Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01602) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
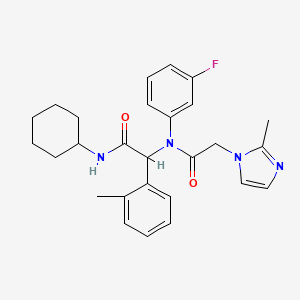
AGI-5198
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AGI-5198; 1355326-35-0; IDH-C35; N-cyclohexyl-2-(N-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-(2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamido)-2-(o-tolyl)acetamide; AGI 5198; AGI-5198(IDH C35); N-cyclohexyl-2-(N-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-(2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamido)-2-o-tolylacetamide; CHEMBL2180727; AGI5198; N-cyclohexyl-2-(3-fluoro-N-[2-(2-methylimidazol-1-yl)acetyl]anilino)-2-(2-methylphenyl)acetamide; AGI-5198 (IDH-C35); MLS006010252; GTPL9240; SCHEMBL15118942; C27H31FN4O2; AOB5947; DTXSID30718166; EX-A171; QCR-214; HMS3653K15; HMS3865J13; AMY24200; BCP07382; BDBM50400272; MFCD24848688; NSC773096; s7185; AKOS026674117; CCG-269371; CS-1429; NSC-773096; SB19576; NCGC00347934-01; NCGC00347934-09; BS-14968; DA-35355; HY-18082; SMR004701328; FT-0768624; SW220036-1; X5817; A854356; Q27074345; S900006220; N-[2-(Cyclohexylamino)-1-(2-methylphenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-N-(3-fluorophenyl)-2-(2-methyl-1H-imidazol-1-yl)acetamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC1=CC=CC=C1C(C(=O)NC2CCCCC2)N(C3=CC(=CC=C3)F)C(=O)CN4C=CN=C4C
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C27H31FN4O2/c1-19-9-6-7-14-24(19)26(27(34)30-22-11-4-3-5-12-22)32(23-13-8-10-21(28)17-23)25(33)18-31-16-15-29-20(31)2/h6-10,13-17,22,26H,3-5,11-12,18H2,1-2H3,(H,30,34)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FNYGWXSATBUBER-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | FGFR-tacc positive glioblastoma [ICD-11: 2A00.01] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R132H (c.395G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.88 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
S
S
K
K
K
K
I
I
S
S
G
G
G
G
S
S
10
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
20
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
E
E
L
L
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
30
|
L
L
I
I
F
F
P
P
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
L
L
D
D
L
L
40
|
H
H
S
S
Y
Y
D
D
L
L
G
G
I
I
E
E
N
N
R
R
50
|
D
D
A
A
T
T
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
K
K
D
D
60
|
A
A
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
K
K
K
K
H
H
N
N
V
V
70
|
G
G
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
80
|
E
E
K
K
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
90
|
Q
Q
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
100
|
R
R
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
110
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
120
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
G
G
W
W
V
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
I
I
130
|
I
I
G
G
R
H
H
H
A
A
Y
Y
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
140
|
R
R
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
V
V
P
P
G
G
P
P
150
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
E
E
I
I
T
T
Y
Y
T
T
P
P
S
S
160
|
D
D
G
G
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
V
V
T
T
Y
Y
L
L
V
V
170
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
E
E
E
E
G
G
G
G
G
G
V
V
A
A
180
|
M
M
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
Q
Q
D
D
K
K
S
S
I
I
190
|
E
E
D
D
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
M
M
200
|
A
A
L
L
S
S
K
K
G
G
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
L
L
210
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
K
K
Y
Y
220
|
D
D
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
230
|
I
I
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
Q
Q
Y
Y
K
K
