Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01477) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Seliciclib
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Roscovitine; Seliciclib; 186692-46-6; R-Roscovitine; (R)-roscovitine; CYC202; CYC-202; CYC 202; 2-(R)-(1-Ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurine; Seliciclib (Roscovitine); Roscovitine (Seliciclib,CYC202); UNII-0ES1C2KQ94; (R)-2-((6-(Benzylamino)-9-isopropyl-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)butan-1-ol; NSC-701554; AL-39256; CHEMBL14762; 0ES1C2KQ94; CHEBI:45307; (2R)-2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-propan-2-ylpurin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol; MFCD02266401; NSC701554; (2R)-2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-isopropyl-purin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol; (2R)-2-{[6-(benzylamino)-9-(propan-2-yl)-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}butan-1-ol; RRC; C19H26N6O; Rosco; (2R)-2-{[6-(benzylamino)-9-(1-methylethyl)-9H-purin-2-yl]amino}butan-1-ol; (2R)-2-[[9-(1-Methylethyl)-6-[(phenylmethyl)amino]-9H-purin-2-yl]amino]-1-butanol; Seliciclib [INN]; NSC 701554; 2-(1-ethyl-2-hydroxyethylamino)-6-benzylamino-9-isopropylpurine; BMK1-E12; 1unl; 3ddq; (2R)-2-((9-(1-methylethyl)-6-((phenylmethyl)amino)-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)-1-butanol; 2a4l; BiomolKI_000048; 1-Butanol, (2R)-; ROSCOVITINE(Seliciclib); BiomolKI2_000054; M02443; CBiol_002016; Lopac0_001102; SCHEMBL94728; BSPBio_001078; KBioGR_000418; KBioSS_000418; MLS006011028; BDBM7533; cid_160355; GTPL6035; Roscovitine, >=98% (TLC); BCBcMAP01_000013; KBio2_000418; KBio2_002986; KBio2_005554; KBio3_000795; KBio3_000796; AOB2095; DTXSID20171928; EX-A052; BCPP000087; Bio1_000302; Bio1_000791; Bio1_001280; Bio2_000379; Bio2_000859; CC205; HMS1362F19; HMS1792F19; HMS1990F19; HMS3229N13; HMS3403F19; AMY10845; BCP01760; Roscovitine (Seliciclib, CYC202); ZINC1649340; HSCI1_000092; NSC800881; s1153; (2R)-2-((6-benzylamino-9-(propan-2-yl)-9h-purin-2-yl)amino)butan-1-ol; 6-(Benzylamino)-2(R)-[[1-(hydroxymethyl)propyl]amino]-9-isopropylpurine; AKOS005146319; AC-2416; CCG-100652; DB06195; NSC-800881; 2-(R)-[[9-(1-Methylethyl)-6-[(phenylmethyl)amino]-9H-purin-2-yl]amino]-1-butanol; IDI1_002134; Roscovitine - CAS 186692-46-6; SMP1_000266; 2,6,9-Trisubstituted purine deriv. 28; NCGC00094374-01; NCGC00094374-02; NCGC00094374-03; NCGC00094374-04; NCGC00094374-05; NCGC00094374-13; NCGC00094374-15; AS-56277; HY-30237; NCI60_036420; SMR004702823; SW220195-1; X7381; K00020; 692R466; A813074; J-011999; J-524224; Q3494619; BRD-K07691486-001-03-1; BRD-K07691486-001-05-6; UNII-AIR55KO85E component BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N; (2R)-2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-propan-2-yl-purin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol; (2R)-2-[[6-[(phenylmethyl)amino]-9-propan-2-yl-2-purinyl]amino]-1-butanol; (2R)-2-[[6-[(phenylmethyl)amino]-9-propan-2-yl-purin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol; (R)-2-((9-(1-methylethyl)-6-((phenylmethyl)amino)-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)-1-butanol; 1-Butanol, 2-((9-(1-methylethyl)-6-((phenylmethyl)amino)-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)-, (2R)-; 1-Butanol, 2-((9-(1-methylethyl)-6-((phenylmethyl)amino)-9H-purin-2-yl)amino)-, (R)-; 2-[[9-(1-Methylethyl)-6-[(phenylmethyl)amino]- 9H-purin-2-yl]amino]-(R)-1-butanol; Seliciclib; ; ; CYC-202; ; ; (2R)-2-[[6-(Benzylamino)-9-propan-2-ylpurin-2-yl]amino]butan-1-ol
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
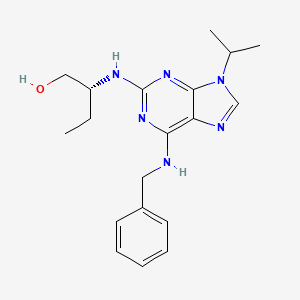
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) | CDK2_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
8
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@H](CO)NC1=NC(=C2C(=N1)N(C=N2)C(C)C)NCC3=CC=CC=C3
|
||||
| InChI |
InChI=1S/C19H26N6O/c1-4-15(11-26)22-19-23-17(20-10-14-8-6-5-7-9-14)16-18(24-19)25(12-21-16)13(2)3/h5-9,12-13,15,26H,4,10-11H2,1-3H3,(H2,20,22,23,24)/t15-/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
BTIHMVBBUGXLCJ-OAHLLOKOSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | |||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y220C (c.659A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.24 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
