Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00829) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Triamterene
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Triamterene; 396-01-0; 6-phenylpteridine-2,4,7-triamine; 2,4,7-Triamino-6-phenylpteridine; Dyrenium; Dytac; Pterofen; Pterophene; Triamteren; Triamteril; Triteren; Ademin; Ademine; Diurene; Noridil; Taturil; Teridin; Urocaudal; Jatropur; Noridyl; Triampur; Diren; Ditak; Dyren; Teriam; Tri-Span; Triamteril complex; Trispan; 6-Phenyl-2,4,7-pteridinetriamine; 2,4,7-Pteridinetriamine, 6-phenyl-; SK&F 8542; 6-Phenyl-2,4,7-triaminopteridine; SKF 8542; Pteridine, 2,4,7-triamino-6-phenyl-; 2,4,7-Triamino-6-fenilpteridina; C12H11N7; UNII-WS821Z52LQ; BRN 0266723; Diucelpin; NSC-77625; SK-8542; WS821Z52LQ; Masuharmin; Triamizide; Triamthiazid; Amteren; Dinazide; Diutensat; Diuteren; Dyberzide; Dytenzide; Esiteren; Hidiurese; Hydrene; Hypertorr; Jenateren; Kalspare; Nephral; Renezide; Reviten; Tricilone; Triurene; Uretren; Diarol; Isobar; Trizid; Anjal; Dazid; Turfa; Apo-triazide; Thiazid Wolff; NCI-C56042; NSC77625; Ademin(e); MFCD00006708; NCGC00016016-10; Triamterena; Triamterenum; CAS-396-01-0; Triazide; Fluss 40; SALI-PUREN; DSSTox_CID_1373; DSSTox_RID_76117; DSSTox_GSID_21373; Triamterenum [INN-Latin]; Triamterena [INN-Spanish]; Dyrenium (TN); CCRIS 5872; Pteridine deriv. 11; HSDB 3405; 2,4,7-Triamino-6-fenilpteridina [Italian]; NCI C56042; SR-01000002968; EINECS 206-904-3; NSC 77625; NSC 639359; AI3-60017; Prestwick_480; SK&F-8542; Dyazide (Salt/Mix); Triamterene [USAN:USP:INN:BAN:JAN]; Spectrum_000508; Triamterene, >=99%; Prestwick0_000034; Prestwick1_000034; Prestwick2_000034; Prestwick3_000034; Spectrum2_000938; Spectrum3_001372; Spectrum4_000366; Spectrum5_001034; Lopac-T-4143; CHEMBL585; T 4143; NCIOpen2_004741; Lopac0_001196; Oprea1_825704; SCHEMBL40707; BSPBio_000127; BSPBio_002924; KBioGR_000831; KBioSS_000988; 5-26-17-00447 (Beilstein Handbook Reference); MLS000069431; BIDD:GT0534; DivK1c_000433; SPECTRUM1500589; SPBio_000876; SPBio_002048; BDBM6644; BPBio1_000141; CHEBI:9671; GTPL4329; Triamterene (JP17/USP/INN); 2,7-Triamino-6-phenylpteridine; 6-Phenyl-2,7-triaminopteridine; DTXSID6021373; HMS501F15; KBio1_000433; KBio2_000988; KBio2_003556; KBio2_006124; KBio3_002144; SKF8542; NINDS_000433; 3'-Bromobiphenyl-3-carboxylicacid; HMS1568G09; HMS2092O17; HMS2095G09; HMS2232B04; HMS3259C08; HMS3263P13; HMS3371D10; HMS3652E10; HMS3712G09; Pharmakon1600-01500589; ZINC120286; 2,7-Pteridinetriamine, 6-phenyl-; Pteridine,4,7-triamino-6-phenyl-; BCP28855; HY-B0575; 2,4,7-triamino-6-phenyl-pteridine; Tox21_110283; Tox21_202021; Tox21_302833; Tox21_501196; CCG-40090; NSC639359; NSC757367; s4080; STK300348; AKOS003790819; Tox21_110283_1; DB00384; LP01196; MCULE-5832721534; NC00544; NSC-639359; NSC-757367; SDCCGSBI-0051163.P004; IDI1_000433; SMP1_000147; NCGC00016016-01; NCGC00016016-02; NCGC00016016-03; NCGC00016016-04; NCGC00016016-05; NCGC00016016-06; NCGC00016016-07; NCGC00016016-08; NCGC00016016-09; NCGC00016016-11; NCGC00016016-12; NCGC00016016-13; NCGC00016016-14; NCGC00016016-15; NCGC00016016-16; NCGC00016016-18; NCGC00016016-28; NCGC00016016-29; NCGC00023458-03; NCGC00023458-04; NCGC00023458-05; NCGC00023458-06; NCGC00023458-07; NCGC00256495-01; NCGC00259570-01; NCGC00261881-01; AC-14066; AS-12471; SMR000059118; SBI-0051163.P003; DB-049442; AB00052116; B2275; BB 0256885; EU-0101196; SW196688-3; T1288; Triamterene 1.0 mg/ml in Dimethyl Sulfoxide; Dyrenium; ; ; 2,4,7-Triamino-6-phenylpteridine; D00386; D95706; WLN: T66 BN DN GN JNJ CZ EZ HR& IZ; AB00052116_13; AB00052116_14; 396T010; A824641; Q221520; SR-01000002968-2; SR-01000002968-4; SR-01000002968-6; BRD-K92049597-001-05-9; BRD-K92049597-001-10-9; Z275128596; Triamterene, British Pharmacopoeia (BP) Reference Standard; Triamterene, European Pharmacopoeia (EP) Reference Standard; Triamterene, United States Pharmacopeia (USP) Reference Standard; Triamterene, Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
