Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01044) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Fosfomycin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
FOSFOMYCIN; phosphomycin; Phosphonomycin; 23155-02-4; Fosfonomycin; Fosfocina; Monurol; Veramina; Fosfomicina; Fosfomycine; Fosfomycinum; [(2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-yl]phosphonic acid; Antibiotic 833A; Phosphonemycin; Phosphonic acid, (3-methyloxiranyl)-, (2R-cis)-; UNII-2N81MY12TE; Phosphomycin disodium salt; (2R-cis)-(3-Methyloxiranyl)phosphonic acid; (1R,2S)-epoxypropylphosphonic acid; L-cis-1,2-epoxypropylphosphonic acid; (-)-(1R,2S)-(1,2-Epoxypropyl)phosphonic acid; CHEMBL1757; Phosphonicacid, P-[(2R,3S)-3-methyl-2-oxiranyl]-; Fosfomycin disodium salt; 2N81MY12TE; CHEBI:28915; FCM; Phosphonic acid, (1,2-epoxypropyl)-, (1R,2S)-(-)-; (1R,2S)-epoxypropylphosphonate; cis-(1R,2S)-epoxypropylphosphonic acid; Calcium fosfomycin; 1R-cis-(1,2-epoxypropyl)phosphonic acid; ((2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-yl)phosphonic acid; Fosfomicin; Infectophos; 1,2-EPOXYPROPYLPHOSPHONIC ACID; Levo-phosphonomycin; Fosfomycin (USAN/INN); Fosfomycine [INN-French]; Fosfomycinum [INN-Latin]; Fosfomicina [INN-Spanish]; Fosfomycin [USAN:INN:BAN]; J01XX01; EINECS 245-463-1; MK-955; BRN 1680831; 883A; NSC-758170; Fosfomycin (compound 1); Fosfomycinfor culture media; SCHEMBL50951; BIDD:GT0448; BRN 1680831, Fosfocina; ZTI-01; DTXSID4048480; GTPL10813; BCP24891; ZINC1530427; BDBM50024894; cis-(2-Methyloxiranyl)-phosphonic acid; DB00828; (2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-ylphosphonate; 25030-76-6; (1R, 2S)-1,2-epoxypropyl-phosphonic acid; FT-0774116; (2R,3S)-3-methyloxiran-2-ylphosphonic acid; (3-Methyl-oxiranyl)-phosphonic acid(Na salt); C06454; D04253; Q183554; W-107422; BRD-K81101512-234-01-9; Phosphonic acid, P-[(2R,3S)-3-methyl-2-oxiranyl]-; 6F066DFF-696A-4A94-AF78-A28430EBE5BA
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
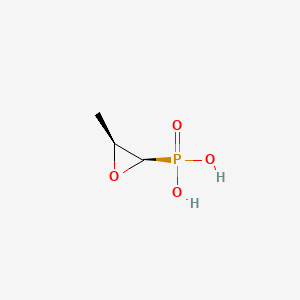
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Validated by in-vivo Model for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Bacterial UDP-N-acetylglucosamine carboxyvinyltransferase (Bact murA) | MURA_ECOLI | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C3H7O4P
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C[C@H]1[C@H](O1)P(=O)(O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C3H7O4P/c1-2-3(7-2)8(4,5)6/h2-3H,1H3,(H2,4,5,6)/t2-,3+/m0/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
YMDXZJFXQJVXBF-STHAYSLISA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: UDP-N-acetylglucosamine 1-carboxyvinyltransferase (MURA) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Escherichia coli infection [ICD-11: 1A03.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Discovered Using In-vivo Testing Model | |||
| In Vitro Model | THP1 cells | Pleural effusion | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0006 |
| Mechanism Description | Overexpression of the murA gene by induction of a regulated promoter can lead to greatly increased MICs, to levels that would afford clinical resistance, while having relatively low effects on fitness (relative to mutations to fosfomycin resistance found in clinical isolates). | |||
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Transmembrane protein 94 (TMEM94) | [2] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Methylation | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | S. aureus isolates | 41687 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR; Docking assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing; Phenotypic assay; MIC assay; Checkerboard microdilution assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | This study aimed to identify the prevalence of erythromycin and erythromycin-induced resistance and assess for potential inhibitors. A total of 99 isolates were purified from various clinical sources. Phenotypic detection of macrolide-lincosamide-streptogramin B (MLSB)-resistance phenotypes was performed by D-test. MLSB-resistance genes were identified using PCR. Different compounds were tested for their effects on erythromycin and inducible clindamycin resistance by broth microdilution and checkerboard microdilution methods. The obtained data were evaluated using docking analysis. Ninety-one isolates were S. aureus. The prevalence of constitutive MLSB, inducible MLSB, and macrolide-streptogramin (MS) phenotypes was 39.6%, 14.3%, and 2.2%, respectively. Genes including ermC, ermA, ermB, msrA, msrB, lnuA, and mphC were found in 82.6%, 5.8%, 7.7%, 3.8%, 3.8%, 13.5%, and 3.8% of isolates, respectively. Erythromycin resistance was significantly reduced by doxorubicin, neomycin, and omeprazole. Quinine, ketoprofen, and fosfomycin combated and reversed erythromycin/clindamycin-induced resistance. This study highlighted the significance of managing antibiotic resistance and overcoming clindamycin treatment failure. Doxorubicin, neomycin, omeprazole, quinine, ketoprofen, and fosfomycin could be potential inhibitors of erythromycin and inducible clindamycin resistance. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
