Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00388) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Quinupristin/Dalfopristin
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Quinupristin-dalfopristin; Quinupristin - dalfopristin mixt; Synercid (TN); 126602-89-9; CHEBI:8733; C08034; D00854; Q1763990
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Structure |
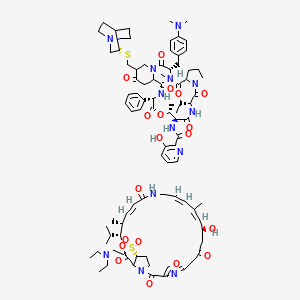
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Clinically Reported Resistance for This Drug
(2 diseases)
[3]
|
||||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C87H117N13O19S2
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CC[C@@H]1C(=O)N2CCC[C@H]2C(=O)N([C@H](C(=O)N3CC(C(=O)CC3C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O[C@@H]([C@@H](C(=O)N1)NC(=O)C4=C(C=CC=N4)O)C)C5=CC=CC=C5)CS[C@@H]6CN7CCC6CC7)CC8=CC=C(C=C8)N(C)C)C.CCN(CC)CCS(=O)(=O)[C@@H]1CCN2C1C(=O)O[C@@H]([C@@H](/C=C/C(=O)NC/C=C/C(=C/[C@H](CC(=O)CC3=NC(=CO3)C2=O)O)/C)C)C(C)C
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C53H67N9O10S.C34H50N4O9S/c1-6-37-50(68)61-23-11-14-38(61)51(69)59(5)40(26-32-16-18-36(19-17-32)58(3)4)52(70)62-28-35(30-73-43-29-60-24-20-33(43)21-25-60)42(64)27-39(62)47(65)57-45(34-12-8-7-9-13-34)53(71)72-31(2)44(48(66)55-37)56-49(67)46-41(63)15-10-22-54-46;1-7-37(8-2)16-17-48(44,45)28-13-15-38-31(28)34(43)47-32(22(3)4)24(6)11-12-29(41)35-14-9-10-23(5)18-25(39)19-26(40)20-30-36-27(21-46-30)33(38)42/h7-10,12-13,15-19,22,31,33,35,37-40,43-45,63H,6,11,14,20-21,23-30H2,1-5H3,(H,55,66)(H,56,67)(H,57,65);9-12,18,21-22,24-25,28,31-32,39H,7-8,13-17,19-20H2,1-6H3,(H,35,41)/b;10-9+,12-11+,23-18+/t31-,35 ,37-,38+,39 ,40+,43-,44+,45+;24-,25-,28-,31 ,32-/m11/s1
|
||||
| InChIKey |
PPKJUHVNTMYXOD-HVWWIRKTSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-01: Infectious/parasitic diseases
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Ribosomal RNA large subunit methyltransferase (CFR ) | [4] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli AS19 | 562 | ||
| Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay; Allelic frequency measurement assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MIC assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Cfr confers resistance to antibiotics binding to the peptidyl transferase center on the ribosome.The primary product of the Cfr-mediated methylation is 8-methyladenosine (m8A), a new natural RNA modification that has so far not been seen at sites other than A2503 in 23S rRNA. | |||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: ABC transporter ATP-binding protein (ABCP) | [1], [2] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Bacterial infection [ICD-11: 1A00-1C4Z] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Missense mutation | p.T450I |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli TOP10 | 83333 | ||
| Enterococcus faecium HM1070 | 1352 | |||
| Enterococcus faecium UCN80 | 1352 | |||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
Whole genome sequence assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | ABC systems constitute one of the largest families of proteins, with most of them being involved in import and export, often called ABC transporters.Several of these class 2 ABC systems have been involved in MLS resistance, such as Msr-, Vga-, or Lsa-like proteins.The observed profile of cross-resistance to lincosamides, streptogramins A, and pleuromutilins conferred by Eat(A)v was similar to those conferred by other Lsa-like proteins. | |||
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: Virginiamycin B lyase (VGBB) | [3] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Staphylococcus aureus infection [ICD-11: 1B54.0] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Inherence |
||
| Experimental Note | Identified from the Human Clinical Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) | 469008 | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
PCR amplification and sequence alignments assay | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
Spectrophotometric and fluorometric assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Virginiamycin B lyase (Vgb) inactivates the quinupristin component of Synercid by lactone ring opening and the enzyme promotes this reaction by intramolecular Beta-elimination without the involvement of a water molecule. Replacement of the conserved active site residues His228, Glu268, or His270 with alanine reduces or abolishes S. cohnii Vgb activity. Residue Lys285 in S. cohnii Vgb is spatially equivalent to the S. aureus Vgb active site residue Glu284. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