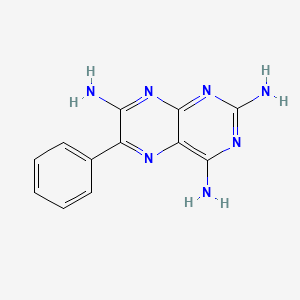
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(3 diseases)
[1]
[1]
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Amiloride-sensitive sodium channel (ENaC) |
SCNNA_HUMAN
; SCNNB_HUMAN ; SCNNG_HUMAN ; SCNND_HUMAN |
[1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C12H11N7
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
C1=CC=C(C=C1)C2=NC3=C(N=C(N=C3N=C2N)N)N
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C12H11N7/c13-9-7(6-4-2-1-3-5-6)16-8-10(14)18-12(15)19-11(8)17-9/h1-5H,(H6,13,14,15,17,18,19)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
FNYLWPVRPXGIIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-11: Circulatory system diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epithelial sodium channel (ENAC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Edema [ICD-11: MG29.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition to pharmacokinetic effects, compensatory upregulation of sodium transporters not blocked by the diuretic also contributes to diuretic resistance. In patients with CKD, plasma aldosterone levels may be elevated even in the presence of normal plasma renin activity and normal serum potassium concentrations. Elevated plasma levels of both angiotensin II and aldosterone can activate sodium transporters in the distal nephron, including the Na+/Cl cotransporter and ENaC. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epithelial sodium channel (ENAC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Hypertension [ICD-11: BA00.Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition to pharmacokinetic effects, compensatory upregulation of sodium transporters not blocked by the diuretic also contributes to diuretic resistance. In patients with CKD, plasma aldosterone levels may be elevated even in the presence of normal plasma renin activity and normal serum potassium concentrations. Elevated plasma levels of both angiotensin II and aldosterone can activate sodium transporters in the distal nephron, including the Na+/Cl cotransporter and ENaC. | |||
ICD-21: Symptoms/clinical signs/unclassified clinical findings
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Epithelial sodium channel (ENAC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Congestive heart failure [ICD-11: BD10.1] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition to pharmacokinetic effects, compensatory upregulation of sodium transporters not blocked by the diuretic also contributes to diuretic resistance. In patients with CKD, plasma aldosterone levels may be elevated even in the presence of normal plasma renin activity and normal serum potassium concentrations. Elevated plasma levels of both angiotensin II and aldosterone can activate sodium transporters in the distal nephron, including the Na+/Cl cotransporter and ENaC. | |||
| Key Molecule: Epithelial sodium channel (ENAC) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Human immunodeficiency virus infection [ICD-11: 1C62.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Mechanism Description | In addition to pharmacokinetic effects, compensatory upregulation of sodium transporters not blocked by the diuretic also contributes to diuretic resistance. In patients with CKD, plasma aldosterone levels may be elevated even in the presence of normal plasma renin activity and normal serum potassium concentrations. Elevated plasma levels of both angiotensin II and aldosterone can activate sodium transporters in the distal nephron, including the Na+/Cl cotransporter and ENaC. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