S
S
S
S
S
S
V
V
P
P
S
S
100
|
Q
Q
K
K
T
T
Y
Y
Q
Q
G
G
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
F
F
110
|
R
R
L
L
G
G
F
F
L
L
H
H
S
S
G
G
T
T
A
A
120
|
K
K
S
S
V
V
T
T
C
C
T
T
Y
Y
S
S
P
P
A
A
130
|
L
L
N
N
K
K
M
L
F
F
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
K
K
140
|
T
T
C
C
P
P
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
W
W
V
V
D
D
S
S
150
|
T
T
P
P
P
P
P
P
G
G
T
T
R
R
V
V
R
R
A
A
160
|
M
M
A
A
I
I
Y
Y
K
K
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
H
H
M
M
170
|
T
T
E
E
V
V
V
V
R
R
R
R
C
C
P
P
H
H
H
H
180
|
E
E
R
R
C
C
S
S
D
D
S
S
D
D
G
G
L
L
A
A
190
|
P
P
P
P
Q
Q
H
H
L
L
I
I
R
R
V
V
E
E
G
G
200
|
N
N
L
L
R
R
V
A
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
D
D
D
D
R
R
210
|
N
N
T
T
F
F
R
R
H
H
S
S
V
V
V
V
V
V
P
P
220
|
Y
C
E
E
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
G
G
S
S
D
D
C
C
230
|
T
T
T
T
I
I
H
H
Y
Y
N
N
Y
Y
M
M
C
C
N
Y
240
|
S
S
S
S
C
C
M
M
G
G
G
G
M
M
N
N
R
R
R
R
250
|
P
P
I
I
L
L
T
T
I
I
I
I
T
T
L
L
E
E
D
D
260
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
R
R
N
D
S
S
270
|
F
F
E
E
V
V
R
R
V
V
C
C
A
A
C
C
P
P
G
G
280
|
R
R
D
D
R
R
R
R
T
T
E
E
E
E
E
E
N
N
L
L
290
|
R
R
K
K
K
K
G
G
E
E
P
P
H
H
H
H
E
E
L
L
300
|
P
P
P
P
G
G
S
S
T
T
K
K
R
R
A
A
L
L
P
P
310
|
N
N
N
N
T
T
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y220C (c.659A>G) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.Y234C (c.701A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.05 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 1.38 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
S
S
S
S
S
S
V
V
P
P
S
S
100
|
Q
Q
K
K
T
T
Y
Y
Q
Q
G
G
S
S
Y
Y
G
G
F
F
110
|
R
R
L
L
G
G
F
F
L
L
H
H
S
S
G
G
T
T
A
A
120
|
K
K
S
S
V
V
T
T
C
C
T
T
Y
Y
S
S
P
P
A
A
130
|
L
L
N
N
K
K
M
L
F
F
C
C
Q
Q
L
L
A
A
K
K
140
|
T
T
C
C
P
P
V
V
Q
Q
L
L
W
W
V
V
D
D
S
S
150
|
T
T
P
P
P
P
P
P
G
G
T
T
R
R
V
V
R
R
A
A
160
|
M
M
A
A
I
I
Y
Y
K
K
Q
Q
S
S
Q
Q
H
H
M
M
170
|
T
T
E
E
V
V
V
V
R
R
R
R
C
C
P
P
H
H
H
H
180
|
E
E
R
R
C
C
S
S
D
D
S
S
D
D
G
G
L
L
A
A
190
|
P
P
P
P
Q
Q
H
H
L
L
I
I
R
R
V
V
E
E
G
G
200
|
N
N
L
L
R
R
V
A
E
E
Y
Y
L
L
D
D
D
D
R
R
210
|
N
N
T
T
F
F
R
R
H
H
S
S
V
V
V
V
V
V
P
P
220
|
Y
Y
E
E
P
P
P
P
E
E
V
V
G
G
S
S
D
D
C
C
230
|
T
T
T
T
I
I
H
H
Y
C
N
N
Y
Y
M
M
C
C
N
Y
240
|
S
S
S
S
C
C
M
M
G
G
G
G
M
M
N
N
R
R
R
R
250
|
P
P
I
I
L
L
T
T
I
I
I
I
T
T
L
L
E
E
D
D
260
|
S
S
S
S
G
G
N
N
L
L
L
L
G
G
R
R
N
D
S
S
270
|
F
F
E
E
V
V
R
R
V
V
C
C
A
A
C
C
P
P
G
G
280
|
R
R
D
D
R
R
R
R
T
T
E
E
E
E
E
E
N
N
L
L
290
|
R
R
K
K
K
K
G
G
E
E
P
P
H
H
H
H
E
E
L
L
300
|
P
P
P
P
G
G
S
S
T
T
K
K
R
R
A
A
L
L
P
P
310
|
N
N
N
N
T
T
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.Y234C (c.701A>G) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.R175H (c.524G>A) |
|||||||||||
| Wild Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.37 Å | |||||||||||
| Mutant Type Structure | Method: X-ray diffraction | Resolution: 2.38 Å | |||||||||||
| Download The Information of Sequence | Download The Structure File | ||||||||||||
-
H
H
M
M
170
|
T
T
E
E
V
V
V
V
R
R
R
H
C
C
|
|||||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.R175H (c.524G>A) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.P98A (c.292C>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.P98A (c.292C>G) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.A159V (c.476C>T) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.A159V (c.476C>T) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
| Key Molecule: Cellular tumor antigen p53 (TP53) | [1] | ||||||||||||
| Resistant Disease | Lung adenocarcinoma [ICD-11: 2C25.0] | ||||||||||||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.S215G (c.643A>G) |
|||||||||||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | ||||||||||||
| In Vitro Model | H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | |||||||||
| H1299 cells | Lung | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0060 | ||||||||||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Immunoblotting analysis | ||||||||||||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Cell death detection ELISA assay | ||||||||||||
| Mechanism Description | The missense mutation p.S215G (c.643A>G) in gene TP53 cause the resistance of Seliciclib by unusual activation of pro-survival pathway | ||||||||||||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