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
240
|
E
E
A
A
Q
Q
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
250
|
L
L
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
M
M
260
|
K
K
S
S
E
E
G
G
G
G
F
F
I
I
W
W
A
A
C
C
270
|
K
K
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
280
|
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
290
|
M
M
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
300
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
V
V
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
310
|
G
G
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
320
|
Q
Q
K
K
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
330
|
I
I
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
340
|
L
L
A
A
H
H
R
R
A
A
K
K
L
L
D
D
N
N
N
N
350
|
K
K
E
E
L
L
A
A
F
F
F
F
A
A
N
N
A
A
L
L
360
|
E
E
E
E
V
V
S
S
I
I
E
E
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
370
|
G
G
F
F
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
C
C
380
|
I
I
K
K
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
V
V
Q
Q
R
R
S
S
390
|
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
T
T
F
F
E
E
F
F
M
M
D
D
400
|
K
K
L
L
G
G
E
E
N
N
L
L
K
K
I
I
K
K
L
L
410
|
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
K
K
L
L
S
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
420
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TS676 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HX | |||||||||
| TS603 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HW | ||||||||||
| TS516 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft agar assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R132H (c.395G>A) in gene IDH1 cause the sensitivity of AGI-5198 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Brain glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R132H (c.395G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.65 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.88 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
M
M
S
S
K
K
K
K
I
I
S
S
G
G
G
G
S
S
10
|
V
V
V
V
E
E
M
M
Q
Q
G
G
D
D
E
E
M
M
T
T
20
|
R
R
I
I
I
I
W
W
E
E
L
L
I
I
K
K
E
E
K
K
30
|
L
L
I
I
F
F
P
P
Y
Y
V
V
E
E
L
L
D
D
L
L
40
|
H
H
S
S
Y
Y
D
D
L
L
G
G
I
I
E
E
N
N
R
R
50
|
D
D
A
A
T
T
N
N
D
D
Q
Q
V
V
T
T
K
K
D
D
60
|
A
A
A
A
E
E
A
A
I
I
K
K
K
K
H
H
N
N
V
V
70
|
G
G
V
V
K
K
C
C
A
A
T
T
I
I
T
T
P
P
D
D
80
|
E
E
K
K
R
R
V
V
E
E
E
E
F
F
K
K
L
L
K
K
90
|
Q
Q
M
M
W
W
K
K
S
S
P
P
N
N
G
G
T
T
I
I
100
|
R
R
N
N
I
I
L
L
G
G
G
G
T
T
V
V
F
F
R
R
110
|
E
E
A
A
I
I
I
I
C
C
K
K
N
N
I
I
P
P
R
R
120
|
L
L
V
V
S
S
G
G
W
W
V
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
I
I
130
|
I
I
G
G
R
H
H
H
A
A
Y
Y
G
G
D
D
Q
Q
Y
Y
140
|
R
R
A
A
T
T
D
D
F
F
V
V
V
V
P
P
G
G
P
P
150
|
G
G
K
K
V
V
E
E
I
I
T
T
Y
Y
T
T
P
P
S
S
160
|
D
D
G
G
T
T
Q
Q
K
K
V
V
T
T
Y
Y
L
L
V
V
170
|
H
H
N
N
F
F
E
E
E
E
G
G
G
G
G
G
V
V
A
A
180
|
M
M
G
G
M
M
Y
Y
N
N
Q
Q
D
D
K
K
S
S
I
I
190
|
E
E
D
D
F
F
A
A
H
H
S
S
S
S
F
F
Q
Q
M
M
200
|
A
A
L
L
S
S
K
K
G
G
W
W
P
P
L
L
Y
Y
L
L
210
|
S
S
T
T
K
K
N
N
T
T
I
I
L
L
K
K
K
K
Y
Y
220
|
D
D
G
G
R
R
F
F
K
K
D
D
I
I
F
F
Q
Q
E
E
230
|
I
I
Y
Y
D
D
K
K
Q
Q
Y
Y
K
K
S
S
Q
Q
F
F
240
|
E
E
A
A
Q
Q
K
K
I
I
W
W
Y
Y
E
E
H
H
R
R
250
|
L
L
I
I
D
D
D
D
M
M
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
M
M
260
|
K
K
S
S
E
E
G
G
G
G
F
F
I
I
W
W
A
A
C
C
270
|
K
K
N
N
Y
Y
D
D
G
G
D
D
V
V
Q
Q
S
S
D
D
280
|
S
S
V
V
A
A
Q
Q
G
G
Y
Y
G
G
S
S
L
L
G
G
290
|
M
M
M
M
T
T
S
S
V
V
L
L
V
V
C
C
P
P
D
D
300
|
G
G
K
K
T
T
V
V
E
E
A
A
E
E
A
A
A
A
H
H
310
|
G
G
T
T
V
V
T
T
R
R
H
H
Y
Y
R
R
M
M
Y
Y
320
|
Q
Q
K
K
G
G
Q
Q
E
E
T
T
S
S
T
T
N
N
P
P
330
|
I
I
A
A
S
S
I
I
F
F
A
A
W
W
T
T
R
R
G
G
340
|
L
L
A
A
H
H
R
R
A
A
K
K
L
L
D
D
N
N
N
N
350
|
K
K
E
E
L
L
A
A
F
F
F
F
A
A
N
N
A
A
L
L
360
|
E
E
E
E
V
V
S
S
I
I
E
E
T
T
I
I
E
E
A
A
370
|
G
G
F
