYP QKRTVAVTIIPSIVNANQIKELVPELSLDTGTLEKKSGACEDHSMAQAGEVVLKMKVEGM TCHSCTSTIEGKIGKLQGVQRIKVSLDNQEATIVYQPHLISVEEMKKQIEAMGFPAFVKK QPKYLKLGAIDVERLKNTPVKSSEGSQQRSPSYTNDSTATFIIDGMHCKSCVSNIESTLS ALQYVSSIVVSLENRSAIVKYNASSVTPESLRKAIEAVSPGLYRVSITSEVESTSNSPSS SSLQKIPLNVVSQPLTQETVINIDGMTCNSCVQSIEGVISKKPGVKSIRVSLANSNGTVE YDPLLTSPETLRGAIEDMGFDATLSDTNEPLVVIAQPSSEMPLLTSTNEFYTKGMTPVQD KEEGKNSSKCYIQVTGMTCASCVANIERNLRREEGIYSILVALMAGKAEVRYNPAVIQPP MIAEFIRELGFGATVIENADEGDGVLELVVRGMTCASCVHKIESSLTKHRGILYCSVALA TNKAHIKYDPEIIGPRDIIHTIESLGFEASLVKKDRSASHLDHKREIRQWRRSFLVSLFF CIPVMGLMIYMMVMDHHFATLHHNQNMSKEEMINLHSSMFLERQILPGLSVMNLLSFLLC VPVQFFGGWYFYIQAYKALKHKTANMDVLIVLATTIAFAYSLIILLVAMYERAKVNPITF FDTPPMLFVFIALGRWLEHIAKGKTSEALAKLISLQATEATIVTLDSDNILLSEEQVDVE LVQRGDIIKVVPGGKFPVDGRVIEGHSMVDESLITGEAMPVAKKPGSTVIAGSINQNGSL LICATHVGADTTLSQIVKLVEEAQTSKAPIQQFADKLSGYFVPFIVFVSIATLLVWIVIG FLNFEIVETYFPGYNRSISRTETIIRFAFQASITVLCIACPCSLGLATPTAVMVGTGVGA QNGILIKGGEPLEMAHKVKVVVFDKTGTITHGTPVVNQVKVLTESNRISHHKILAIVGTA ESNSEHPLGTAITKYCKQELDTETLGTCIDFQVVPGCGISCKVTNIEGLLHKNNWNIEDN NIKNASLVQIDASNEQSSTSSSMIIDAQISNALNAQQYKVLIGNREWMIRNGLVINNDVN DFMTEHERKGRTAVLVAVDDELCGLIAIADTVKPEAELAIHILKSMGLEVVLMTGDNSKT ARSIASQVGITKVFAEVLPSHKVAKVKQLQEEGKRVAMVGDGINDSPALAMANVGIAIGT GTDVAIEAADVVLIRNDLLDVVASIDLSRKTVKRIRINFVFALIYNLVGIPIAAGVFMPI GLVLQPWMGSAAMAASSVSVVLSSLFLKLYRKPTYESYELPARSQIGQKSPSEISVHVGI DDTSRNSPKLGLLDRIVNYSRASINSLLSDKRSLNSVVTSEPDKHSLLVGDFREDDDTAL Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| 3D-structure |
|
||||
| Function |
ATP-driven copper (Cu(+)) ion pump that plays an important role in intracellular copper ion homeostasis. Within a catalytic cycle, acquires Cu(+) ion from donor protein on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and delivers it to acceptor protein on the lumenal side. The transfer of Cu(+) ion across the membrane is coupled to ATP hydrolysis and is associated with a transient phosphorylation that shifts the pump conformation from inward-facing to outward-facing state. Under physiological conditions, at low cytosolic copper concentration, it is localized at the trans-Golgi network (TGN) where it transfers Cu(+) ions to cuproenzymes of the secretory pathway. Upon elevated cytosolic copper concentrations, it relocalizes to the plasma membrane where it is responsible for the export of excess Cu(+) ions. May play a dual role in neuron function and survival by regulating cooper efflux and neuronal transmission at the synapse as well as by supplying Cu(+) ions to enzymes such as PAM, TYR and SOD3. In the melanosomes of pigmented cells, provides copper cofactor to TYR to form an active TYR holoenzyme for melanin biosynthesis.
