Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00404) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Probenecid
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Apurina; Bencid; Benecid; Benemid; Benemide; Benuryl; Panuric; Parabenem; Probalan; Probampacin; Probecid; Proben; Probenecida; Probenecide; Probenecidum; Probenemid; Probenicid; Probenid; Probexin; Prolongine; Robenecid; Sulprin; Tubophan; Uricosid; Urocid; Biokanol Brand of Probenecid; ICN Brand of Probenecid; IDIS Brand of Probenecid; Major Brand of Probenecid; Martec Brand of Probenecid; Merck Brand of Probenecid; Ophthalmic Brand of Probenecid; Parmed Brand of Probenecid; Probenecid Major Brand; Probenecid Martec Brand; Probenecid Parmed Brand; Probenecid Weimer; Probenecid Zenith Brand; Probenecid acid; Synergid R; Valdecasas Brand of Probenecid; Zenith Brand of Probenecid; Benemid (TN); Benuryl (TN); Col-BENEMID; ColBenemid (co mponent of); ColBenemid (component of); P-[Dipropylsulfamoyl]benzoic acid; Polycillin-BRB; Pro-Cid; Probenecida [INN-Spanish]; Probenecide [INN-French]; Probenecidum [INN-Latin]; P-(Dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid; P-(Dipropylsulfamyl)benzoic acid; Polycillin-PRB (component of); Probenecid [INN:BAN:JAN]; Probenecid (JP15/USP/INN); 4-((Dipropylamino)sulfonyl)benzoic acid;4-(Di-n-propylsulfamoyl)benzoesaeure; 4-(Dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoic acid; 4-(N,N-Dipropylsulfamoyl)benzoesaeure; 4-[(dipropylamino)sulfonyl]benzoic acid
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 2 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
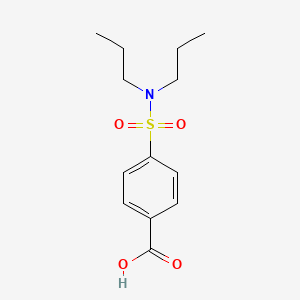
|
||||
| Target | Solute carrier family 22 member 8 (SLC22A8) | S22A8_HUMAN | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C13H19NO4S
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CCCN(CCC)S(=O)(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)C(=O)O
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C13H19NO4S/c1-3-9-14(10-4-2)19(17,18)12-7-5-11(6-8-12)13(15)16/h5-8H,3-4,9-10H2,1-2H3,(H,15,16)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
DBABZHXKTCFAPX-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| VARIDT ID | |||||
| INTEDE ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Sensitivity Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ATP-binding cassette sub-family C2 (ABCC2) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell autophagy | Inhibition | hsa04140 | |
| Cell cytotoxicity | Activation | hsa04650 | ||
| In Vitro Model | PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| 22RV1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, probenecid only weakly inhibits ABCG2. Thus, probenecid enhanced the efficacy of anticancer drugs against 22Rv1 spheroids by inhibiting drug resistance-related transporters such as MRP; at high probenecid concentrations, the chemosensitization effect may be reduced owing to promotion of alternate drug excretion pathways via upregulated ABCG2 expression. | |||
| Key Molecule: Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 (MRP1) | [1] | |||
| Sensitive Disease | Prostate cancer [ICD-11: 2C82.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Down-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| Cell Pathway Regulation | Cell colony | Inhibition | hsa05200 | |
| In Vitro Model | PC3 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0035 |
| 22RV1 cells | Prostate | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1045 | |
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Western blot analysis | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTT assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | However, probenecid only weakly inhibits ABCG2. Thus, probenecid enhanced the efficacy of anticancer drugs against 22Rv1 spheroids by inhibiting drug resistance-related transporters such as MRP; at high probenecid concentrations, the chemosensitization effect may be reduced owing to promotion of alternate drug excretion pathways via upregulated ABCG2 expression. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