F
M
M
T
T
K
K
D
D
L
L
A
A
A
A
C
C
380
|
I
I
K
K
G
G
L
L
P
P
N
N
V
V
Q
Q
R
R
S
S
390
|
D
D
Y
Y
L
L
N
N
T
T
F
F
E
E
F
F
M
M
D
D
400
|
K
K
L
L
G
G
E
E
N
N
L
L
K
K
I
I
K
K
L
L
410
|
A
A
Q
Q
A
A
K
K
L
L
S
S
L
L
E
E
H
H
H
H
420
|
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
H
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TS676 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HX | |||||||||
| TS603 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HW | ||||||||||
| TS516 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft agar assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R132H (c.395G>A) in gene IDH1 cause the sensitivity of AGI-5198 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Oxalosuccinate decarboxylase (IDH1) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Sensitive Disease | Brain glioma [ICD-11: 2A00.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R132C (c.394C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.93 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.20 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
-
M
-
S
-
K
-
K
-
I
-
S
-
G
-
G
-
S
10
|
-
V
-
V
-
E
-
M
-
Q
-
G
-
D
-
E
-
M
-
T
20
|
-
R
-
I
-
I
-
W
-
E
-
L
-
I
-
K
-
E
-
K
30
|
-
L
-
I
-
F
-
P
-
Y
-
V
-
E
-
L
-
D
-
L
40
|
-
H
-
S
-
Y
-
D
-
L
-
G
-
I
-
E
-
N
-
R
50
|
-
D
-
A
-
T
-
N
-
D
-
Q
-
V
-
T
-
K
-
D
60
|
-
A
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
I
-
K
-
K
-
H
-
N
-
V
70
|
-
G
-
V
-
K
-
C
-
A
-
T
-
I
-
T
-
P
-
D
80
|
-
E
-
K
-
R
-
V
-
E
-
E
-
F
-
K
-
L
-
K
90
|
-
Q
-
M
-
W
-
K
-
S
-
P
-
N
-
G
-
T
-
I
100
|
-
R
-
N
-
I
-
L
-
G
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
F
-
R
110
|
-
E
-
A
-
I
-
I
-
C
-
K
-
N
-
I
-
P
-
R
120
|
-
L
-
V
-
S
-
G
-
W
-
V
K
K
P
P
I
I
I
I
130
|
I
I
G
G
S
C
H
H
A
A
Y
Y
G
G
D
D
-
Q
-
Y
140
|
-
R
-
A
-
T
-
D
-
F
-
V
-
V
-
P
-
G
-
P
150
|
-
G
-
K
-
V
-
E
-
I
-
T
-
Y
-
T
-
P
-
S
160
|
-
D
-
G
-
T
-
Q
-
K
-
V
-
T
-
Y
-
L
-
V
170
|
-
H
-
N
-
F
-
E
-
E
-
G
-
G
-
G
-
V
-
A
180
|
-
M
-
G
-
M
-
Y
-
N
-
Q
-
D
-
K
-
S
-
I
190
|
-
E
-
D
-
F
-
A
-
H
-
S
-
S
-
F
-
Q
-
M
200
|
-
A
-
L
-
S
-
K
-
G
-
W
-
P
-
L
-
Y
-
L
210
|
-
S
-
T
-
K
-
N
-
T
-
I
-
L
-
K
-
K
-
Y
220
|
-
D
-
G
-
R
-
F
-
K
-
D
-
I
-
F
-
Q
-
E
230
|
-
I
-
Y
-
D
-
K
-
Q
-
Y
-
K
-
S
-
Q
-
F
240
|
-
E
-
A
-
Q
-
K
-
I
-
W
-
Y
-
E
-
H
-
R
250
|
-
L
-
I
-
D
-
D
-
M
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
A
-
M
260
|
-
K
-
S
-
E
-
G
-
G
-
F
-
I
-
W
-
A
-
C
270
|
-
K
-
N
-
Y
-
D
-
G
-
D
-
V
-
Q
-
S
-
D
280
|
-
S
-
V
-
A
-
Q
-
G
-
Y
-
G
-
S
-
L
-
G
290
|
-
M
-
M
-
T
-
S
-
V
-
L
-
V
-
C
-
P
-
D
300
|
-
G
-
K
-
T
-
V
-
E
-
A
-
E
-
A
-
A
-
H
310
|
-
G
-
T
-
V
-
T
-
R
-
H
-
Y
-
R
-
M
-
Y
320
|
-
Q
-
K
-
G
-
Q
-
E
-
T
-
S
-
T
-
N
-
P
330
|
-
I
-
A
-
S
-
I
-
F
-
A
-
W
-
T
-
R
-
G
340
|
-
L
-
A
-
H
-
R
-
A
-
K
-
L
-
D
-
N
-
N
350
|
-
K
-
E
-
L
-
A
-
F
-
F
-
A
-
N
-
A
-
L
360
|
-
E
-
E
-
V
-
S
-
I
-
E
-
T
-
I
-
E
-
A
370
|
-
G
-
F
-
M
-
T
-
K
-
D
-
L
-
A
-
A
-
C
380
|
-
I
-
K
-
G
-
L
-
P
-
N
-
V
-
Q
-
R
-
S
390
|
-
D
-
Y
-
L
-
N
-
T
-
F
-
E
-
F
-
M
-
D
400
|
-
K
-
L
-
G
-
E
-
N
-
L
-
K
-
I
-
K
-
L
410
|
-
A
-
Q
-
A
-
K
-
L
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | TS676 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HX | |||||||||
| TS603 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HW | ||||||||||
| TS516 cells | Brain | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_A5HY | ||||||||||
| In Vivo Model | SCID mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | |||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Soft agar assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R132C (c.394C>T) in gene IDH1 cause the sensitivity of AGI-5198 by aberration of the drug's therapeutic target | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