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Uniprot ID | |||||
| Ensembl ID | |||||
| HGNC ID | |||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Complete Species Lineage | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Molecule
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Drug
Investigative Drug(s)
1 drug(s) in total
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Non-small cell lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25.Y] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Platinum | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Lung cancer [ICD-11: 2C25] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.05E-01 Fold-change: 1.28E-02 Z-score: 1.63E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell apoptosis | Activation | hsa04210 | |
| In Vitro Model | A549 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0023 |
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ATP7A is a direct target gene of miR-495 and can be negatively regulated by miR-495. The inhibition of miR-495 reduced the cell sensitivity to CDDP in A549 and H1299 cells; miR-495 regulates the cell response to platinum drug resistance by modulation of ATP7A expression. | |||
Approved Drug(s)
3 drug(s) in total
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73.0] | |||
| Sensitive Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Differential expression of the molecule in resistant disease | ||||
| Classification of Disease | Ovarian cancer [ICD-11: 2C73] | |||
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovarian tissue | |||
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.19E-01 Fold-change: -5.04E-02 Z-score: -1.06E+00 |
|||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell viability | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | CAOV3 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0201 |
| SNU119 cells | Ovary | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5014 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | The expression of ATP7A/B was up-regulated in cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cell lines; miR-139 inversely regulates ATP7A/B expression through direct targeting, and affects ovarian cancer chemoresistance through regulation of ATP7A/B. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Cisplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | EC109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of ATP7A in EC109/cisplatin cells might increase pumping platinum out of cells or binding and sequestration of platinum drugs, then decrease cellular platinum concentration or keep them away from accessing their key cytotoxic targets in the nucleus, finally result in cisplatin-resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Carboplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | EC109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of ATP7A in EC109/cisplatin cells might increase pumping platinum out of cells or binding and sequestration of platinum drugs, then decrease cellular platinum concentration or keep them away from accessing their key cytotoxic targets in the nucleus, finally result in cisplatin-resistance. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Disease Class: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma [ICD-11: 2B70.3] | |||
| Resistant Drug | Oxaliplatin | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | EC109 cells | Esophagus | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_6898 |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR; Western blotting assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of ATP7A in EC109/cisplatin cells might increase pumping platinum out of cells or binding and sequestration of platinum drugs, then decrease cellular platinum concentration or keep them away from accessing their key cytotoxic targets in the nucleus, finally result in cisplatin-resistance. | |||
