Drug Information
Drug (ID: DG00277) and It's Reported Resistant Information
| Name |
Abexinostat
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
PCI-24781; 783355-60-2; ABEXINOSTAT; PCI 24781; CRA-024781; CRA 024781; UNII-IYO470654U; 3-((dimethylamino)methyl)-N-(2-(4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)phenoxy)ethyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide; CRA-02478; Abexinostat(PCI-24781); PCI-24781 (Abexinostat); Abexinostat (PCI-24781); IYO470654U; 3-[(Dimethylamino)methyl]-N-[2-[4-[(hydroxyamino)carbonyl]phenoxy]ethyl]-2-benzofurancarboxamide; 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-N-(2-(4-(hydroxycarbamoyl)-phenoxy)ethyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide
Click to Show/Hide
|
||||
| Indication |
In total 8 Indication(s)
|
||||
| Structure |
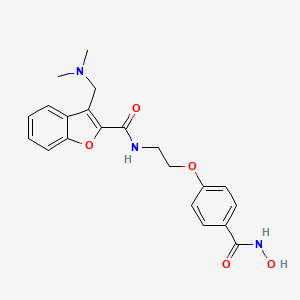
|
||||
| Drug Resistance Disease(s) |
Disease(s) with Resistance Information Discovered by Cell Line Test for This Drug
(1 diseases)
[1]
|
||||
| Target | Histone deacetylase (HDAC) | NOUNIPROTAC | [1] | ||
| Click to Show/Hide the Molecular Information and External Link(s) of This Drug | |||||
| Formula |
C21H23N3O5
|
||||
| IsoSMILES |
CN(C)CC1=C(OC2=CC=CC=C21)C(=O)NCCOC3=CC=C(C=C3)C(=O)NO
|
||||
| InChI |
1S/C21H23N3O5/c1-24(2)13-17-16-5-3-4-6-18(16)29-19(17)21(26)22-11-12-28-15-9-7-14(8-10-15)20(25)23-27/h3-10,27H,11-13H2,1-2H3,(H,22,26)(H,23,25)
|
||||
| InChIKey |
MAUCONCHVWBMHK-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|
||||
| PubChem CID | |||||
| ChEBI ID | |||||
| TTD Drug ID | |||||
| DrugBank ID | |||||
Type(s) of Resistant Mechanism of This Drug
Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Diseases
ICD-02: Benign/in-situ/malignant neoplasm
| Drug Resistance Data Categorized by Their Corresponding Mechanisms | ||||
|
|
||||
| Key Molecule: X inactive specific transcript (XIST) | [1] | |||
| Resistant Disease | Breast cancer [ICD-11: 2C60.3] | |||
| Molecule Alteration | Expression | Up-regulation |
||
| Experimental Note | Revealed Based on the Cell Line Data | |||
| In Vitro Model | MDA-MB-231 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0062 |
| MDA-MB-436 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_0623 | |
| HCC1954 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_1259 | |
| BrCa-MZ-01 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5495 | |
| CRCM226X cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| CRCM311X cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| CRCM389X cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| CRCM392X cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| S68 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5585 | |
| Sk-BR-7 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5218 | |
| SUM149 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_3422 | |
| SUM159 cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | CVCL_5423 | |
| Xist med cells | Breast | Homo sapiens (Human) | N.A. | |
| In Vivo Model | NOD/SCID nude mouse xenograft model | Mus musculus | ||
| Experiment for Molecule Alteration |
qRT-PCR | |||
| Experiment for Drug Resistance |
MTS assay | |||
| Mechanism Description | Abexinostat induced CSC differentiation in low-dose sensitive BCLs, whereas it did not have any effect on the CSC population from high-dose sensitive BCLs. Abexinostat effect is mediated at the cellular level through the modulation of the CSC pool. Only the PDX with low Xist expression displayed a significant decrease of its CSC population after abexinostat treatment, whereas HDACi treatment induced an increase of the CSC population in PDX with high Xist expression. | |||
References
If you find any error in data or bug in web service, please kindly report it to Dr. Sun and Dr. Yu.
