Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00544) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Erlotinib HCI
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Erlotinib hydrochloride; 183319-69-9; erlotinib HCl; Tarceva; N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride; OSI-774; OSI 774; Erlotinib (Hydrochloride); CP 358774; CP-358774; UNII-DA87705X9K; erlotinib, hydrochloride salt; Erlotinib HCl (OSI-744); Tarceva (Erlotinib Hydrochloride); NSC 718781; DA87705X9K; 6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-(3-ethynylanilino)quinazoline hydrochloride; N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazolin-4-amine;hydrochloride; MFCD07781272; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-, hydrochloride (1:1); NSC-718781; 6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-(3-ethynylanilino)quinazoline hcl; 183319-69-9 (HCl); CP-358,774-01; C22H24ClN3O4; [6,7-BIS-(2-METHOXY-ETHOXY)-QUINAZOLIN-4-YL]-(3-ETHYNYL-PHENYL)-AMINE HYDROCHLORIDE; N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine Monohydrochloride.; CHEBI:53509; OSI-744; SMR002529980; NSC718781; 4-(m-Ethynylanilino)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)quinazoline monohydrochloride; RG-1415; 183319-69-9 pound not183321-74-6; R-1415; Erlotinib, HCl; erlotinib hcl salt; Erlotinib hydrochloride [USAN:INN]; Tarceva (OSI); tarceva hydrochloride; erlotonib hydrochloride; Erlotinib hydrochlroide; Erlotinib(OSI-744); MLS003899192; MLS004774139; C22H23N3O4.HCl; CHEMBL1079742; NSC 718781) HCl; DTXSID10171412; EX-A064; SYN1039; Erlotinib Hydrochloride (Tarceva); BCPP000238; AOB87784; BCP02600; AC-400; CP-358; s1023; AKOS015849087; BCP9000658; CCG-269002; CS-0123; KS-1202; MCULE-9498970160; PB30965; SB16917; 4-Quinazolinamine, N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-, monohydrochloride; Ro-50-8231; BE164421; BP-30224; HY-12008; M375; (CP358774; DB-011534; AM20090622; FT-0651479; EC-000.2313; CP-358774-01; E-4007; J10200; 319E699; Q27124083; F0001-2385; Erlotinib Hydrochloride,CP-358774, OSI-774, NSC 718781; 6,7-Bis-(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-(3-ethynylanilino)quinazoline hydrochloride; [6,7-Bis(2-methoxy-ethoxy)-quinazolin-4-yl]-(3-ethynyl- phenyl)amine hydrochloride; N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(1-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine hydrochloride; N-(3-ETHYNYLPHENYL)-6,7-BIS(2-METHOXYETHOXY)-4-QUINAZOLINAMINE HYDROCHLORIDE; N-(3-ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-4-quinazolinamine, monohydrochloride; N-(3-Ethynylphenyl)-6,7-bis(2-methoxyethoxy)-quinazolin-4-amine hydrochloride
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 3 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
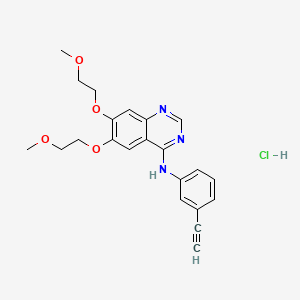
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[2]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C22H24ClN3O4
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
COCCOC1=C(C=C2C(=C1)C(=NC=N2)NC3=CC=CC(=C3)C#C)OCCOC.Cl
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C22H23N3O4.ClH/c1-4-16-6-5-7-17(12-16)25-22-18-13-20(28-10-8-26-2)21(29-11-9-27-3)14-19(18)23-15-24-22;/h1,5-7,12-15H,8-11H2,2-3H3,(H,23,24,25);1H
|
||||
| InChIKey |
GTTBEUCJPZQMDZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Y-box-binding protein 1 (YBX1) | [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Chordoma [ICD-11: 2B5J.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | EGFR/AKT signaling pathway | Regulation | N.A. | |
| Cell invasion | Activation | hsa05200 | ||
| In Vitro Model | Chordoma tissue | N.A. | ||
| In Vivo Model | NOD/SCID/IL2Rgamma null (NOG) mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
CCK-8 assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | YBX1 regulated protein expression of pEGFR, pAKT and its downstream target genes that influenced cell apoptosis, cell cycle transition and cell invasion. YBX1 activated the EGFR/AKT pathway in chordoma and YBX1-induced elevated expression of key molecules in the EGFR/AKT pathway were downregulated by EGFR and AKT pathway inhibitors. These in vitro results were further confirmed by in vivo data. These data showed that YBX1 promoted tumorigenesis and progression in spinal chordoma via the EGFR/AKT pathway. YBX1 might serve as a prognostic and predictive biomarker, as well as a rational therapeutic target, for chordoma. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