Disease- and Tissue-specific Abundances of This Molecule
ICD Disease Classification 02

| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Esophagus | |
| The Specified Disease | Esophageal cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 7.39E-01; Fold-change: -2.67E-01; Z-score: -4.42E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
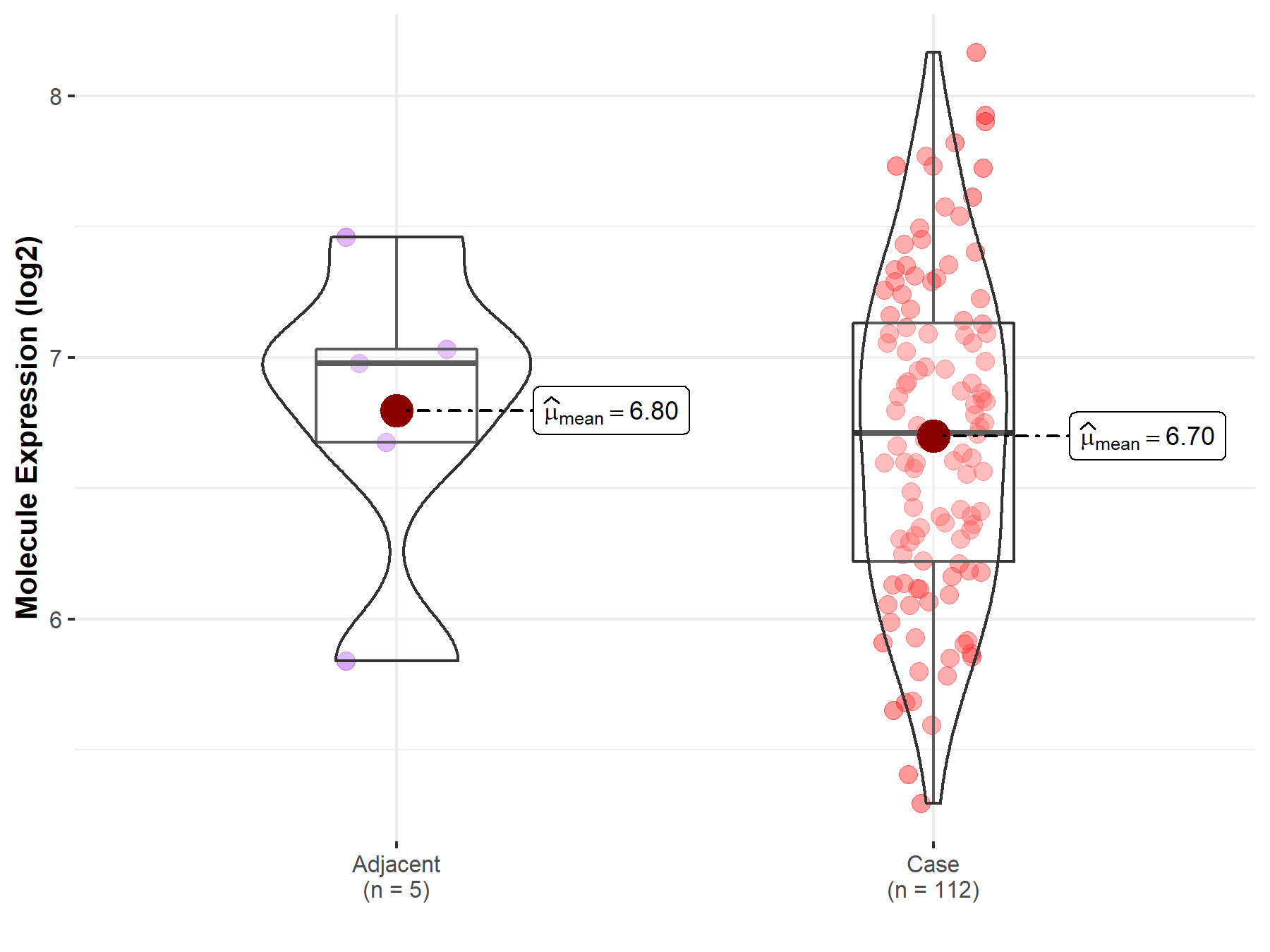
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Lung | |
| The Specified Disease | Lung cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 1.05E-01; Fold-change: 1.07E-01; Z-score: 2.37E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.35E-02; Fold-change: 8.54E-02; Z-score: 1.99E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |

|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
| Differential expression of molecule in resistant diseases | ||
| The Studied Tissue | Ovary | |
| The Specified Disease | Ovarian cancer | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Healthy Individual Tissue | p-value: 3.19E-01; Fold-change: -3.71E-01; Z-score: -5.33E-01 | |
| The Expression Level of Disease Section Compare with the Adjacent Tissue | p-value: 1.99E-01; Fold-change: -4.01E-01; Z-score: -6.06E-01 | |
|
Molecule expression in the normal tissue adjacent to the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the diseased tissue of patients
Molecule expression in the normal tissue of healthy individuals
|
||
| Disease-specific Molecule Abundances |
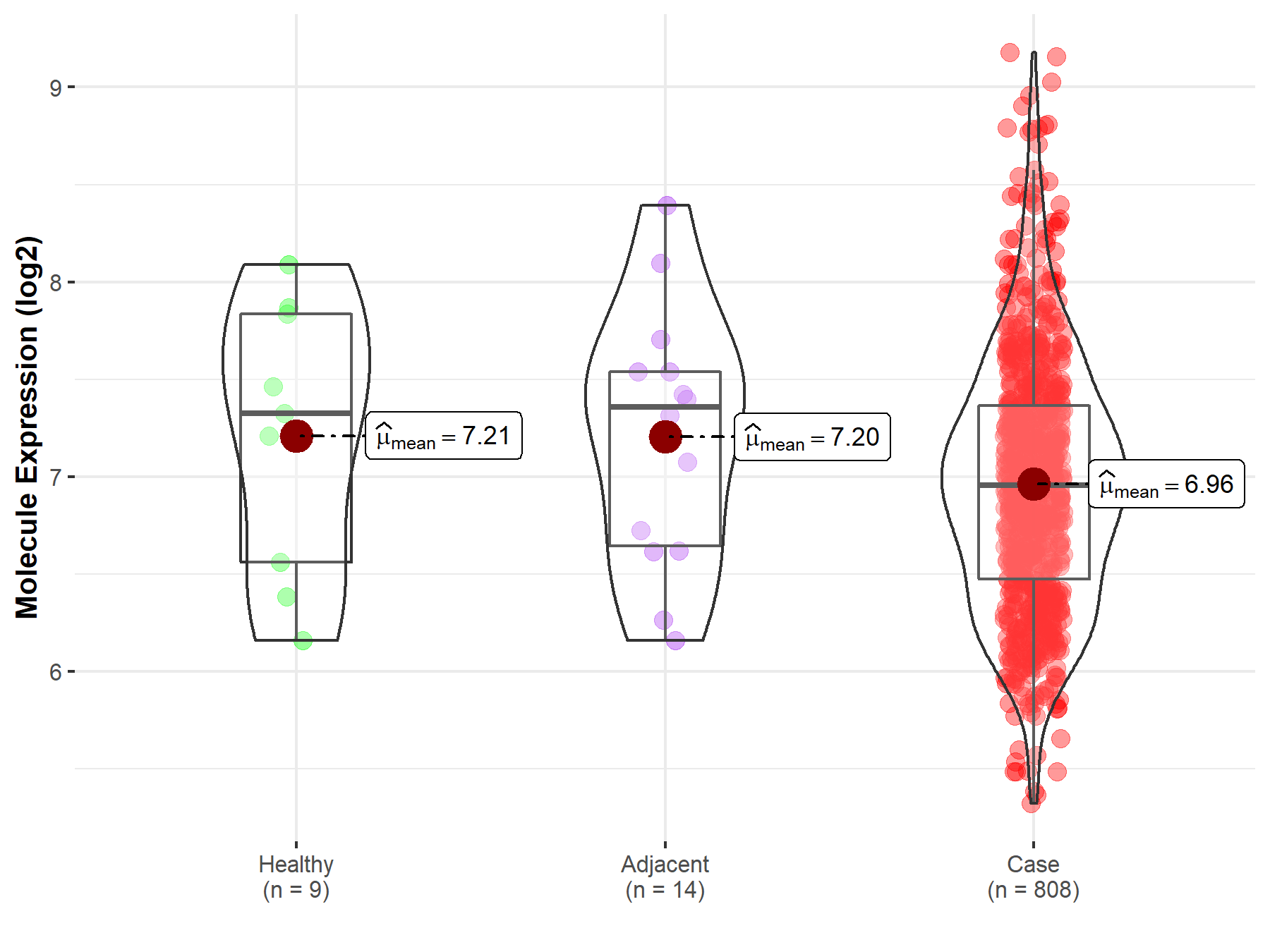
|
Click to View the Clearer Original Diagram |
Tissue-specific Molecule Abundances in Healthy Individuals

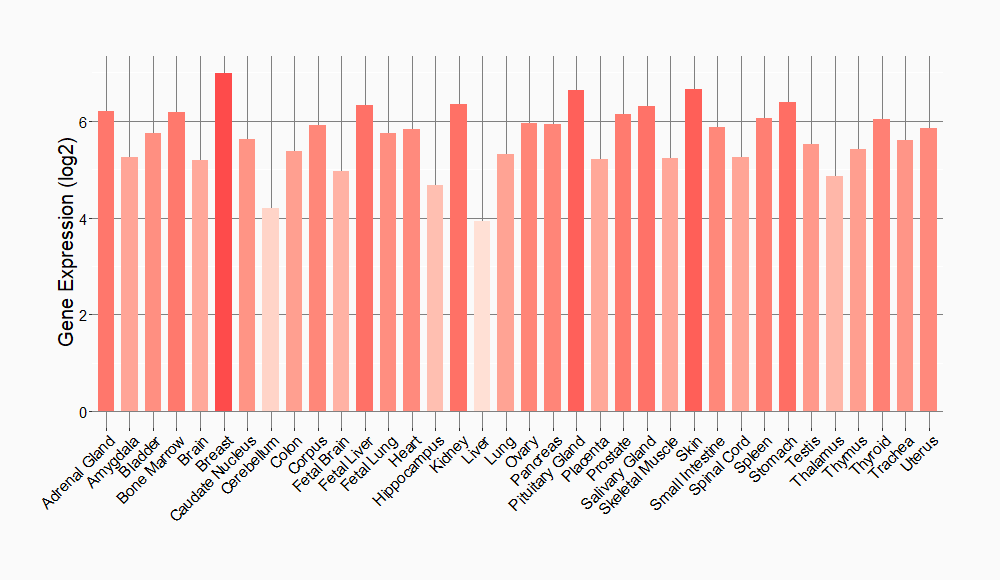
|
||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
