Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG01038) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Vinpocetine
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Vinpocetine; 42971-09-5; Cavinton; Ceractin; Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; Ethyl apovincamin-22-oate; Bravinton; TCV-3B; Ethyl (+)-apovincaminate; Ultra-Vinca; RGH 4405; RGH-4405; cis-Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; (+)-Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; Ethyl (+)-cis-apovincaminate; (+)-cis-Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; AY 27,255; TCV 3B; Ethyl apovincaminate; UNII-543512OBTC; 3-alpha,16-alpha-Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; CHEMBL71752; MLS000069635; 543512OBTC; MFCD00211233; NSC-760093; (41S,13aS)-ethyl 13a-ethyl-2,3,41,5,6,13a-hexahydro-1H-indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridine-12-carboxylate; NCGC00018204-09; Vinpocetinum; C22H26N2O2; SMR000058241; AY-27,255; Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester, (3alpha,16alpha)-; DSSTox_CID_3740; DSSTox_RID_77176; DSSTox_GSID_23740; ethyl (41S,13aS)-13a-ethyl-2,3,41,5,6,13a-hexahydro-1H-indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridine-12-carboxylate; Vinpocetinum [INN-Latin]; Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester, (3a,16a)-; Apovincaminate d'ethyle; Vinporal; Apovincaminate d'ethyle [French]; 1H-Indolo[3,2,1-de]pyrido[3,2,1-ij][1,5]naphthyridine, eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid deriv.; SR-01000075633; EINECS 256-028-0; BRN 0900803; Vinpocetin; Vinpocetine (JAN/USAN/INN); Vinpocetine-ethyl apovincaminate; 3A,16A-Apovincaminic acid ethyl ester; NCGC00016854-03; Vinpocetine [USAN:INN:BAN:JAN]; Prestwick_963; Vinpocetin- Bio-X; CAS-42971-09-5; Spectrum_001400; Vinpocetine (Cavinton); AY 27255; SpecPlus_000327; Opera_ID_1325; Prestwick0_000268; Prestwick1_000268; Prestwick2_000268; Prestwick3_000268; Spectrum2_001529; Spectrum3_000961; Spectrum4_001075; Spectrum5_000966; V 6383; Lopac0_001257; SCHEMBL50081; BSPBio_000116; BSPBio_002561; KBioGR_001430; KBioSS_001880; MLS001076294; DivK1c_006423; SPECTRUM1503115; Vinpocetine, >=98%, solid; ethyl (3alpha,16alpha)-eburnamenine-14-carboxylate; SPBio_001318; SPBio_002335; BPBio1_000128; cid_443955; GTPL5285; Vinpocetine, analytical standard; DTXSID5023740; REGID_for_CID_443955; CHEBI:32297; KBio1_001367; KBio2_001880; KBio2_004448; KBio2_007016; KBio3_001781; HMS1568F18; HMS1922G05; HMS2090J22; HMS2092L06; HMS2095F18; HMS3263L16; HMS3402D12; HMS3411H11; HMS3675H11; HMS3712F18; HMS3887E17; Pharmakon1600-01503115; (3alpha, 16alpha)-Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; 68780-77-8; AMY39087; BCP04123; Tox21_110648; Tox21_110839; Tox21_501257; BDBM50059033; CCG-39307; Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid, ethyl ester, (3-alpha,16-alpha)-; NSC760093; PD-185; s2110; ZINC19796031; AKOS015896480; Tox21_110648_1; CS-0545; DB12131; LP01257; NSC 760093; SDCCGSBI-0051224.P003; Vinpocetine 1.0 mg/ml in Acetonitrile; (3S,16S)-apovincaminic acid ethylester; NCGC00018204-05; NCGC00018204-06; NCGC00018204-07; NCGC00018204-08; NCGC00018204-10; NCGC00018204-11; NCGC00018204-13; NCGC00021727-04; NCGC00021727-05; NCGC00021727-06; NCGC00021727-07; NCGC00168782-01; NCGC00261942-01; NCGC00263865-01; NCGC00263865-04; AC-22612; AS-13868; AY-27255; BV164528; HY-13295; Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid ethyl ester;; EU-0101257; D01371; J10479; AB00052317_02; 971V095; Q420288; SR-01000000118; SR-01000000118-3; SR-01000075633-1; SR-01000075633-3; SR-01000075633-4; W-202748; BRD-K53318339-001-05-8; (3 ,16 )-Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; Vinpocetine, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; (3alpha,16alpha)-Eburnamenine-14-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; Vinpocetine, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; (11aS,11bS)-11a-Ethyl-2,3,4,5,11a,11b-hexahydro-1H-3a,9b-diaza-benzo[cd]fluoranthene-10-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; (3aS,11bS)-3a-ethyl-1,2,3,3a,10,11b-hexahydro-11H-5a,11a-diaza-benzo[cd]fluoranthene-5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester; 115986-87-3; 11a-Ethyl-2,3,4,5,11a,11b-hexahydro-1H-3a,9b-diaza-benzo[cd]fluoranthene-10-carboxylic acid 2-nitrooxy-ethyl ester(Vinpocetine); ethyl (15S,19S)-15-ethyl-1,11-diazapentacyclo[9.6.2.0^{2,7}.0^{8,18}.0^{15,19}]nonadeca-2,4,6,8(18),16-pentaene-17-carboxylate; ethyl (15S,19S)-15-ethyl-1,11-diazapentacyclo[9.6.2.02,7.08,18.015,19]nonadeca-2,4,6,8(18),16-pentaene-17-carboxylate
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 1 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
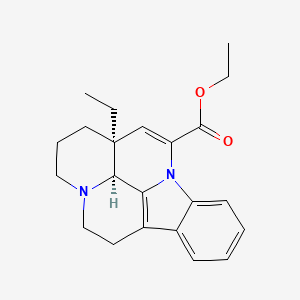
|
||||
| Target | Phosphodiesterase 1 (PDE1) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H26N2O2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@]12CCCN3[C@@H]1C4=C(CC3)C5=CC=CC=C5N4C(=C2)C(=O)OCC
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H26N2O2/c1-3-22-11-7-12-23-13-10-16-15-8-5-6-9-17(15)24(19(16)20(22)23)18(14-22)21(25)26-4-2/h5-6,8-9,14,20H,3-4,7,10-13H2,1-2H3/t20-,22+/m1/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DDNCQMVWWZOMLN-IRLDBZIGSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Glycogen synthase kinase-3 beta (GSK3B) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Hepatocellular carcinoma [ICD-11: 2C12.2] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Function | Activation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling pathway | Activation | hsa04931 | |
| In Vitro Model | Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain | 4932 | ||
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron strain | 818 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Sulforhodamine blue (SRB) assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Enhanced anticancer activity by the combination of vinpocetine and sorafenib via PI3K/AKT/GSK-3beta signaling axis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Our study revealed that vinpocetine plus sorafenib could suppress the cytoprotective autophagy induced by vinpocetine and subsequently show synergistically anti-HCC activity via activating GSK-3beta and the combination of vinpocetine and sorafenib might reverse sorafenib resistance via the PI3K/protein kinase B/GSK-3beta signaling axis. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
